
By H R u b i j a n t o
The challenges and opportunities facing the new paradigm of global business, in the form of expanding information technology, new and sophisticated markets, increasing competition and mounting regulatory pressures are evolving as foreseen. Correspondingly, as anticipated, increasing requirements for fast, flexible information access are accompanying this changing business enviroment. At the same time, the growing need for Information Systems required the maintenance and enhancements to the production systems developed in the past as well as the increasing complexity which accompanies the shift from a batch type enviroment to an online enviroment.
The Characteristics of the New Paradigm of Global Business, includes
1. Shift from big technology to high technology, so it enables to mass customization, a unique setof preferences, unlike anyone else’s
2. The new consumer are not what they used to be, more affluent and better educated. They have expectations that say they can have any product, any time,any place and they expect to get it at low cost
3. Potential market is going to emerge from the internet. What the people know as E-Commerce is the most exciting potential for the future in terms of retail channels. Being able to access information globally, systematically is quite attractive marketing technologies to show, promote and customize product service.
4. Activate direct marketing. Using E-mail,households with high incomes are the prime target for virtually all mail from business. This kind of targeted business mailing will most likely follow this wealthier household as they age and higher individual income.
5. The company as production users work achieving target based on network technology, easily get information from any suppliers around the world at any time and dealing with them at their first convinience.
6. The end of the middleman. In the second curve new consumers making direct connection to the producers using familiar IT – technology in the new geographic markets, so the channel of distribution is not just shortened, but moreover the unnecessary chain as middleman will be eliminated.
The use of KMIS (Knowledge Management Information System), have confirmed the existence of an already appreciable comprehensive information system in viable applications development. It is equally apparent that this system will escalate rapidly as newer information requirements are identified and needed for setting up a strategic management and business policy.
KMIS Strategic Management and Business Policy Outlook. It is necessary to understand who the customers of KMIS, more specifically who is ‘the server’ and who is ‘the client’. Generally, the customers of KMIS as the client are all the internal users of data processing, this includes all departments from Product Management, Market Anlysis and Planning, Customer Services, ComputerComm., Network Services, Supply, Corporate Planning, Human Resource Development and Corporate Secretary. In anticipating newparadigm, KMIS does some work for associated companies and subsidiaries, evolving direct interactives to the market, suppliers and producers based on IT networks.
As a corporate function, KMIS carries out its responsibility of providing a corporate direction toward overall information resource management and interactive information processing activities related to the adoption of intranet-internet technology as a vehicle for encouraging organization-wide knowledge sharing within a large, global bank. The outcome of intranet adoption was that, integrate individuals across this particular organization, the intranet actually helped to reinforce the existing functional and national boundaries. This could be partly explained by the idea emphasis on decentralization within the organization, which configure the use of the intranet as a decentralizing, organization-wide tool. This is possible because the intranet via LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network) can be described as an interactive and decentred technology, which therefore has the potential for multiple features and effects. Thus, while the intranet is often promoted as a technology that enables processes of communication, collaboration and social coordination it also has the potential to enable such processes.

Moreover, it is argued that to develop an intranet for knowledge-sharing requires a focus on information technology facets of development. These different facets may require related, sometimes independent, sets of strategies for blending the technology and the organization, thus making it possible for a project team to work effectively on all facets simultaneously. This was evidenced by the fact that the independent intranet-implementation projects considered actually managed to encourage knowledge-sharing as intended, within the relatively homogeneous group, or even across the border into internet, for which it was designed. Broader knowledge-sharing across the wider organizational context occur even among those who were working on what were defined as ‘knowledge management’ projects. The idea is that knowledge-sharing via intranet-internet technologies may be most possible to achieve in contexts where knowledge management is the key objective.
Cost/Benefit and Performance Improvements. Use of KMIS is often justified on the basis of cost/benefit and performance improvements as a result of operational efficiencies and productivity improvements on the application of business policies. Other consideration often include flexibility, ability to grow, better and faster management information. While these represents the end results customers buy and consider to be of value, the functionalities they consume or utilize are services such as computer and network systems operations, hardware and software maintenance, systems development and specific phases within the systems life cycle.
In making ‘buy’ decisions, customers consider factors associated with the product or services beyond, such as stability, longevity, reliability, credibility, trust, knowledge, professional reputation, commitment and the capacity to direct all arising problems toward the integrity of strategic objectives. The value of ‘Company’s Knowledge’ is often described as "Intellectual Capital"; it is generally regarded as the difference between ‘Company organization's book price’ (how accountants value the organization) and ‘its market value’ (how the market values the organization). This idea could bring about the executives to increase their market value by employing higher educated and more experienced staffs, besides applying newer information technology, implementing KMIS and infrastructure equipments. Company should aware that knowledge management can facilitate development of structuring the data and information, processing capacity of information technologies and continuously improving and leveraging knowledge of the innovative capacity of human beings. It requires initiatives toward the interactive of participants to produce the dimension of knowledge sharing to ensure the abilities of controlling the business of information product service. In this concept intellectual leadership will lead to an unprecedented breakthroughs in organizational performance, business and social value.
KMIS Market Segmentation. To identify the Markets KMIS services, usually two parameters should be chosen, Business Planning Units and Core Business Functions. Business Planning Units (BPU) is chosen because it is the fundamental to the business of the corporate and use of BPU approach for planning purposes is beig implemented by the corporate planning department. The core business functions parameter is chosen because it allows KMIS to view the organization from a purely functional point of view and thus develop a better core business perspective. The mainline core business functions Product Service Development, Product Service Provisioning, Sales and Customer Services, Operation and Maintenance represent the basic line operations in the company,and the support businessfunctions Human Resource Development, Accounting, Finance, Corporate Planning and Administration are the major categories of specialized support to the mainline business functions. By implementing KMIS there should be laid down two basic infrastructure of information technology, the information system services and network services.
From Strategic to Operational Management. Within the management discipline, planning and control processes take place at different levels, the management activities at each level covering a speific time span and having a specific purpose. The three levels, generally recognized, are strategic management (covering a 5 year period or longer), tactical management (covering a one or two year period) and opeational management (on a daily, weekly or monthly basis). Strategic management is concerned with adjusting the business overtime according to the everchanging conditions and requirements of the enviroment. It involves the setting of long range objectives, the establishment of overall priorities and the selection of strategies (i.e. the approaches and methods) to be used to meet the objectives.
Tactical management concerns the planning and control of resources within the framework of the established strategic objectives. In breaking down the long range goals into shorter range objectives, determining the resources needed; setting upand implementing specific programs to meet the objectives; and ensuring that the resources are brought in and used by the organization in a best possible way. Tactical management is performed in many parts of an organization, in the form of, for example personel planning, user portfolio planning, and capacity planning. Budgetting and other financial management activities play a key role at this level, because such activities provide data and information about the combined financial effects of other tactical decisions in the company.
Operational management is directed toward the planning and control of individual activities and tasks within the framework of given resources. It is primarily aimed atensuring that individual staff members perform their tasks as efficiently as possible. Planning the work to be done, following up the work accomplished and making detailed production schedules are examples of management activities in this category. The center of each planning and control loop is a decision maker who needs accurate, meaningful and interelated information with which to measure the progress of the work activities being managed and an organization structure and standards guideline to allow this activities to be directed and controlled in the most effective way on the platform of KMIS.
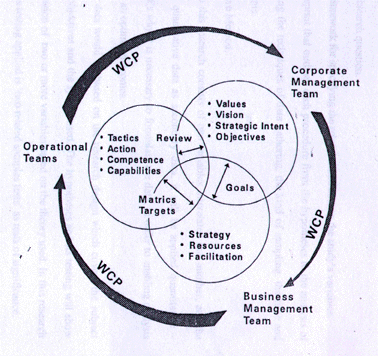
The Implementation of KMIS for Strategic Management and Business Policy toward WCP (World Class Performance). Conducting todays business management almost no place to hide from the changes and its impact to the whole organization, and this condition stimulate managers to be familiar to discontinous changes in the enviroment. Managers concerned with assuring a promising future for the company, always try to find out a conceptual framework for managing discontinuities, a systematic approach to making srategic decisions, and a methodology for guiding the implementation.
And corporate planners will find a critical evaluation of the up to date techniques of strategic analysis, procedures for tailoring the techniques to the needs of a perticular company, and a series of step by step problem solving procedures. They can also extend their field of competence beyond strategic planning to the larger perspective of strategic management by learning concepts and techniques of capability analysis of strategic implementation based on information technology available in learning organization.
The evolution of strategic management was begun in the late nineteen fifties, when companies invented a systematic approach to deciding where and how the company will do its future business. The analytic part of this approach has been named strategy formulation, and the process by which managers jointly formulate strategy has been given the name of strategic planning, The next step was taken in the nineteen seventies, when it was discovered that the internal configuration (capability) of thr company has to be transformed whenever a company makes a discontinous change in its strategy. The process of determining the capability needed to support the new strategy has been named capability planning. The third step is the late nineteen seventies, was taken in response to the growing frequency of rapidly developing discontinuities in the enviroment which were unpredictable intheir consequences, particularly socio-political and technological discontinuities.
To cope with this, companies have begun to use a real time strategic response technique called issue management. The fourth and most recent step evolved from the organizational resistance which was encountered by early efforts to implant strategic planning into the company. The nineteen eighties emerging comprehensive approach is management of discontinous change, which take account of psychological, sociological, political and systematic characteristic of complex organizations.
The currently emerging information technology approach is an approach of strategic management for managing gap towards the second curve based on the capabilities of information technology. The discontinous change is better defined by term ‘paradigm shift’, in which the life-cyle of business product in the first curve is followed clearly by the second curve. Anyhow the definition of ‘strategic management’ by H Igor Ansoff is still valid until today, provided we use the information technology as the supporter of the whole idea. “Strategic management is a systematic approach for managing strategic change which consist of positioning of the firm through strategy and capability planning; real-time strategic response through issue management; systematic management of resistance during strategic implementation. Strategic management is a systematic approach to a major and increasingly important responsibility of generl management: to position and relate the firm to its enviroment in away which will assure its continued success and make it secure from surprises” 1)
The changes of companies enviroment recently, is identified by the application of new technology of information consist of terminal or mobile terminal, the network which connects one to another, the multimedia contents and all of it are explored for the sake of global competition by knowledge management.
1) H Igor Ansoff “Implanting Strategic Management” Prentice Hall, London – 1995, page xvi
In the near future there will be no doubt, most companies will eager to implementing ‘knowledge management’ as their strategic management, provided this program conducted in more favorable atmosphere by better mastering information technology of infotech leaders and awareness to adapt smart culture in learning organization.To response the implementation of KMIS, considering an alternative or even different strategy become the most considerable decision of corporates management. The rise of the new open, networked enterprise constitutes a new organizational paradigm.
The nature and purpose of computing are being altered and a new technology era is unfolding, entering a second era of information technology in which the business application of computers and the leadership for use of technology are all going profound change. Organization that cannot understand the new era and navigate a path through the transition are vulnerable and will be bypassed.
One department is no longer content to depend on another department to get any information needed, they want to control its use and determine the effect it will have on their on work. Managers more understand that their effective use of information technology will determine their personal and organizational success. An important change is is the shift in focus from traditional highly structured and hierarchical organization to the dynamic business team, which cuts across traditional organizational boundaries, to be thiny and smart learning organization.
Organizations are establishing new form of flatened corporate layers and at the same time are changing the way people work. The pyramid structure that has been part of the business culture for decades is being replaced by a new responsive form. In both front liner and managers are being organized into laterally based work teams with new accountabilities and responsibilities. The open networked organization is based on cooperative, multidiciplinary teams nad business networked together across the enterprise and linked to the external customer and partners. The advantage of streamlined, small and smart organization is possessing flexibilitis factors such as dynamic, fluid and adaptive. On the other hand its simplication aspects will eliminate overcontrolled hierarchies, reduce restrictive job description and simplify procedure, supported by integrated, holistic and project based system. “Rather than a rigid structure, it is a modular organizational architecture in which business teams operate as a networked of what we call ‘client’ and ‘server’ functions. Teams are both clients and servers for other teams, who are both internal and external to the organization.” 1)
On the other hand the old style of leadership is not adequate for the transformation that is required. Dealing with the typical management challenges created by competitive intensity the management challenge appears sometimes to be almost overwhelming. But in many situations today, the technological, competitive, market, economic, and political uncertainties make strategic decision making more complicated. Fortunetly the work based team and networked management emerges as a smart and cooperative team to overcome business problem solving. 1) Don Tapscott and Art Caston, “Paradigm Shift – The New Promise of Information Technology”, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1993, page 191
In general, it will be a world in which the leadership factor in management will become increasingly important for companies prosperity and even survival. The main expression of turbulent of the emerging global civilitation is the constant restructuring of business sectors. The global up and down in all industries, manufacturing and service is strong influence by emerging markets that are engaged in selective global expansion. To deal with this condition some companies are consilidating through mergers and acquisition to reach the scale considered necessary to compete in the global arena.
The global alliances and market means several countries and many different cultures to consider. And a kind of succesful cross cultural leadership should be build under the awareness of different values in different countries and regions. The appreciation of different values will bring about the succesfull adaptation in the period of adjusment and long life production process. Infotech Business Management needs to operate in the many new extended network and alliance structures. These have emerged in order to adopt new competitive approaches and because the technology requirements of many products and services exeed the competencies of any one organization. The organization challenge here is to find a common purpose, to derive common strategies and to engage in common action. This often means recognizing segments of customer opportunity and mobilizing the different players in a loose network of organizational alliances to seize that opportunity.
Technology’s impact used to be limited mainly to product improvement and manufacturing process improvement. It was concentrated in the high technology sectors of the economy. While even smaller companies leaders could not ignore technology, it seemed posible to them to manage it through others with more technical competence. Today, these leadership career paths are in question. Technology is providing new ways to integrate supply, manufacturing and distribution, and is producing large gains in customer value at much lower cost.
Nowadays technology’s role is not limited to high technology, it is becoming a decisive factor many others sector such as distribution, services even public administration and government. In all this field, the leadership or the superleadership challenge to build and use technology effectively and responibly. Leaders therefore need to have a much firmer grasp of technology and a greater ability to manage it than in the past. Because leaders today need ‘two sides coin’ strategy, they have to run their business as efficiently as possible, yet at the same time they have to change it. They need to have a much firmer grasp on technology, which is providing new ways to integrate supply, manufacturing, distribution and e- com. which is redrawing the boundaries between historically separate industries.
In implementing Infotech-Management, we have to take into account the main forces are affecting the process of leadership like the development of newer, flatter matrix forms of organization, the growing number of alliances and informal networks and people’s changing expectations and values. Recently, leadership has become more foccused on customer satisfactionand the empowering bottom line, but the pressure is increasingly to create moremeaningful employment and to confront broader social and enviroment issues, and quality of life. In the modern business world intensive competition, everywhere and every day managers confront shattering and accelerating change, change paced by constant innovations in computer and telecommunications technologies.
To survive and become superlative in today’s economic enviroment there is an urgent imperative beyond competitive, the wisdom and open mindedness to build infotech-leadership as the source of excellence business advantage. This is the key of for tomorrow’s winners which is targetting prominent areas of management including responsiveness, innovation, empowering staff, and information technology. Tomorrow’s managers will create new roles for their people, converting today’stechnology to tomorrow’s needs; finding new niches and customers through their capabilities using infotechnology. Managers will become more dedicated to attracting and retaining experts and will become skilled in coordinating their talents in professional networking.
Development discussions and knowledgesharing will focus on what contribution isneeded to allow the organizationand individual togrow.Effective leaders will balance shortterm achievement with long-term development, integrating programsdepartments into thewhole objective of organization. Leaders who seek to ensure long-termviability commit time,money,and resources to research and development. Supporting thecompany’s researchplans helps us to keep in touch with industriestrends, new technologies,growth opportunities, and changes incompetency and skill requirements. Learning shows upin results, bringing in clients from other cultures, seeing a way to use a technical processfrom another company, recognizingfinancial patterns that suggest the need for a new pricingor payment schedule. We each have our unique ways of learningalone, with others, throughexperimenting, reading, preparing papers for conferences, researching, tinkering, shadowing the best, scanning the Internet. Organizations that foster learning reward breakthroughs in thinking, solving problems,creating new products, or Expanding existing lines of service. They recognize and rewardlearning that serves the mission and strategy, and applaud the inventionsof their experts.They expect people to keep learning and adding value.
In the strategy selection process should show how business portfolio and the whole management information support the corporate including to identify the present corporate strategy; conduct the business portfolio analysis; consider the whole network of information system; select the corporate strategy; evaluate the selected strategy. It is highly recommended to implement knowledge management backed up by information network and skillful creative managers charge in this program. The prominet elements of ‘knowledge management’, includes elicit knowledge, create knowledge, disseminate knowledge, networked information, artifial intelligence, virtual reality and interactive media.Management must understand where the company is now and what strategies are currently being followed. Skillful identification of present corporate strategy provides the foundation for selecting new or confirming existing strategies.The business portfolio analysis process can be pursued as the most important step of strategy selection, but do not lose sight of the idea that portfolio analysis is only one step of the overall strategy selection process.
Taking into account the whole network of information system, should be calculated the hardware, applied software and the obselence of the system. The directions of network to customers, suppliers and distributors require overall reviews due to the implementation of different or new strategy. Management should now be in an excellent position to select an overall corporate strategy, or a combination of strategies, that adds new business units to the portfolio; delete business unit(s) from the portfolio; modifies business strategies of one or more business unit; modofies corporate performance objectives; focuses on altering those conditions responsible for forecast perfomance or maintains the status quo. To evaluate the strategy selected, management should ask and answer some penetrating questions regarding the strategies and the most important question is: Will the the strategy achieves the objectives.