Q u e s t i o n s
Multiple Choice
Definition of Economics
1. The fact that wants cannot be fully satisfied with available resources reflects the definition of
a. the standard of living.
b. scarcity.
c. the output-inflation tradeoff.
d. for whom to produce.
2. Studying the effects choices have on the national economy is part of
a. scarcity.
b. microeconomics.
c. macroeconomics.
d. global science.
Three Big Microeconomic Questions
3. Which of the following is NOT one of the three big microeconomic questions?
a. What goods and services are produced?
b. How are goods and services produced?
c. For whom are goods and services produced?
d. Why are goods and services produced?
4. The question, ¡§Should personal computers or mainframe computers be produced?¡¨ is an example of the
a. ¡§what¡¨ question.
b. ¡§how¡¨ question.
c. ¡§where¡¨ question.
d. ¡§who¡¨ question.
5. People have different amounts of income. This observation is most directly related to which of the big microeconomic questions?
a. The ¡§what¡¨ question.
b. The ¡§how¡¨ question.
c. The ¡§why¡¨ question.
d. The ¡§who¡¨ question.
Three Big Macroeconomic Questions
6. Of the following, which country or region has the highest standard of living?
a. Japan
b. Central and Eastern Europe
c. The United States
d. Africa
7. During an inflation, the cost of living is ____ and the value of the dollar is ____.
a. rising; rising
b. rising; falling
c. falling; rising
d. falling; falling
8. Which of the following is the correct order for the parts of a business cycle?
a. expansion, trough, recession, peak
b. expansion, recession, trough, peak
c. expansion, recession, peak, trough
d. expansion, peak, recession, trough
The Economic Way of Thinking
9. The fact that Intel decides to produce CPU chips rather than memory chips best reflects a ____ tradeoff.
a. what
b. how
c. for whom
d. standard of living
10. The standard of living tradeoff reflects trading off
a. consumption in the United States for consumption in Africa .
b. higher inflation for higher consumption.
c. current consumption for economic growth.
d. consumption and equality.
11. From 9 to 10 A . M . , Fred can sleep in, go to his economics lecture, or play tennis. Suppose that Fred decides to go to the lecture but thinks that, if he hadn't, he would otherwise have slept in. The opportunity cost of attending the lecture is
a. sleeping in and playing tennis.
b. playing tennis.
c. sleeping in.
d. one hour of time.
12. When the government chooses to use resources to build a dam, these resources are no longer available to build a highway. This choice illustrates the concept of
a. a market.
b. macroeconomics.
c. opportunity cost.
d. marginal benefit.
13. To make a choice on the margin, an individual
a. ignores any opportunity cost if the marginal benefit from the action is high enough.
b. will choose to use his or her scarce resources only if there is a very large total benefit from so doing.
c. compares the marginal cost of the choice to the marginal benefit.
d. makes the choice with the smallest opportunity cost.
Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost
14. Production points on the PPF itself are
a. efficient but not attainable.
b. efficient and attainable
c. inefficient but not attainable.
d. inefficient and attainable.
15. If the United States can increase its production of automobiles without decreasing its production of any other good, the United States must have been producing at a point
a. within its PPF .
b. on its PPF .
c. beyond its PPF .
d. None of the above are correct because increasing the production of one good without decreasing the production of another good is impossible.

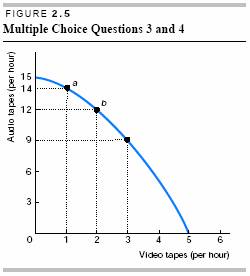
16. In Figure 2.5, at point a what is the opportunity cost of producing one more video tape?
a. 14 audio tapes
b. 3 audio tapes
c. 2 audio tapes
d. There is no opportunity cost.
17. In Figure 2.5, at point b what is the opportunity cost of producing one more video tape?
a. 12 audio tapes
b. 3 audio tapes
c. 2 audio tapes
d. There is no opportunity cost.
18. Production efficiency means that
a. scarcity is no longer a problem.
b. producing more of one good without producing less of some other good is not possible.
c. as few resources as possible are being used in production.
d. producing another unit of the good has no opportunity cost.
19. The existence of the tradeoff along the PPF means that the PPF is
a. bowed outward.
b. linear.
c. negatively sloped.
d. positively sloped.
20. The bowed-outward shape of a PPF
a. is due to capital accumulation.
b. reflects the unequal application of technology in production.
c. illustrates the fact that no opportunity cost is incurred for increasing the production of the good measured on the horizontal axis but it is incurred to increase production of the good measured along the vertical axis.
d. is due to the existence of increasing opportunity cost.
A nation produces only two goods ¡X yak butter and rutabagas. Three alternative combinations of production that are on its PPF are given in Table 2.1. Use this information to answer the next three questions.

21. In moving from combination a to b , the opportunity cost of producing more rutabagas is
a. 6 pounds of yak butter per rutabaga.
b. 4 pounds of yak butter per rutabaga.
c. 2 pounds of yak butter per rutabaga.
d. 0 pounds of yak butter per rutabaga.
22. In moving from combination b to a , the opportunity cost of producing more pounds of yak butter is
a. 0.10 rutabaga per pound of yak butter.
b. 0.50 rutabaga per pound of yak butter.
c. 1.00 rutabaga per pound of yak butter.
d. 2.00 rutabagas per pound of yak butter.
23. Producing 400 pounds of yak butter and 50 rutabagas is
a. not possible for this nation.
b. possible and is an efficient production point.
c. possible, but is an inefficient production point.
d. an abhorrent thought.
Using Resources Efficiently
24. Moving along a bowed-out PPF between milk and cotton, as more milk is produced the marginal cost of an additional gallon of milk
a. rises.
b. does not change.
c. falls.
d. probably changes, but in an ambiguous direction.
25. The most anyone is willing to pay for another purse is $30. Currently the price of a purse is $40, and the cost of producing another purse is $50. The marginal benefit of a purse is
a. $50.
b. $40.
c. $30.
d. An amount not given in the answers above.
26. If the marginal benefit from another computer exceeds the marginal cost of the computer, then to use resources efficiently,
a. more resources should be used to produce computers.
b. fewer resources should be used to produce computers.
c. if the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible, the efficient amount of resources are being used to produce computers.
d. none of the above is correct because marginal benefit and marginal cost have nothing to do with using resources efficiently.
Economic Growth
27. Economic growth
a. creates unemployment.
b. has no opportunity cost.
c. shifts the PPF outward.
d. makes it more difficult for a nation to produce on its PPF .
28. The PPF shifts if
a. the unemployment rate falls.
b. people decide they want more of one good and less of another.
c. the prices of the goods and services produced rise.
d. the resources available to the nation change.
29. An increase in the nation's capital stock will
a. shift the PPF outward.
b. cause a movement along the PPF upward and leftward.
c. cause a movement along the PPF downward and rightward.
d. move the nation from producing within the PPF to producing at a point closer to the PPF .
30. One of the opportunity costs of economic growth is
a. capital accumulation.
b. technological change.
c. reduced current consumption.
d. the gain in future consumption.
31. In general, the more resources that are devoted to technological research, the
a. greater is current consumption.
b. higher is the unemployment rate.
c. faster the PPF shifts outward.
d. more the PPF will bow outward.