 Reference
Reference
 Size
Contact
Size
Contact
Don's Home
 Reference
Reference
 Size
Contact
Size
Contact
|
Under Construction 
Outer Space | Inner Space (germs) The largest thing we know about, the universe (1,477 septillion [1024] meters) is a trillion, trillion, trillion, billion (1045) times larger than the smallest thing, a quark (1 attometer [10-18 m]) . Big Things
The cosmos is 13.7bn years old but the stretching of space with its expansion after the Big Bang means that simple distance measurements do not apply. 2. Pluto's orbit varies from 30-50 AUs from the sun. In 2003 a new planet, Sedna, was discovered with an orbit which varries from 76-850 AU in its 10,500 year orbit. It is nearly 97 AU away from the sun now. Using Sedna, the diameter of the solar system is 926 AU. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.Planets to Scale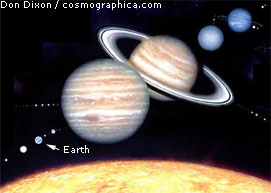 Jupiter is 142,796 km in diameter Reduction = 1 / 6 billion (109) (Distances between planets are not to scale.) |
Outer Solar System Pluto's orbit is 12 billion km in diameter. Reduction = 1 / 200 trillion (1012) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Milky Way Galaxy Diameter = 150,000 light Years (1.4 quintillion [1018] km) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Small Things
* Note: micrometer (µm) is the preferred term but micron is still commonly used. † angström (Å) (10-10 m) was used in the older "CGS" (centimeter-gram-second) version of the metric system, but nanometers (nm) 10-9 is preferred in the newer "SI" (International System) version of the metric system.
A. milimeter mm
B. micrometer µm (or micron)- Dust - Cells | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Respirable dust - Those dust particles that are small enough to penetrate into the lungs. |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
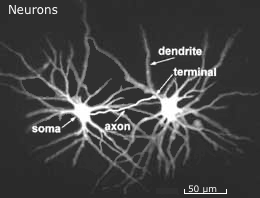
| Neurons vary from 4 - 100 µm. A single sensory neuron from your fingertip has an axon that extends the length of your arm, while neurons within the brain may extend only a few millimeters. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
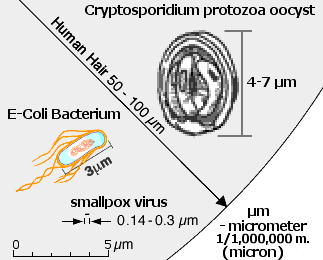 about 5,000 x magnification |
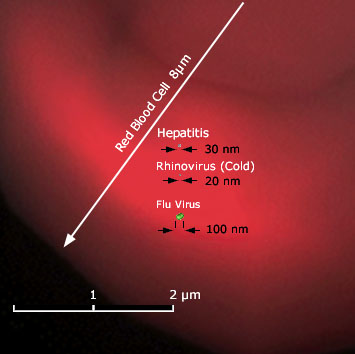 20,000 x magnification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(actual magnification varies slightly depending on your display resolution)
Cell sizes vary greatly. Bacteria, single celled organisms, range from 0.2 to 20 µm;
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
C. Nanometer - Molecule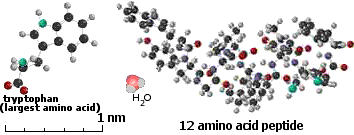 25,000,000 x magnification | The 12 amino acid peptide folds up on itself, so is only a few times larger than a single amino acid. Proteins (made up of one or more polypeptide molecules, up to 300 amino acids) range from 3 - 10 nm. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- A molecule with 60 carbon atoms is about 1 nm Molecule size is frequently measured by molecular weight or Daltons (Da.). One hydrogen atom has mass of 1 Da. Proteins and other macromolecule molecular weights are usually measured in kDa or kD (kilodaltons) - 1000 Da. See Also: Basic Physical Scales Relevant to Cells and Molecules D. A hydrogen atom is about 0.5 Å in diameter, a carbon atom is about 2 Å in diameter. Atom sizes are not proportional to the number of protons and electrons, because the extra protons in larger atoms have a stronger force to attract the electrons to smaller orbits.
Interactive demo of size at CellsAlive.com
Resolving Power and Electron Microscopes Objects smaller than about 400 nanometers (wavelenght of violet light) will always be invisible to the human eye, because a ray of light can only resolve objects that are larger than its wave length. The Scanning electron microscope (SEM) gets resolution down to 5 nm. The transmission electron micrograph/microscope (TEM) is the prefered tool of biologists. It's resolving power is 3 nm. High-resolution versions can get down to 0.2 nm. See Mediscan. Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) is a generic term for a group of techniques that scan a fine probe (or tip) over a surface, either very close to the surface or just touching it, constantly or intermittently. Scanning tunneling microscopes (STM) and atomic force microscopes (AFM) allow you to image down to individual atoms (0.1 nm).
X-ray diffraction (XRD) can resolve things down to about 1/100 the size of an atom (one picometer). D. The "size" of atomic and sub-atomic particles loses its meaning, because these "particles" behave as though they are waves, or wave packets. their masses are usually given in energy units of c2 from the Einstein relation E = mc2. Physicists have determined an upper limit on the size of the quark to be 10-18 meters based upon data from high energy collisions.
Smallest theoritical limit: Super Unification Theory (Gravitation unified with combined force and matter fields) predicts a natural end of space and time at 10-43 sec. and 10-35 m (Plank length) This is the Planck scale and time - space-time becomes quantized and gains infinite curvature, so that the classical concepts of space and time become meaningless. No faster times or shorter distances. There is one unified field. There are some who believe that the next level of fundamental particle, if any exists, may be found at the incredibly small scale of the Planck length. See Also: Measuremenet notation/units Conversion tables here Weights Particle Physics A Sense of Scale at PBS's NOVA
Size of Cells and Molecules
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||