 Access 2000
Access 2000
Microsoft Assess is a database program with which you can create, organise and manage data collections. After you set up databases, enter and edit your database data, you can analyse, sort, summarise, and report on that database data.
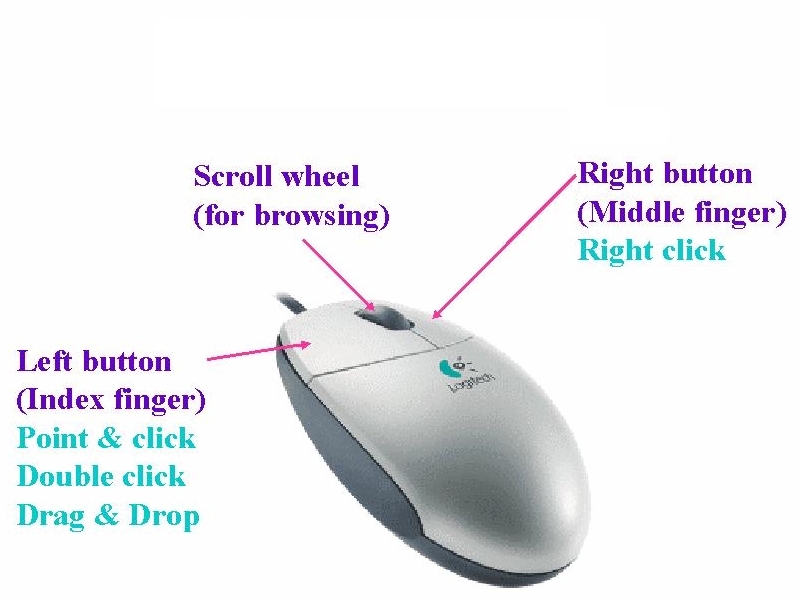
(1) How to use the Mouse to click :
The Start button <Start> from which you display the Windows 2000 Start Menu (you can start any Windows program).

The Taskbar is the Windows bar at the bottom of your screen that displays all programs currently running.
(2) Short-cut Menu:
Mouse right-click (Select Short-cut Menu)
(3)
How
to start or launch Access 2000 :
Point and click (Select) <Start>, <Programs>, <Microsoft Office>, <Microsoft Access>

Point
and click (Select)
<Start>, <Programs>,
<Microsoft Office Tools>  to create
a Microsoft Office Shortcut Bar.
to create
a Microsoft Office Shortcut Bar.
Point
and click (Select)
![]()
<Microsoft Access> icon to start quickly.
(4) Database Basics : Design Structure, Database Table, Collections of Data, Organising Database Data for Meaningful Information for Forms, Queries and Reports Analysis.

Analyse the Design up front to determine the Database Structure, then Create the Database - Tables organised by the various Topics by putting specific records and fields.
Microsoft Access is a relational database - relates data from multiple tables instead of duplicating data in more than one location. However, not all Database values will directly relate to one another. Access is extremely flexible, so you can change any Database Structure when you begin using the database.
(5) Creating Access - a new database using :

(a) Access database wizards, pages, and projects : a database design wizard with a step-by-step set of dialog box that guide you through the creation of a customised database using a pre-defined wizard formats.
(b) Blank Access database : You can create a blank database from scratch, which requires the setting up of the entire database structure including tables, fields, and other pertinent database structure information.
(c) Open an existing database : so that you can modify the database structure or work with the database information.
(d) Template : is a preset database layout, so that you can modify to create a particular kind of database.
Menu, Point and click <File>: click New <New> when you need to create a new database, you can select the list of design templates.
(6) Menu Commands and Toolbars : Database
Others, need to customise
Menu Point and click <View><Toolbars> :
click Customize

e.g. with Internet Explorer Interface.
Menu with corresponding toolbars icons
Point and click <View><Toolbars> :
click Database, click Menu Bar, click Web
Database, Menu Bar & Web Toolbars

(7)
Working
with database - Open Document, Templates and Wizards :
Open Document is to transfer a database file (.mdb filename extension) from disk into memory.
Menu, Point and click <File>: click Open
Template is a preset document layout, so that you can modify to create a particular kind of databaset.
Menu, Point and click <File>: click New
Database's Templates : Template's toolbar such as invoices, purchase orders at <File>, <New>, <Databases>. Customise a template, e.g. Inventory Control.
Wizard is a step-by-step set of dialog box that guide you through the creation of a database.
(8) Working with Database Windows - Central Control Panel for listing the database object names of tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules within the database with the options in design view, using wizard, or entering data :
Tables - related data within a database.

Queries - stored instructions that select data from one or more tables for reporting, analysis, and data-management purpose.

Forms - on-screen representations of paper forms for users to enter data into tables.

Reports - printed listings of database data or printed table output.

Pages - publish as a web page

Macros - lists of tasks you want Access to perform.
Modules - programs written in Visual Basic programming language with which you can automate any database task.
(9) Working with Tables.
Tables - related data within a database.

Access
Practice 2 : Create
Your Own Database Step by Step




a. Creating
a Table : collection of data organised in rows and columns for
the entry of Numerical Values, Character Text. The cell is the
value at a Table's row and column intersection.
Moving around a Table :
Tab
(Next
Cell)
Shift-Tab
(Previous
Cell)
Alt-PageUp
(Column's
Top Cell)
Alt-PageDown
(Column's
Bottom Cell)
Ctrl-Home
(Current
Row's First Cell)
Ctrl-End
(Current
Row's last Cell)







b. Formating Data or Character or Tables on the workbook - add style and flair to your database.

c. Sorting of data for simple query - select data from the data field.


(10) Creating and Using Queires.
Queries - stored instructions that select data from one or more tables for reporting, analysis, and data-management purpose.

(11) Designing a Form.
Forms - on-screen representations of paper forms for users to enter data into tables.

(12) Designing a Report.
Reports - printed listings of database data or printed table output.

(13) Publish as a Web Page (exporting) : Save as HTML page, so that data can be view in a browser, but will not amended.
Pages - publish as a web page

Are
you ready for MOUS  Certification?
Certification?
Microsoft Access 2000 Core Task Skills
 Edwin
Koh : Congratulations
in Your New
Knowledge and Skills.
Edwin
Koh : Congratulations
in Your New
Knowledge and Skills.
