 |
Pneumonia |
| |
 |
Commonest is bronchopneumonia |
 |
Due to Haemophilus Influenzae or Streptococcus Pyogenes |
 |
Characterised by tachypnoea, tachycardia, pyrexia, cyanosis and purulent sputum |
 |
ABG |
| |
 |
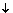 PaO2 = respiratory failure PaO2 = respiratory failure |
 |
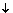 PaCO2 = Type I respiratory failure PaCO2 = Type I respiratory failure |
 |
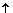 pH = Alkalosis (respiratory) pH = Alkalosis (respiratory) |
 |
N HCO3 = Acute (no metabolic compensation) |
|
 |
Culture sputum |
 |
Antibiotics - amoxycillin |
 |
Physiotherapy and deep breathing exercises |
|
 |
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) |
| |
 |
Risk factors - Women and catheterisation |
 |
Clinical features |
| |
 |
Pyrexia |
 |
Irritative symptoms |
| |
 |
Dysuria |
 |
Frequency |
 |
Nocturia |
 |
Urgency |
 |
Incomplete voidance |
|
|
 |
Treatment - Adequate fluids + antibiotics (Trimethoprim) |
|
 |
Cellulitis |
| |
 |
Occurs at wound site |
 |
Characterised by erythema, tenderness and discharge |
 |
Due to staphylococci or streptococci |
 |
Swab wound discharge & blood culture |
 |
Usually settles without treatment, but may require antibiotics |
 |
May lead to an abscess, requiring surgical drainage |
|
 |
Phlebitis |
| |
 |
Occurs at IV, or central line site |
 |
Characterised by erythema, tenderness and discharge |
 |
Due to staphylococci or streptococci |
 |
Swab discharge & blood culture |
 |
Usually settles without treatment, but may require antibiotics |
|
 |
Sepsis |
| |
 |
Causes |
| |
|
 |
Clinical features (Hyperdynamic circulation) |
| |
 |
Tachycardia |
 |
Tachypnoea |
 |
Hypotension (Septic shock) |
 |
Pyrexia |
|
 |
Commonest organisms |
| |
 |
Gram -ve bacteria |
|
 |
Management |
| |
|
|