Alcohol is natural substance formed by the fermentation that occurs
when sugar reacts with yeast and is the major active ingredient in wine, beer,
and distilled spirits. Although there
are many kinds of alcohol, the kind found in alcoholic beverages is ethyl
alcohol. Alcohol is a ”psychoactive” or
mind-altering drug, as are heroin and tranquilizers. It can alter moods, cause changes in the body, and become habit
forming. Alcohol, which is legally
available in beverages except to those under legal drinking age, is a
drug. Alcohol is the most used drug in
our country today. It’s the number one
drug problem of teenagers and children, and alcoholism is the 3rd
leading cause of death in this country after heart disease and cancer.
 What exactly is alcohol?
What exactly is alcohol?
Alcohol is a depressant that acts as a sedative when ingested. In medical terms, it is C2H5OH
(Ethyl Alcohol or Ethanol). It slows
down the activity of the brain and spinal cord. Whether one drinks a 12-ounce can of beer, a shot of
distilled spirits, or a 5-ounce glass of wine, the amount of pure alcohol per
drink is about the same – ˝ ounce.
Drinks with more than one liquor such as a Black Russian is counted
as two drinks because each contains two (vodka and Kailua) servings of
alcohol. Each ˝ ounce carries a
level of .02% BAC (Blood Alcohol Concentration). Alcohol is also found in other products used
by the consumer. Some nighttime cold
relief medicines and cough syrups contain up to 25% alcohol. It is the ethanol (alcohol) that sedates
your brain and allows you to fall asleep.
To a recovering alcoholic, an alcoholic in need, or a child, using one
of these nighttime cold relief medicines or cough syrups can have a devastating
effect.
Why drink alcohol?
Many people think of drinking as a way to cope, and to relax. But in truth, alcohol dulls the brain and
keeps you from sleeping properly. After
drinking, the normal sleep patterns are impaired and you awake un-rested and
feeling tired. It hasn’t helped your
coping ability; instead it has probably made it worse. Ethyl Alcohol can produce feelings of
well-being, sedation, intoxication, or unconsciousness, depending on the amount
and way in which it is consumed.
|
·
When alcohol is consumed, 20% of the alcohol in it is
absorbed immediately into the bloodstream through the stomach walls. ·
The other 80% of the alcohol enters the bloodstream almost
as fast after being quickly processed through the gastrointestinal tract. ·
Alcohol immediately acts on the brain’s central control
areas to slow down or depress brain activity. ·
The higher blood alcohol levels depress brain activity to
the point that memory, as well as muscle coordination and balance, may be
temporarily impaired. ·
It takes 1˝ hour for the liver to burn off each drink. ·
Once the alcohol has entered the system, nothing can be
done about the effects until the liver has processed it. ·
If a person over-indulges in alcohol they experience a
common occurrence referred to as a hangover. Symptoms of hangovers may include,
headache, upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, unclear thinking, aching muscles,
and dehydration. A person, who
becomes nauseated when inebriated and passes out, can die of asphyxiation. ·
Taking larger amounts of alcohol within a relatively short
period of time such as “chug-a-lug” contests and “marathon” drinking can depress
deeper parts of the brain which severely affect judgment and dulls the senses
which can lead to blackouts (loss of consciousness) or alcohol
poisoning. ·
Alcohol poisoning can lead to brain damage, respiratory
arrest, and possibly death. |
What are the dangers associated with using alcohol with
cocaine?
Researchers in Florida are studying a rash of deaths involving the
simultaneous use of alcohol and cocaine.
The use of these two chemicals is producing a compound in the liver
called coca ethylene, which travels to the brain through the bloodstream. In the brain coca ethylene causes the
release of dopamine that scrambles regulating signals to the heart.
Are today’s views on drinking changing?
Yes. People are much more
concerned about their health, driving record, and keeping their job. Its socially acceptable, even trendy, to
drink non-alcoholic drinks. People are
more accepting of those who do not drink because of less peer pressure,
especially for adults. The realities of
the consequences of drinking and driving and the increased public awareness of
the damage you can inflict on yourself and others make some people quit
drinking.
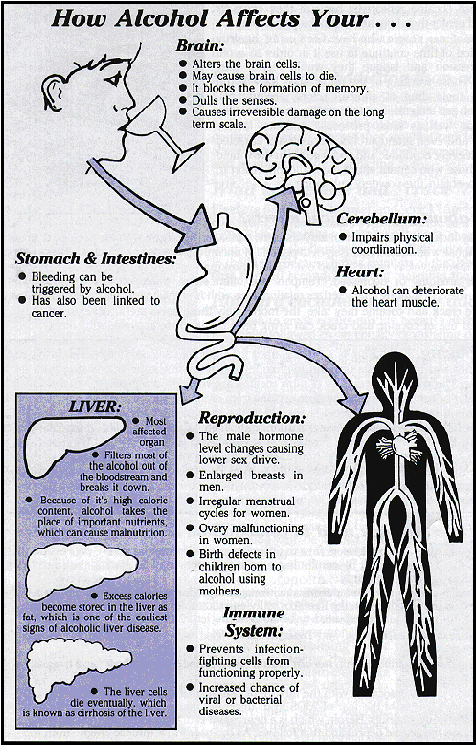
Do only alcoholics have problems with alcohol?
No. Alcohol affects more
than just the user. Many social
problems stem from the use of alcohol.
Every year, for example, many young people lose their lives in
alcohol-related automobile accidents, drownings, and suicides. Serious health problems occur before
drinkers reach the stage of addiction or chronic use, such as birth defects,
memory loss, shakiness, etc. Some
studies have shown more that 25% of hospital admissions were alcohol-related.
Serious diseases associated with chronic alcohol use include alcoholism
and cancers of the liver, stomach, colon, larynx, esophagus, and breast.
Alcohol use can lead to serious physical problems: damage to the
brain, pancreas, and kidneys, high blood pressure, heart attacks, strokes,
alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, stomach and duodenal ulcers,
colitis, irritable colon, impotence, infertility, premature aging, and other
disorders such as diminished immunity to disease, sleep disturbances, muscle
cramps, and edema. Other problems
include birth defects and Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, which causes
retardation, low birth weight, small head size, and limb abnormalities.
Reference Material:
·
National Drug & Safety League (A non-profit
charitable organization).
