![]()
Plants and their colour
 |
|
|
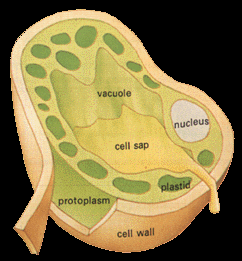
| GREEN | The most common colour, green is present in 0.01mm diameter convex lens shaped plastids in the leaves, stems fruits and seedsof plants. Leaf colour is modified by surface texture, hairyness or gloss |
| BROWN | Brown pigments are usually located in cell walls when they are damaged and the chemicals oxidise. A bruised apple or autumn leaves are typical. Brown colours in healthy flowers are the result of pigments, eg red and green chlorophyll lying beside each other. |
| YELLOW | The primrose is coloured with anthoxanthin yellow dissolved in the cell sap. Others may be coloured by carotenoid plastid pigments. When chlorophyll breaks down is produces yellow carotenoid pigments to give the yellow autumn leaves of plants like the Ginko. |
| ORANGE | Tomato and carrot contain carotenoids. An orange skin though has large cells containing a bright yellow oil, other cells have red sap and there is a yellow waxy coating. |
| RED | Red in roses, geraniums and autumn leavescomes from anthocyanin pigments in the cell sap. Rose hips and very red tomatoes contain red plastid pigments. |
| BLUE | Blue in plants is usually due to anthocyanins. |