A new model for
the Photon: New Field Theory:
D. James
The first one hundred years of the
photon:
Practically everything we know about the Universe appears to us through the medium of the photon. This is because of the amazing fact that a photon is able to preserve its identity ( energy ) intact over the almost measureless distances of space. One of the reasons that it is able to do so is because it possesses no charge , a charged particle such as an electron would soon lose its energy , through radiation , over a very short distance and come to a stop , another reason that the photon can travel these huge distances is that it possesses no rest mass and so can travel at the speed of light , nothing in the Universe can travel faster , because of these properties of the photon , scientists are in a position to probe the very beginnings of the Universe . The photon possesses even more remarkable attributes , all electro-magnetic radiation may be thought of as being made up of photons , so that the number of possible photon energies runs into more than a million trillion possible energies. Lastly the photon is the ultimate expression of the property known as wave-particle duality. It manifests the properties of both a particle and those of a wave depending on the way in which it is observed.
Almost exactly a hundred years have passed since 1905 , when Albert Einstein’s theory of the photo-electric effect first brought to the attention of the scientific world the possibility of the existence of the photon , little more has been learnt of the photon’s physical structure since , than was known then. It is extraordinary to think that the physical structure of sub-atomic particles other than the photon have been successfully plotted using far less extensive information than is available for the photon. As an example it has been found through experiment that the mass m of an electron is equal to 9.1 x 10 -28 g , ( the masses of all other sub-atomic particles are measured against the mass of the electron ) , hence ; a proton has 1836 m , a neutron 1839 m and a muon 207 m. Pions have a mass of about 207m and kaons about 290m . The magnitude of the electric charge of all micro-particles is similarly a multiple of the magnitude of the charge of an electron , which is equal to 1.6 x 10 -19 C. In spite of this extraordinary progress in gaining physical insights into the structure and properties of other sub-atomic particles there has been considerable reticence in trying to attribute any kind of a physical structure to the photon.
In order to trace the reason for this reticence it is necessary to go back in time to the early twentieth century when the secrets of the atom were first being unlocked. It was soon apparent that the laws of classical physics which had worked so well in describing and defining the macro world , failed completely when applied to the sub-atomic world.
For instance
classical physics predicted
that electrons orbiting the nucleus
of the atom would lose their energy through radiation and spiral in towards the
nucleus. This is a notable example
of the complete failure of classical physics when applied to the sub-atomic
world. By making use of obvious
conclusions drawn from the principles of classical physics , namely the instability of any stationary structure of charged
particles and the emission of
radiation by a particle moving with acceleration , it is concluded that
atoms cannot exist ! This
illustrates the most impressive
contradiction derived from the difference between the predictions of classical
physics and experiment.
It was in order to resolve these differences between the observed facts
and their incompatibility with the theories of classical physics that quantum
physics came into existence.
The central core of principles governing quantum mechanics is highly rigid and regulated . In this
respect it might be thought of as resembling one of the modern dances , possessing stringent rules and protocol , which are
rigorously enforced and observed , yet outside these rules open to astonishing variations in
interpretation , and innovation.
Much the same could be said of quantum mechanics with its core of intricate mathematical theorems woven
around certain inviolable principles . Yet , apart from this open to practically
any suggestion. To illustrate this
unrivalled openness to new ideas that quantum mechanics brought to the study of
science , Neils Bohr coined the expression “Crazy
theory “ meaning a theory that was just crazy enough to be true. Such an
approach was necessary , the conventional ideas then in existence were deeply
rooted and were bound in formalism , a complete break from this tradition was
needed if progress was to be made.
New ideas were not slow in coming , already Einstein’s path breaking
theory of Special relativity and
General relativity had turned the scientific world on its head , more was soon
to follow . Werner Heisenberg , a one time student of Neils Bohr , proposed his
Uncertainty relation which states
that “ A sub-atomic particle cannot have
simultaneously a definite co-ordinate and a definite momentum. “ Mathematically stated this is as follows
, where p stands for momentum and x
for position : ![]() p
p![]() x
x![]() h/(4p ). This goes completely against Newtonian physics
which state that the speed and position of every object can be measured at any point in time. The wave-particle duality of matter
proposed by de Broglie and derived by him from Einstein’s equation for the
equivalency of energy and matter E = mc2 , was another such new theory. Although
strictly speaking de Broglie waves resemble a mathematical construction rather than
classical waves as they are normally thought of. The remarkable aspect of these
ideas is that they are seen to be moving away from the physically observed
domain where empirical evidence is
the main criteria , into the realm
of philosophical thought based on theoretical precepts. For instance
Werner Heisenberg’s Uncertainty principle bears an uncanny similarity to Immanuel Kant’s philosophy. According to
Kant the scientist can never be completely “aware” of an external physical world : such
a world exists but in the act of perceiving or discovering it , we inevitably
colour and process it. While the wave-particle duality bears an amazing
resemblance to Bishop Berkely’s philosophy , one aspect of which states that
when for example no-one is present
in a room , the room and its contents are in fact non-existent. The fundamental
difference between science and philosophy seems to lie mainly in the fact that while the former
is supported by mathematical logic the latter is not.
h/(4p ). This goes completely against Newtonian physics
which state that the speed and position of every object can be measured at any point in time. The wave-particle duality of matter
proposed by de Broglie and derived by him from Einstein’s equation for the
equivalency of energy and matter E = mc2 , was another such new theory. Although
strictly speaking de Broglie waves resemble a mathematical construction rather than
classical waves as they are normally thought of. The remarkable aspect of these
ideas is that they are seen to be moving away from the physically observed
domain where empirical evidence is
the main criteria , into the realm
of philosophical thought based on theoretical precepts. For instance
Werner Heisenberg’s Uncertainty principle bears an uncanny similarity to Immanuel Kant’s philosophy. According to
Kant the scientist can never be completely “aware” of an external physical world : such
a world exists but in the act of perceiving or discovering it , we inevitably
colour and process it. While the wave-particle duality bears an amazing
resemblance to Bishop Berkely’s philosophy , one aspect of which states that
when for example no-one is present
in a room , the room and its contents are in fact non-existent. The fundamental
difference between science and philosophy seems to lie mainly in the fact that while the former
is supported by mathematical logic the latter is not.
The wave particle duality of
matter :
The introduction of discreteness and the indisputable proof of the
quantum nature of light and energy to the physical picture of the world had led
to incomprehensible and
controversial quantum “jumps” which if accepted at face value seemed to
have no logical explanation . The idea of duality , which asserts the specific
nature of micro-particles , eliminated the need for quantum “jumps”
by suggesting a “manipulation” between the particle and wave
concepts while at the same time
making irrelevant the issue posed by classical physics of the loss of energy of
the orbiting electron , since by this model the electron was no longer
localised. The uncertainty
principle and the theory of
the wave-particle duality of matter, when taken together seemed to offer a
solution to the underlying question
of how and why atoms could
exist.
It was largely due to these criteria that the wave-particle duality of matter , in
concert with the idea of discreteness became one of the corner
stones of quantum mechanics and an inviolable principle . While on the one
hand , the discreteness of
light and energy had been proven by physical experiments conducted in the
classical style , on the other , the wave particle duality of matter was
supported by theory and
mathematical logic . Wave-particle duality is considered
to exist not only for sub atomic particles , but for all
matter , the photon being a particle with no mass is regarded as being the ultimate
expression of wave-particle duality. The contradiction underlying the existence
of mutually exclusive wave-like and particle like behaviour in
a single entity ,
is one of the hall marks of quantum physics.
Albert Einstein was one of the opponents of the implementation of the
Heisenberg uncertainty principle in the quantum mechanics model of the working
of the atom which allowed the electron to assume the property of wave-particle
duality , it is in this regard that
he made his now famous remark that :
“ God does not play dice with the
Universe …”. With Einstein
among the opponents of quantum theory , it is difficult to believe that
criticism of quantum mechanics stem from nothing more than the
inertness of human nature in responding to anything new. Einstein’s opposition
to the implementation of the Heisenberg uncertainty relation lay in the manner
in which it had been implemented which was more or less a blanket implementation
over the whole of atomic physics and allowed for no dispute. To quote Neils Bohr : “ in quantum mechanics we are not dealing
with an arbitrary renunciation of a
more detailed analysis of atomic phenomenon , but with a recognition that such
an analysis is in principle excluded.
“
From an everyday perspective the Heisenberg uncertainty principle does seem to border on the absurd , we sense intuitively that it should be possible to identify both the position and the velocity of an object at any given time . Take for instance the case where it is possible to shrink to the size of an atom , the rapid development in nano-technology make this a viable argument , would it be possible , in such a case , to both see and record the position and velocities of sub-atomic particles ? The continuing perfecting of attosecond laser pulses raises the possibility of accurately tracing the electron’s path within an atom , putting the question of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and wave-particle duality in further doubt. The inconsistent nature of the first Heisenberg uncertainty principle as stated above demonstrates that our conception of reality or classical principles can still apply to sub-atomic phenomenon.
Wave-particle duality no longer
a fundamental requirement
:
It is ironic that with the advances made in our
understanding of the structure
and working of the atom , wave-particle duality is
no longer needed to explain how electrons can orbit within the atom without
losing their energy and going into a spiral towards the nucleus , or of how quantum jumps by the electron are
made possible . The person mainly
responsible for this development was the American physicist , Richard
Feynman (among others ) , who suggested the
possibility of virtual interactions
taking place between electrons , a hypotheses which experiments seem to bear out
. It is equally ironic that this explanation was made possible by the implementation
of another aspect of the Heisenberg uncertainty relation . The second
uncertainty relation states that if an event takes place within a very short
space of time , one thousand
trillionth ( 10 -15 ) of
a second , or with a very low energy ,
the conservation laws are
not violated. Stated as
![]() E
E![]() t
t![]() h/(4p ) where E stands for energy and t stands for time.
Thus it was concluded that electrons in orbit around the nucleus
constantly emit and absorb “virtual “ photons . “Virtual” photons being exactly the same as real photons with
the distinction that the interactions (emissions and absorptions ) are performed
in such a short time that they are to all purposes “virtual” transactions or
interactions and do not therefore
affect the Laws of Conservation .
h/(4p ) where E stands for energy and t stands for time.
Thus it was concluded that electrons in orbit around the nucleus
constantly emit and absorb “virtual “ photons . “Virtual” photons being exactly the same as real photons with
the distinction that the interactions (emissions and absorptions ) are performed
in such a short time that they are to all purposes “virtual” transactions or
interactions and do not therefore
affect the Laws of Conservation .
Quantum
mechanics:
The evolution of Quantum
theory marked a milestone in the progressive history of physics , it
opened new doors to knowledge and expanded the frontiers of human perception to the uttermost
bounds and even beyond. The research and supporting mathematical documentation
were meticulous , sometimes ,
as in the case of ascertaining Yukawa’s theory on the
mediation of nucleons , extending over a period of several
decades until supporting proof was available. Many of the incredible advances made in
technology including the computers we use today , nuclear reactors , X-rays ,
the scanning tunnel microscope and the internet to name just a very few , are a direct result of advances made in
Quantum mechanics . However in every epoch of human learning there have been
always been some misconceptions on the nature of observed phenomenon , an
inevitable consequence of the
limited knowledge available at that
particular time. It is not
surprising that while the empirical based theories of quantum mechanics still
hold good , many of the theory based perceptions are gradually unravelling . The
theory of quantum electrodynamics might be one such instance. QED based its own theory on the precepts
put forward by Maxwell , which have proven to be false.
Inconsistencies in Maxwell’s
equations :
It has been demonstrated , earlier in this article , that the wave-particle duality of the photon had been deduced , not from direct observations of the photon , but from observation of unrelated phenomenon arising out of the necessity for explaining how atoms could exist. Today that necessity no longer exists , or at least the necessity no longer exists at such a fundamental level . The possibility therefore is present that a more rigorous examination of the properties of the photon will yield evidence that the photon has all along been just what it seems , namely the symbiosis of a particle and a wave.
The key to a better understanding of the photon lies in re-examining the related
phenomenon of electricity . It is an amazing but irrefutable fact that
Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetic
radiation is based upon a false premise. The whole theory of electromagnetic
radiation was founded on the
observation of how an electric current behaved within a capacitor . It was observed that an
electrical current was established in
what to all purposes was an open circuit. Maxwell made the deduction that
this flow of current was due to a displacement current , and was thereby said to
have cut the Gordian knot , a logical corollary to this was that
electromagnetic waves could travel
through space. Thus Maxwell treated current flow through a capacitor as being
different to the flow of current in a circuit : { Maxwell, Article
610: "One of the chief peculiarities of
this treatise is the doctrine which asserts, that the true electric current, I, that on which the electromagnetic
phenomena depend, is not the same thing as i, the current of conduction,
but... I = i + dD/dt
(Equation of True Currents)." } The premise was that the field around a
capacitor was an electric field , this premise has since found to be false . The reason that this statement is so strongly worded is that a simple
experiment can be carried out to verify the validity of the statement. Two metal
strips are placed side by side , separated by a small distance on a non
conducting surface and strongly
charged with opposing polarities. When the plates are isolated , a field is found to exist
around the plates ( i.e to all purposes a capacitor ) which is indistinguishable from an
electromagnetic field , iron filings sprinkled on the non-conducting surface on
which the plates have been positioned , arrange themselves along the lines of
force between the two plates and
compass needles are deflected in the direction of the lines of force. Consider now what happens when the
plates are moved further apart , the iron filings no longer align themselves
along the lines of force and the compass needle does not undergo
deflection. What conclusions are to be drawn from this ? Do we conclude that the
field around the plates is an electromagnetic field when the plates are close
together and an electric field when they are further apart ? Or do we conclude
that a strong charge results in an electromagnetic field and that a weak charge
results in an electrical field ? The only conclusion that can safely be drawn
from this experiment is that there are no electric monopoles and hence no
electric fields. In either case the
answers are irrelevant here , because Maxwell based his conclusions on the
premise that the field around a capacitor was an electric field. In the light of
the new information that the field around a capacitor is an electromagnetic
field , it is obvious that Maxwell’s theories were based upon a false premise
and that in reality there is no displacement current and that the current flow through the dielectric of a
charging and discharging
capacitor is no different
than the current flow in a normal
circuit.
This discrimination
between the type of energy inside an electrical conductor and outside it in the
form of electromagnetic fields is one of the major barriers to reaching a fully
comprehensive theory of electrical conduction. It has been suggested , and
experimentally supported that Maxwell's original equation : I = i +
dD/dt Could be replaced by
: I = i = dD/dt ( with the
proviso that symbol D = E x electric constant). (Catt, Davidson,
Walton)
In this equation, there is an "=" sign whereas in Maxwell's
equation there is a "+" sign. This says it all. In other words, Maxwell
treats wire electricity (i) as being different to the current flow I in the vacuum dielectric of a
charging or discharging capacitor (dD/dt), whereas the simple experiment
outlined above proves that there is
no distinction for pulses of electromagnetic energy in wires and for that
flowing in the vacuum dielectric of a capacitor . Hence , Maxwell is mathematically wrong.
There also exist
several discrepancies in the quantum mechanics model for the flow of electrical
energy in a conductor. For instance according to quantum
mechanics there are no fields as such , therefore by the classical view
electrical phenomenon was described as electron -> field -> electron and by the quantum view
as electron -> photon ->
electron . Yet the quantum explanation for the flow of energy in an electrical
conductor , based on a simple perturbation theory , is essentially a field
theory . Hence an electron is moved by the difference of potential established
across the ends of the conductor , this creates a disturbance in the electric
field within the conductor which is
conveyed to the next electron and so on , the process moving through the
conductor at speeds near to the speed of light. This explanation is essentially
at odds with the quantum mechanics axiom
which states that all interactions between electrons are mediated by photons. However , according to the Pauli
exclusion principle , photons are barred from the electrical conduction process
and therefore cannot take part in interactions between electrons in the
conductor.
A new model of the
photon:
Little has been done to explain these inconsistencies , they have been
side-lined by phenomena which required more immediate attention. Yet if the time
is taken to address them , an inevitable conclusion would be that it is the
photon that is the agent of electrical conduction. Every , possible criteria and
even the conclusions of quantum mechanics itself point in this direction. Disregarding
for the moment the Pauli exclusion principle and its conclusions , which will be
discussed later ,every observable fact leads to the conclusion that electrical energy is carried by photons.
This makes sense because we know that photons are essentially carriers of energy. The primary reason that photons have
been rejected as carriers of electrical charge is because they are electrically
neutral , if it is photons that carry electrical energy , physicists argue , what would
account for the electromagnetic field ?
The solution to this might lie in the fact that photons not only carry electrical
energy but that they also make up
the electromagnetic field.
In order to understand how this might take place we
need a model of the photon structure.
Banishing for the moment all extraneous observations and concentrating
solely on the photon and its observed properties and using common sense
deductions to build the photon model offers a solution. Given that photons are emitted by
electrons and that electrons are charged particles , it follows that what the electron maybe
emitting is electrical energy . Let us suppose then that this electrical energy
is emitted by the electrons in short bursts creating bands of electrical energy
, which are separated by a di-electric. Let us suppose also that the bands of
energy released first are more highly charged than the bands of electrical
energy which are released subsequently resulting in a positive –negative polarity. What results is a capacitor
like structure , as we have seen a structure like this results in a solenoidal
electromagnetic field being formed around it . (Fig. 1)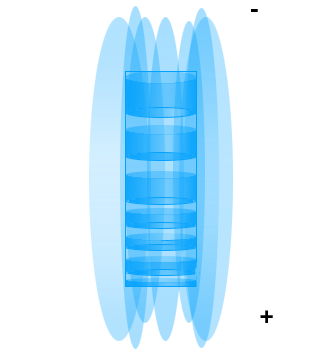 Model
of the Photon.
Model
of the Photon.
Therefore if this model is taken to its ultimate conclusion it must be
assumed that the photon is the smallest possible , most fundamental manifestation of electromagnetism. It is immaterial for
the moment whether the electromagnetic “field” surrounding the photon is the
result of yet smaller particles
flowing through and around the photon or whether it is merely a re-distribution
of the electrical energy of the photon in a localised manner which gives rise to
electromagnetic phenomenon , what is material to the discussion is that such a
physical structure of the photon would fulfil all the known properties of
photons. For instance , the capacitor or condensor was first used as a device for storing of electric charge ,
therefore the photon structure suggested would explain one of the central
properties of the photon , namely its ability to retain its energy or identity
unchanged over unimaginable
distances . The suggested photon structure would be electrically neutral. The
suggested structure would also have no mass and would possess the properties of
both a particle and a wave. If a charged condenser is connected to a line of
uncharged condensers and the whole system is earthed , the energy would travel along the line
of condensors with the speed of light and deliver all its energy at the
culminating point , this point will be elaborated further. The most important
aspect of such a photon structure is that it would allow photons to connect with
other photons , in much the same
way that solenoidal magnetic fields can interlink and that this linkage can take place in
two orientations , either in parallel (Fig 2.)
 Photons
in parallel
Photons
in parallel
Fig 2.
or in series (Fig 3.
)
 Photons
in series
Photons
in series
Fig 3.
To take the matter a little further , it
is the present understanding that photons have wave lengths from as small as 10
-12 m. for gamma rays to as long as 5 x 10 5 m. resulting
from AC current used in power
transmissions . Now it is manifest
, to even the smallest child , that an electron having dimensions of 10 -12 m or less cannot , under any circumstances, emit waves 500,000 metres in length.
Many explanations have been given for this , none of which seems to make
sense. The introduction of virtual interactions has resulted
in gauge theories which have become increasingly complicated and abstruse , in
order to explain these phenomenon.
A common sense approach to this problem would be to
limit the size of photons that electrons can emit. The upper limit of such a
size would seem to lie just at the border of the low infra-red at about 10
-6 m . I have termed these photons as “conduction “ photons , since
they are the photons that conduct electrical energy. The physical structure of
the photon outlined and illustrated above would allow photons to link together ,
either in parallel or in series.
This would explain all electrical , electromagnetic and magnetic
phenomenon as we at present understand them.
It is time to put to the test the issue of how the flow of electrical energy
would be effected in an electrical conductor using photons as the agents of
electrical energy . The best
sequence in which to undertake such an exercise is to start with proven
phenomenon and to extrapolate from there . It is known that electrons when excited emit photons , let us suppose then
that by some means ( a battery or an electric generator etc., ) electrons are excited with an energy
that causes them to emit conduction
photons , these photons travel through the conductor and are absorbed either by
a free electron or by an electron
in the outer orbit and are
immediately re-emitted , thus conduction photons travel through the
conductor from atom to atom or electron to electron arriving at their
destination at the speed of light and there giving up their energy. Free electrons which emit electrons are in a quandary , they are in the middle of nowhere
travelling in the vast interstitial
spaces in the atom lattices of the
conductor , they have an urgent need to re-absorb the energy they have given up
, the emitted photons are in a comparable situation since they need to be
absorbed by electrons of similar energy ,
thus conduction photons are dedicated to the electrons which have emitted
them , they therefore travel through the conductor and if not absorbed , leave
the conductor at the positive pole , link up with other photons ( “Virtual”
photons ) to form chains or lines of linked photons which travel at the speed of light and re-enter the conductor at the negative pole to be
re-absorbed by another free electron , or by an electron in the outer orbit. The
flow of electrical energy in an electrical conductor might therefore be thought
of as a continuous process of emission and absorption of conduction
photons. With the conduction photons travelling through the conductor
exiting it through the positive end linking up with other photons to make chains
or lines and re-entering the conductor at the negative end. As a corollary to
this it follows that the chains or lines of photons outside the conductor must
be “virtual” photons (i.e one true photon for each composite photon
wave-length.)
The next issue to attempt to understand is the process by which conduction photons carry electrical energy. It has been explained that photons , because of their solenoidal structure , can link to or connect up with other photons and that this linkage has two orientations , in series and in parallel. It has been established that the energy of a photon is dependent on its frequency or wave-length by the relation e = hc/λ and e = hf . According to the New Field Theory proposed here , a photon cannot have a wave-length of greater than 10-6 m. The longer wavelengths are therefore composite waves consisting of strings of linked up or connected photons , which since their energy is shared have a progressively lower energy depending upon the wave length of the composite wave, i.e longer wave-lengths would have less energy. This simple model of the structure of the photon solves all the problems related to photons and their wave-lengths and frequencies , they are as easily linked together as Lego blocks.
Just as “conduction “ photons link together with “virtual” photons to form composite waves responsible for longer wave-lengths such as radio waves , it must be assumed that all other photon wave lengths are also the result of such linking up. In order for this hypotheses to work it must be assumed that there exists a fundamental photon wave-length (i.e a photon possessing the smallest wave length and highest frequency and energy. ) it is possible that this fundamental photon wave-length is about 10 -13 m. Thus all other photons are made up of additives of the fundamental photon wave length. Such a system would considerably simplify the mechanism by which photons can exist in such vast variations ranging as has been said before from gamma rays with wave lengths of 10 -12 m. to radio waves of 10 5 m and more.
It
has been suggested that conduction photons are emitted and absorbed not only by
electrons in the outer orbits of the atom but also by free electrons , this type
of interaction is at present expressly forbidden by the Pauli exclusion
principle , for the reason that
most free electrons do not
possess enough energy (always
excepting electrons in lasers ) ,
or because they lack the inertial stability such as is found in attached
electrons , which would enable them to
cope with the forces of recoil entailed by the emission of a photon .
This is the situation of a
free electron in an electrical conductor , according to quantum physics as it is
at present understood ,it is forbidden
to emit a photon by the conservation laws. It is often stated that
electrons in the outer orbit are loosely connected and that even the force due
to light friction caused by rubbing or the latent heat present in a hand is
enough to release them from their orbits .
Yet if we are to take quantum mechanics at its face value , even such a
process must involve the emission or absorption of photons. Further , if we consider the physical
implications of the propagation of
“conduction “ photons it is apparent that the free electron would have very
little say in the matter , the physical dimensions of the conduction photon
would make collision and absorption with a free electron a more likely
occurrence than not !
If this line of reasoning is followed through , it shows that conduction photons in
this situation are even more highly energy specific (i.e follow the restricted energy level principle rather more than less rigidly ) than those of the higher frequency photons such as visible light . For instance an emitted photon of this energy has to (is compelled ) to return to an electron which is missing exactly the same amount of energy , just as the electron in its turn has to absorb a photon of the same specific energy , hence the loops of electromagnetic radiation surrounding an electrical conductor , once this linkage is broken (as for instance by a reversal of current polarity ) the chain of linked electrons moves away from the source (like all photons ) at the speed of light , when they are detected (absorbed) they (like all photons ) preserve their initial identity.
The remarkable thing to note here is that the photons attempt to return to the electrons which are missing their particular energy level through the shortest and most direct route , which because of the electro-dynamic forces in the conductor , happens to be the negative pole of the conductor , although points along the surface of the conductor might also serve as places of entry. The photons , if not absorbed , therefore issue from the positive pole of the conductor and immediately try to make their way back to their source via the negative pole of the conductor forming the characteristic loops which we refer to as electromagnetic lines of force. Thus instead of the electromagnetic field giving rise to photons as was thought to be the case , we now realise the possibility that in fact it is the other way around and that it is photons which give rise to electromagnetic fields.
Consider also the fact that photons have no rest mass , once released they are supposed to move away from the electron that emits them at the speed of light . This being so how does one account for the fact that photons in an electromagnetic field around a wire carrying a current stay bound to the vicinity of the conductor ? According to all known principles , once emitted or otherwise formed , they should leave the vicinity of the conductor at the speed of light . The second question is why when there is a change in polarity do they suddenly change roles , start to behave like real photons assume a direction away from the conductor and move away at the speed of light ? The quantum mechanics attempt to solve this question is highly convoluted and involves a great deal of mathematical abstraction which is impossible to go into at this point.
Creation destruction and preservation
:
The present quantum theory of electromagnetic radiation states that electromagnetic radiation is caused by the vibration or oscillation of ions and electrons in the crystal lattice of the conductor , under the influence of an electric field within the conductor.
This vibration or oscillation , results in the formation of an electromagnetic field around the conductor , the energy of the electromagnetic field gives rise to “virtual” photons . This is the process of creation , matter being formed out of energy. In the second stage , that of propagation , it is assumed that the whole of space is permeated by “virtual” particles , these particles electrons and positrons , always exist in pairs and are formed out of “virtual” photons , the particles being representative of matter and anti-matter annihilate themselves giving rise in the process to a “virtual “ photon. This is the process of destruction. If the electron-positron pair interact with a real photon , the product of the annihilation process is also a real photon . This is the process of perpetuation or preservation. This in plain language is the essence of the gauge theory .
The concept is not new and reflects the Hindu philosophy of the Universe , that of creation , destruction and preservation.
However
, as has been noted previously , the implementation of preconceived philosophical concepts to
account for observed physical phenomenon has seldom been successful as has been
noted with regard to the first Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle , which new
research with attosecond pulsed lasers has almost rendered obsolete , or at the
least untenable. The same may also
be said of Louis de Broglie’s theory of wave –particle duality. A very simple , mathematically irrefutable , statement can easily
be formulated to substantiate , Bishop’s Berkley’s statement that : “
when no-one is present in a room , the
room and its contents are in fact non-existent.” Yet the mathematical
logic behind this statement would essentially be an oversimplification ,
although the equivalency of energy and matter , do make the statement a distinct
possibility.
It is interesting , here , to note the similarities between , “New Field
Theory “
and quantum theory:
· Both theories believe that the electromagnetic field is made up of “virtual” photons. While quantum theory states that these “virtual” photons are created out of the energy of the electromagnetic field. “New Field Theory” states that the electromagnetic field itself is made up of “virtual” photons and form the lines of force as have been observed.
· While quantum theory believes in electron-positron pairs. “New field theory “ states that the field is made up of virtual photons , which , because of their very low energy , can be visualised as being , essentially , photon shells , which can take on the identity of practically any photon energy up to the “conduction” photon.
It is interesting to note that while quantum physics seems to depend upon philosophical concepts “New Field Theory” leads again and again to the fine structure constant 1/137, as for instance in the relation between the speed of light and the dimensions of space or in the relation between time and energy in the second Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
Reactive and radiative fields:
Perhaps the most telling proof of New Field Theory as stated here lies in the difference between reactive and radiative fields around a conductor carrying an AC current. When an alternating current is present in an electrical conductor , two types of fields are observed an inductive field and a radiating field . The inductive field of an ac current is often called the near field because it is concentrated near the source. Similarly, the radiating field is referred to as the far field because its effects extend far from the source. The boundary between the inductive field and the radiative field is generally represented as being approximately l/2pi . The principal point of interest here is that qualitatively , both fields are regarded as being the same , the only discriminating factor being the distance from the conductor at which the field undergoes interaction. This poses a problem for in spite of calculating the energy values of the different wave-lengths which such an oscillating current would give rise to , using fourier analysis , the end result is that the sum of the energies so available does not make sense when compared to the reality as proposed by the equation hc/ l . One of the ways in which this problem has been circumvented is by basing calculations on actual measurements made in the near field rather than by the implementation of any theory . Working backwards from these measurements it is possible to conclude that the near field has a higher energy component ( which translates to shorter wave-lengths and higher frequencies ) than the far field and is based on pure observation more than any sound theory .
The difference between inductive and radiative fields according to “New Field Theory “ depends solely on the orientation of the photons. If the photons are aligned length wise in series ( like bar magnets arranged in a line with a north to south alignment ) then the composite wave-length would carry the energy of a single conduction photon. If on the other hand the photons were arranged in parallel (bar magnets placed in a row side by side ) the photons would have the composite wave eigen value .(i.e., hc/l). To give you an example of how this works , take for instance the ordinary house-hold supply of 60Hz. This gives a wave-length of about 5 x 10 5 m. The energy corresponding to this wave-length would be 3.972 x 10 -32 J , which is infinitesimal , about 2.47 x 10 -13 eV . Yet the induced current due to this field is measured in hundreds of Amperes and thousands of Volts , how can there be any connection between the two ? There seems to be no connection whatever between the energy value of the composite wave energy (field )and the energy in the conductor. To elaborate on this further, the energy in the field when used in an induction process results in almost the same current (98%) flowing in the secondary as was present in the primary , yet if the two conductors are separated by some distance , and the same frequency is used , the energy in the secondary conductor due to the field is hardly detectable and is in the order of microamps . This reduction in energy is not in proportion to the inverse square law. It must be pointed out here that the orientation of the photons making up the composite wave and the frequency or wave-lengths resultant from an oscillating current as based upon the present theory are by no means restricted to a single frequency or wave-length , which has been used here in the interests of greater clarity , but can result in a spectrum of wave-lengths and frequencies .
Using New Field theory it is immediately possible to account for this discrepancy in the calculated energy and the observed energy of the far and near fields. ( i.e inductive fields and radiative fields. ) . If we use the orientation of the photons in the composite wave it is possible to see that when the photons are connected in series , regardless of the wave-length of the composite wave the value of energy delivered to the conductor would remain unchanged , the linear orientation of the composite wave as it enters the conductor yielding up the correct amount of energy (i.e that of a single conduction photon).. In this case it would be as follows : - (Composite wave-length divided by conduction photon wave length multiplied by the composite wave eigen value )i.e (5x106 / 10-6 ) x (4 x 10-32 ) =19x10-20 J which is the energy of the conduction photon (i.e., hc/l = 6.62 x 10-34 x 3 x 105 / 10 –6 = 19 x 10 –20 J. ) and is equal to about 1.9eV. Now if we take the radiative value of the same field the photons have been oriented in parallel and the energy value at the receiving conductor (antenna ) 5km (or even 500m ) away , would be the intensity value I multiplied by the energy of the composite wave i.e 3.972 x 10-32 J (approx) which is several orders of magnitude lower than what we would have expected if conventional reasoning is used. Here again it must be assumed that when dealing with such wave-lengths , that the composite wave at such distances from the conductor is more or less disassociated with the conductor and take on a parallel orientation.
Thus the New Field
Theory as stated above deals definitively with the qualitative difference
between radiative and reactive electromagnetic fields.
The Field :
The Universe consists of atoms containing charged particles (electrons ) moving with non-zero acceleration and constantly emitting electromagnetic radiation ergo , photons , or “virtual” photons . Thus the Universe is filled with “virtual “ photons. When a real photon (i.e one having energy in significant amounts and for significant times when taken on the sub-atomic level.) makes its appearance , the “virtual “ photons immediately re-orient themselves forming a line whose ends rest on infinity and passing the energy of the photon along at the speed of light. Since “virtual” photons are , when taken in this sense of being , all pervading , synonymous with space itself . The question of why photons travel at the speed of light when taken from this view-point is simply that to go any faster would mean arriving there before starting out !An evident implementation of the fine structure constant.
When considering the radiation due to an isotropic conductor , the suggested structure of the photon , allows them to link up both laterally and in series with virtual photons. This means that photons which link up laterally with virtual photons , share some of their energy to the photons on either side. There is a limit to the amount of energy that can be shared if this limit is exceeded the real photons themselves turn into virtual photons , the radiating structure is broken up and ceases to exists. This kind of shared structure is in agreement with the inverse square law. On the other hand if the radiation source lasts for some duration of time , re-enforcement takes place , meaning that the distance covered is dependent on the duration for which the radiation is maintained by the source. The existence of the red shift and the blue shift , measured in nano metres , tend to support this theory that a photon can lose only so much energy before losing its identity and ceasing to exist.
Conclusions:
So there it is , an explanation for all electromagnetic radiation and related phenomenon , explained in a , when compared to present gauge theories , simple manner. Yet this deceptively simple theory unifies many at present disparate phenomenon . I would like to stress here that “New Field Theory is not a criticism of quantum mechanics , in fact it should be considered as being more of a rationalisation of facts previously brought to light by quantum mechanics . For instance , to take the points one by one:
Ø To begin with the conduction of electricity in a conductor is according to quantum mechanics , due to a field theory , this is at variance with the central theory of discreteness underlying quantum mechanics . New Field Theory , suggests that it is photons that are the agent of electrical energy conduction , bringing the theory of electrical conduction into line with mainstream quantum thinking.
Ø Again the present quantum mechanics thinking with regard to the electromagnetic field due to currents is that it is the result of the agitation of electrons and ions in the lattice of the conductor and that this gives rise to an electric field the energy of which in turn gives rise to “virtual” photons. Once again quantum theory seems to be at variance behind the central idea of discreteness. While New Field Theory states that the electromagnetic field due to a current is composed of “Virtual” photons it also explains how these fields are formed due to the interaction between real photons and “virtual” photons which results in lines of “force” being formed around the conductor.
Ø New Field Theory , at least with regard to the propagation of electromagnetic radiation , rejects present quantum thinking that “virtual” particles always exist in electron-positron pairs , but states instead that , electromagnetic radiation is propagated through “virtual” photons , which pervade the whole of space , and which initially moving at random , align themselves in the direction of propagation into a line who ends rest on infinity , as soon as the presence of a real photon is sensed . The physical structure of the photon suggested by New Field Theory , makes it possible for photons to propagate in straight lines without loss of energy , thereby avoiding the intuitive interaction which interaction with electron-positron pairs. A matter / anti-matter annihilation should supposedly be more powerful than even a fusion reaction , how is it possible under these circumstances for the end result to yield actually the correct value out of the trillions of possible photon energy values ? Again the low energy allowable to “Virtual” photons by the application of the second Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle , means that they can exist for quite a long time , making possible the method of propagation of electromagnetic radiation as suggested by New Field Theory.
Ø An important point is that the physical structure of the photon as suggested by New Field Theory , still maintains all the earlier observations of quantum mechanics , for instance such a photon structure would still maintain its wave-particle duality properties , although for a different reason than that attributed for these properties by quantum mechanics . Secondly the idea of discreteness is still observed , the photon structure suggested by New Field Theory being definitely an energy packet of fixed energy levels , further it can retain this energy for considerable periods of time.
Ø Finally by limiting the size of the largest photon which an electron can emit , New Field Theory does away with the complicated Mathematical gymnastics necessary to explain how an electron with a size of about
10-13 m. can emit wave-lengths of 10 5 m. and more. Photon structure as suggested by New Field Theory allowing these “conduction “ photons to link together to form composite waves , of any wave –length. Again the fact that this linkage of photons can take place in two orientations , in series and in parallel , explains in the former case , how photons can deliver up electrical energy measured in thousands of amperes and also how , in the latter case , energy is inversely proportional to wave-length and frequency.
Ø Critics of the New Field Theory might point to the fact that longer wave-lengths such as micro-waves are known to react with matter in a different manner than shorter wave-lengths and that the same objection might hold good for “conduction “ photons. To this it must be said firstly that (a) conduction photons are about two hundred thousand times shorter than micro-waves ( micro-waves used commercially have wave-lengths of about 20cm. ) and (b) that from the point of view of New Field Theory any wave-length greater than the “conduction “ photon wave length is considered as being a composite wave. Therefore , New Field Theory does not state that micro-waves interact with matter in a different manner than they have been observed to do , but in fact supports such an interaction. Micro-waves because of their comparatively long wave-lengths interact with matter at the molecular level and not at the atomic level.
The advantages of adopting the New Field Theory are numerous . To start with it simplifies and unifies numerous disciplines which have been hitherto thought of as being disparate. The phenomenon of magnetism can easily be explained if the theory of electrical conduction as outlined above is extrapolated , and offers a more easily understandable and cohesive theory than the present theory of constantly flipping magnetic domains. Perhaps the most important contribution of New Field Theory is that all electromagnetic phenomenon is unified under it. Under quantum mechanics , electromagnetic radiation of wave lengths consisting of visible light and smaller were considered to be different from wave-lengths longer than visible light. New Field Theory shows that all electro-magnetic radiation follows the same rules and is the same physical manifestation of the photon. Similarly fields as related to electromagnetic phenomenon are eliminated and shown to be made up of “virtual” photons. Similarly the manner in which light propagates through a solid and the way in which electrical energy propagates within a conductor are unified. The difference between radiative and inductive electromagnetic fields is conclusively explained by New Field Theory.