Ozone in the treatment of herniated discs
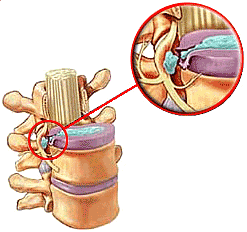 Inter-vertebral discs are responsible for the union of vertebral bodies,
providing flexibility and absorbing the loads that are exerted on the
spine.
Inter-vertebral discs are responsible for the union of vertebral bodies,
providing flexibility and absorbing the loads that are exerted on the
spine.
Due to age or traumatic injuries, the discs undergo important changes in their volume and shape, in addition to an alteration in their composition and biochemical properties.
Herniated discs are produced by damage of the Inter-vertebral disc or discs, that shift off their normal position, pressing the nerves that pass throughout the spinal medulla.
Many of these injuries are dealt with open surgery, which can be highly aggressive and not very effective, with a percentage of patients superior to 30% that do not achieve positive long-time results.
Throughout numerous clinical studies carried out to evaluate the results on patients who received treatment with ozone by intradiscal injection at cervical and lumbar levels, it was detected that three or four months after the application of the ozone injection, the extruded fragment that was clearly visible in the images of the magnetic resonance, had completely dissolved, whereas the rest of the disc got re-hydrated and re-expanded.
A study focused on the action of ozone on the cartilage that forms the Inter-vertebral discs, presented at one of the last world-wide congresses of the specialty, showed that after the application of Ozone-therapy, took place a restoration of the liquid of the cartilage, resulting in an expansion of the disc, and eventually producing a complete disc regeneration. Even in those cases when the slipped disc has no possibility of regeneration, Ozone can help to dissolve the parts of the extruded disc pressing the nerves.
Medical applications of Ozone
| General Medicine |
Angeology and Phlebology |
|
|
|
|
| Neurology |
Rheumatology and Traumatology |
|
|
|
|
| Aesthetician |
Ophtalmology |
|
|
|
|
| Dermatology |
Immunology |
|
|
|
 Administration
Administration
- Topical
- Subcutaneous
- Intramuscular
- Intrarticular
- Paravertebral
- Intradiscal
- Intravenous
- Intrarterial
Forms of Application

- Injection (intramuscular, subcutaneous, intrarticular, intradiscal)
- Major autohemo-transfusion
- Minor hemo-transfusion
- Topical treatment with stock with plastic or crystal containers
- Application of creams and ozonized oils
