|
Kepler's Laws
 Kepler's 1st law:
Kepler's 1st law:
Each planet orbit in ellipses, with the sun at one focus.
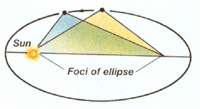
Kepler's 2nd law:
The product of the distance from the focus and the transverse velocity is a constant. (The transverse velocity is the velocity perpendicular to a line drawn from the object at focus). [The line from the planet (comet) to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal periods of time].
*When a planet (or comet) is at aphelion or perihelion, all of the velocity is transverse.
 The planet or object moves faster when it is closer
The planet or object moves faster when it is closer
to the Sun. It takes the same time to travel from C to D and A to B.
Return to top
Kepler's 3rd law:
The ratio of the square of the period, P (amount of time to complete one full orbit), and the cube of the semi-major axis, A, (radius of the orbit). When P is measured in years, and A in astronomical units, AU. (Au is the average distance from the earth to the Sun)
P2 = A3
Kepler's 3rd law can also be expressed as this second equation using Newtonian mechanics.
P2 = (4p2A3) / g (m+M)
m and M are the masses of the 2 bodies & p=3.14
This equation can be used to determine the masses of objects outside of our solar system.
 During an Earth orbit, Mars makes just 1/2 an orbit,
During an Earth orbit, Mars makes just 1/2 an orbit,
Jupiter about 1/12 off an orbit & Saturn about 1/30 of an orbit.
Return to top
Circular Velocity
If an object has a constant speed if it moves in a circular orbit around a much more massive object:
Vc=(GM/d)1/2
m is mass of body in the center
d is the distance between the objects
G is the gravitational constant :
(6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
PROBLEM:
An asteroid's closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is 2 AU, and farthest distance from the Sun (aphelion) is 4 AU. What is the period of the asteroid?
Solution:
P2 = A3
P = (33/2)
P = 5.2 years
The period of the asteroid is approximately 5 years.
Return to top
|






