|
|
 |
|
|
|
|

|
ATP is a natural molecule, also known as adenosine triphosphate, in your body that is the main energy source currency of cells. Mitochondria, an organelle, gathers energy from organic compounds to make most of the ATP, while other ATP can be made in the cytoplasm. ATP is made up of a single nucleotide with two additional energy storing phosphate groups. After cells separate food molecules, some of the energy in the molecules are released as heat, while the remaining energy is stored in molecules of ATP. Cells can use some of that energy and require a adequate amount of ATP to operate properly, for ATP provides cells with the energy they need to perform the activities of life. ATP serves as an important role in biology because cells mainly get their energy from ATP. ATP also helps by bringing energy wherever energy is needed in a cell, and releasing the energy, which can be used to power other chemical reactions, such as the ones that can make molecules. Because cells usually require less energy released from ATP, the energy released from ATP is enough to propel most of a cell’s activities. ATP contains three phosphate groups that form a chain that branches from a five-carbon sugar called ribose. The phosphate groups store energy, so whenever the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together are broken, the energy is released. The phosphate groups store energy like a compressed spring does. The phosphate groups are negatively charged, so they are driving back each other, so the phosphate tail is unstable.
Whenever the outer phosphate bond is broken, a phosphate group is removed
from ATP. The breaking of the outer phosphate bond requires a large amount
of energy, but in the end more energy is released because of the reaction.
ADP, shortened for adenosine diphosphate is produced whenever a phosphate
group is removed from ATP. The chemical reaction releases energy in a way
that makes it possible for cells to use the energy to power metabolism.
The chemical reaction is summarized in the following equation: In some chemical reactions two phosphate groups are removed from ATP instead of just one, which can make the chemical reaction have an unchangeable effect. The effect cannot be changed because the pair of phosphate groups removed are not available for the reverse chemical reaction. After the two phosphate groups are removed, they will split into two single phosphate groups. ATP = organic
molecule that functions as the main energy source of cells; adenosine
triphosphate; has three phosphate groups, a base (adenine) and a sugar
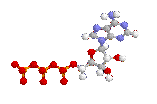
(ribose) As the diagram shows, ATP contains a sugar (ribose), 3 phosphate groups, and a base (adenine). When the outer phosphate bond is broken, a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy. This produces ADP, with two phosphate groups, a sugar, and a base. |
What is ATP?
|