|
Partitioning is one of the necessary steps to prepare a drive for use. It is the process of defining certain areas of the hard disk for the operating system to use. A volume is a section of the drive with a letter, like
C: or D:. All hard drives must be partitioned, even if they will only have one partition.
It is a way of dividing your hard disk so that each section functions as a separate unit. You can create a partition to organize information, for example, to back up data, or to dual boot with another operating system. Each partition can be accessed as if it were a separate disk.
When you create partitions on a disk, you divide the disk into one or more areas that can be formatted for use by a file system, such as
FAT or NTFS.
You can create up to four Primary Partitions per disk, or you can create three
Primary Partitions and an Extended
Partition. You can use the free space in the Extended
Partition to create unlimited Logical
Drives.
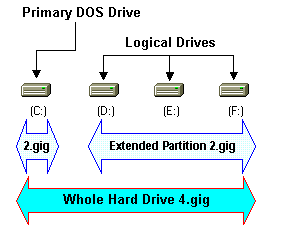
Generally, the first partition of a hard drive is a Primary
Partition, normally the
C: drive, when it's the Primary-Master
drive.
Extended partitions are required for hard drives with more than one partition. Only
one Extended partition is allowed per hard disk. You can't do anything with an Extended Partition without first creating a Logical DOS drive
in the Extended Partition .. which leads to our next point.
Logical DOS drives are created in Extended
partitions. They are handy, since you can have only one Extended partition per hard disk, giving you the ability to create more than two partitions per hard disk.
These would be your Logical DOS drives. For example, they would be your
D: drive, your E:
drive, etc. Each Logical DOS drive gets its own (drive) letter. You can create more Logical DOS drives on a hard drive than you'll ever have need for.
Advantages of Multi-Partition Drives
Advantage #1:
A hard drive containing multiple partitions allows you to lower your drive's effective access time, providing you with a more responsive system.
If you create a partition at the outer/leading edge of your drive and install your operating system & applications there .. and use the inner/slower parts of the disk for storing files that don't require access during normal system operating (i.e. downloads, drivers, back-ups, Drive Images, etc.) .. you'll limit/restrict your drive's seeks to the fastest part of the drive.
In other words, the drive's read/write heads won't have to travel (seek) to the far end of the drive (during normal system usage). This will provide you with a more responsive system by decreasing the drive's effective seek/access time.
If you install your operating system to a single, large partition, there's nothing to prevent both system & program files, over time, from winding up at the far end of the drive (Windows updates, program updates, driver updates, etc.).
System and program files that wind up at the far end of the drive take longer to access, and are transferred at a slower rate, which translates into a less-responsive system.
Access times are the #1 factor for determining how well a hard drive will perform, when we talk about running an operating system & applications.
In other words, it doesn't matter how high of a transfer rate a drive can *sustain* .. if it's spending all it's time *seeking*. A Ferrari won't do you much good if you have to keep stopping at each red light in town. The car will never be able to 'get up to speed'. It's not the best example, but it might help you understand the underlying principle.
Keeping your frequently-accessed files close to the drive's leading edge will improve both access times *and* sustained transfer rates for files stored there. Have I rode this horse into the ground yet?
Advantage #2:
A drive with multiple partitions allows you to defrag only those partitions that actually need defragging. This saves wear and tear on your drive, and may even help keep it from failing prematurely.
It can take literally hours to defrag 60GB worth of fragmented data, not to mention 120 or 160 gigs. This means you have to plan your defrags much more carefully than you do with a drive containing smaller, multiple partitions. A small partition can be defragged in the time it takes to grab a cup of coffee, or take a .. uh, I mean, go to the bathroom. =)
Single-partition advocates claim that they defrag *overnight*. This is fine, but it needn't be that way. And you shouldn't have to run your PC all night if you don't want to. You shouldn't have to wait until bedtime before defragging, cuz your drive will take hours to finish. And you shouldn't have to defrag 60 gigs worth of data when only a small percentage of it is actually fragmented.
Advantage #3 (my
favourite):
A drive with multiple partitions allows you to easily create & restore images using programs such as
PowerQuest's DriveImage
or Norton's Ghost
These programs will not allow you to write an image to the source partition. In other words, the image's source & destination partitions cannot be the same.
This would mean you'd be changing the contents of the partition as you created the image .. which is not possible.
If you want to learn more about creating & restoring images (you should), I've put together a guide
here
The ability to create & restore back-up images is a skill that you definitely want to include in your bag of digital tricks.
|
