FORCE / SEPARATION GRAPH
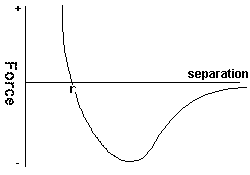 When the forces of attraction and repulsion for two molecules
at various separations are added together this is the resultant graph, the is an equalibrium position at r where the particles do not
exert any force on each other. At a closer separation a repeling force (taken as +ve) acts on the molecule, at a larger separtion there is a (-ve)
attractive force.
When the forces of attraction and repulsion for two molecules
at various separations are added together this is the resultant graph, the is an equalibrium position at r where the particles do not
exert any force on each other. At a closer separation a repeling force (taken as +ve) acts on the molecule, at a larger separtion there is a (-ve)
attractive force.
POTENTIAL ENERGY / SEPARATION GRAPH
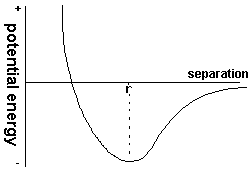 This graph of potentil energy (or work done in bring the molecule to that point from infinity)
is found from integrating the above graph of force with respect to distance (from the definition of work). From infinity
to r work is done by the particle after r, work has to be done on the particle. Normally a particle in this system has a certain
amount of energy, in the form of potential energy due to it position and kinetic energy, if we draw a straightline through the bottum of the graph
parallel to the x axis, then the kinetic energy will be equal to the perpendicular distance between this line and the curve. It should be noted that
there is a minimum value of potential energy at r, a molecule at this point on the curve is at absolute zero and does not have any K.E.
The point where the potential energy is zero (and the curve crosses the x axis) is said to be the distance of closest approach.
This graph of potentil energy (or work done in bring the molecule to that point from infinity)
is found from integrating the above graph of force with respect to distance (from the definition of work). From infinity
to r work is done by the particle after r, work has to be done on the particle. Normally a particle in this system has a certain
amount of energy, in the form of potential energy due to it position and kinetic energy, if we draw a straightline through the bottum of the graph
parallel to the x axis, then the kinetic energy will be equal to the perpendicular distance between this line and the curve. It should be noted that
there is a minimum value of potential energy at r, a molecule at this point on the curve is at absolute zero and does not have any K.E.
The point where the potential energy is zero (and the curve crosses the x axis) is said to be the distance of closest approach.
 PHASES OF MATTERForce-separation curve and potential energy-separation for two neutral atoms/molecules.
PHASES OF MATTERForce-separation curve and potential energy-separation for two neutral atoms/molecules.

