General Relativity (aka: "Gravity")

General Relativity (aka: "Gravity")
My first serious interest in physics began around the time I read about black holes, big massive objects floating through space who's gravity is so strong that not even light can even escape from it. All the weird effects that describe how a black hole beahaves was made possible through equations invented by Einstein, I later became interested in the math as it was the only to truly understand why a point within a black hole can make reality as we know it cease to exist, no kidding. I consider myself to be a gravitational researcher as I do a lot of work on the effects of gravity, although I do study other things such as the nature of Quantum Mechanics for example. Below I give a very brief explanation of what is known of gravity from the works of Newton and Einstein as to get a feel for what exactly it is that I study.
| Probably the most important equation in physics is F=ma (force equals mass times acceleration), F=m(kg)a(delta d/s), developed long ago by Sir Isaac Newton, most things in the world can be explained through the laws established by Newton, such as how the hell your car works (or in my case why it doesn't). However I am trying to discuss gravity, oddly gravity is explained by slightly changing F=ma, in Newtonian physics the force of gravity is F=G(M1m2)/r2, where G is a small acceleration that exist between two bodies in space measured in N*m/s, which is simply F times some distance measured in meters, in essence gravity is just a force that acts at a distance. Now apples fall to earth because they have a mass m and the earth has a mass of M, which produces an acceleratory force on an apple of 9.8 m/s2 or 32 ft/s2. The Moon is falling to, except it happens to have forward momentum which causes it to fall around earth instead of into it, we call such a path do to gravity an orbit. |  |
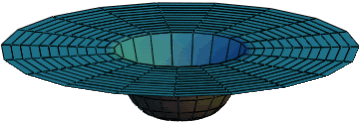
Gab=8pkTab
Where Gab represents how space is curved 8p represents that there exist 3 space dimension and 1 time dimension that continues into infinity. k is Newton's G divided by the speed of light squared and Tab is the amount of matter is space, Einstein's theory of gravity is simply that matter and energy bend space and time. Think of G as the surface of a trampoline and T as a bowling ball that is bending its surface, now we know more is happening to the Moon than it just falling around the Earth (see the Newton section). The moon is forced to travel along the curvature of space produced by the Earth, and so instead of a force causing gravity it is now known to be a cause of geometry.
[Note: this is NOT a crazy premise the sun has bent star
light, some galaxies do. There have also been clocks put onto airplanes
that slowdown relative to ground clocks, the effects of relativity are
very bizarre and very real.]