Introduction
General Information about Harappa
The Indus Civilization existed from approximately 2500 B.C. to 1500 B.C. and was one of the greatest achievements in the Indus Valley. Harappa, one of the major cities, is located in the province of Punjab in Pakistan near the Ravi River and was an urban center in the Indus Valley. The Harappans built part of their city on a enormous hill and on it was a huge citadel that was 1,445 ft long and 600 ft wide Architects built a wall around it to protect it from sand, rocks, or anything that could damage the citadel. The wall had a towers and a defense railing on it to protect it from invaders.
Mohenjo-Daro, another important city, was very organized. These two cities probably had the same type goverment and no evidence has been found that either had armies. It is said that Harappa was a peaceful civilization and the people only used bronze knives, spears, and arrowheads for hunting. Both cities were made with the same type of construction, and were said to be the capitals of their provinces. There is evidence that Harappa didn't have social classes as remains of temples or palaces have not been found. People did not have protection because none of them had rivals.

Mound B
Location
In Pakistan, we live in the province called Punjab. In that province is located ruins of the Indus Valley Civilization. One of the main cities, Harappa, is a half an hour drive from Sahiwal. We live in the city of Lahore. For us, it takes three hours to drive from Lahore to Sahiwal. and then a half hour drive onward to Harrapa.
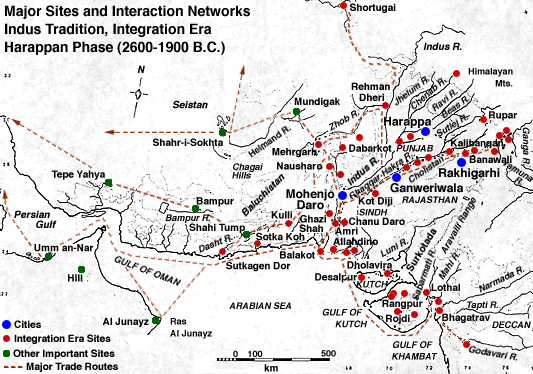
Information on Mohenjo-Daro
Mohenjo-daro, or the "the mound of the dead", is the twin city of Harrapa and it is one of the major cities of the Ancient Indus Valley Civilization. It was discovered in 1922 by an archoelogist called Sir John Marshall. Mohenj-daro is located in Pakistan's province of Shidh and is 440 Kilometers northwest of Karachi.
Mohenjo-daro is quite well preserved. It is large, well planned, and was believed to have a population of about 5000 people. Many of these people had houses made of brick. Two types of brick were used for building. Baked brick was used the basesof buildings and for the wals of important buildings. Sun-dried brick were softer and used for the wall of private homes.
Mohenjo-Daro is better preserved than Harappa and not believed to be as old. One of its main attractionis the Great Bath. The city is now on the world cultural list of UNESCO.

Student model of Mohenjo-daro
Trade
At the sites in the Indus Valley and far away places, archeologists found evidence of a trade network. With the help of seals archeologists foundout about the Indus Valley trade network . They found pieces similar to those in the Indus Valley in faraway areas. That gave them clues that Indus Valley trade was very strong. Historians think that merchants used seals to mark their property. Some of these seals turned up in Ancient Southwest cities. On the back of one of the seals is the imprint of course cloth.
Jewelry and beads are other clues that archeologists used to work out puzzles about the past. Indus beads have been found in Syria and beads from areas of the Indus Valley have been found in Sumeriun cities. Neither the ocean to the south nor the mountains to the north were barrirs to Indus Valley traders. At Lothal, an Indus Valley site, near the Arabian Gulf archeologists have found the ruins of a dockyard. From there ships could have sailed up the Persian Gulf to Mesopotamia.
 Student model of an ancient well.
Student model of an ancient well.