Fig. 1.
|
|
|
Regedit Guide:
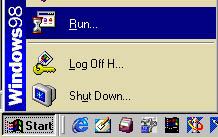
Regedit means Registry editor (Reg - edit). You start regedit by (path
to start regedit: Start|Run[see fig.1]).
 |
|
Fig. 1. |
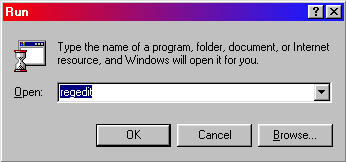
When the run dialog box is open, type "Regedit" and press "OK" [see fig.2].
 |
|
Fig. 2. |
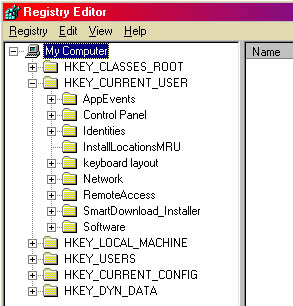
This will start regedit. (see fig.3).
 |
|
Fig. 3. |
The Registry is a database used to store settings and options for Microsoft Windows 32 bit version operating systems (which includes 95, 98, ME and NT/2000); and it contains information and settings for all the hardware, software, users, and preferences of the PC.
The structure of registry is hierarchal and in regedit - and other similar
registry utilities - you will find it similar to the directory structure of
Windows Explorer.
There are six main branches (HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, HKEY_CURRENT_USER,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, HKEY_USERS, HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG, HKEY_DYN_DATA) which
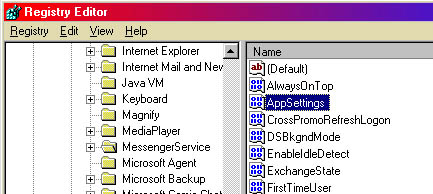
are called Hives. Hives contain keys and keys can contain values
as well as keys. Values holds the information for the registry. There are
three types of values; String, Binary, and DWord
(see fig.4).
 |
|
Fig. 4. |
Registry Tips:
Registry (Backup, Restore, Fix etc):
Here's a nice utility for most of your registry problems. To use it
just exit windows to dos prompt and type "SCANREG/?" this will show
you how to use it, however. Here are the options for your convenience.
Usage:
SCANREG/<options>
|
Options |
Description |
| ? | Displays usage. |
| BACKUP | Backups the registry and related system configuration files. |
| COMMENT = "Your comment here" | Adds the specified comment to the backup. |
| RESTORE | Gives you 5 choices of most recent backups. (Note: Windows backup registry every time you boot.) |
| FIX | Repairs the registry. |
Example:
SCANREG/FIX [This will repair the registry]
(Tip: Before modifying the registry it's a safe practice to backup your registry first. Therefore, if you mess up something during the modification, you can always go back to your old settings.)