 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Note: some images may not be suitable for all readers] |
 |
Pelvic laparoscopy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
| Ovarian cyst |
|
|
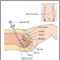
Pelvic laparoscopy is a surgical procedure used to view the interior of the lower abdomen without major surgery. Small optical instruments can be inserted through the abdominal wall to directly visualize the interior of the abdomen. Some surgeries can be done using laparoscopic techniques. Recovery from this type of surgery, unlike open surgery, often takes only a day and the patient usually returns home the next morning.
[
Alternative Names |
|
 |
|
|
Pelvic laparoscopy
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
band-aid surgery; celioscopy; peritoneoscopy |
|
|
|
Definition |
|
|
|
Surgical procedure to examine and treat abdominal and pelvic organs through a small surgical viewing instrument (laparoscope) inserted into the abdomen. |
|
|
|
Description |
|
|
|
While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), a one-half inch incision is made in the skin below the navel (umbilicus). Air is pumped into the abdomen to make the organs of the abdominal cavity more easily visible. The laparoscope is inserted and the area can be viewed. Instruments can be inserted through the scope to obtain tissue samples or to perform certain surgical procedures. After the laparoscopy, the gas is released and the incision is stitched. |
|
|
|
Indications |
|
|
|
Pelvic laparoscopy is used both for diagnosis and for treatment and may be recommended for: |
|
|
|
pelvic pain due to |
|
|
|
uterine tissue found outside the uterus in the abdomen (endometriosis)
infections (pelvic inflammatory disease) not responsive to drug therapy
suspected twisting (torsion) of an ovary
ovarian cyst |
|
|
|
Ovarian cyst |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
scar tissue (adhesions) in pelvis |
|
|
|
puncture through the uterus (uterine perforation) following D&C or by IUD
evaluation of infertility
sterilization (tubal ligation)
evaluation of a pelvic mass (such as in a Fallopian tube or ovary) that was confirmed previously by abdominal ultrasound |
|
|
|
Pelvic laparoscopy is not recommended for: |
|
|
|
severe obesity
existing severe pelvic adhesions from previous surgeries
signs of abdominal infection |
|
|
|
Risks |
|
|
|
Risks for any anesthesia are: |
|
|
|
reactions to medications
problems breathing |
|
|
|
Risks for any surgery are: |
|
|
|
bleeding
infection |
|
|
|
Expectations After Surgery |
|
|
|
Laparoscopies are growing more popular with physicians, especially with the advent of more "high-tech" laparoscopes. This procedure can be done on an outpatient basis, but an overnight stay may be necessary. The operating time averages 1 hour.
Whether used as a diagnostic or as a therapeutic procedure, this procedure may avoid major surgery at a minimal cost. Unless major problems are uncovered during the procedure (such as appendicitis, severe bleeding, or certain cases of ectopic pregnancy), laparoscopy may be the only operation needed. |
|
|
|
Convalescence |
|
|
|
The gas pumped into the abdomen may cause abdominal discomfort for 1 or 2 days after the procedure. However, you should be back to normal activities in less than 2 days. Sexual activities may resume as soon as bleeding, if any, has stopped. Call your doctor if you have severe abdominal pain, persistent fever, or vaginal bleeding.
|
|
|
| The information provided herein should not be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions |
|

