Alexei Shemyakin and Levente
Kapás
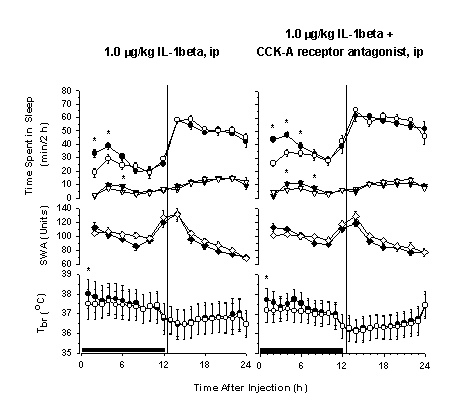
Introduction: Several cytokines and cholecystokinin (CCK) have been shown to induce sleep. They have overlapping biological activities and have mutual stimulatory effects on each otherís secretion or function. For example, administration of interleukin-1 (IL-1) increases CCK plasma levels, IL-1 sensitizes peripheral vagus afferents to the effects of CCK. The effects of IL-1 on the vagus nerve and on food intake are suppressed by CCK-A receptor antagonists. CCK stimulate the production of IL-1, tumor necrosis factor-a and granulocyte/monocyte colony-stimulating factor from monocytes. Increased feeding stimulates the secretion of CCK as well as the expression of IL-1b mRNA in the liver and the brain. The aim of the present experiments was to investigate the role of CCK in IL-1b-induced sleep by using L-364,718, a selective CCK-A receptor antagonist. Methods: On the baseline day, rats received 0.5% methylcellulose (1 ml/kg, ip, solvent for L-364,718) followed by saline injection (1 ml/kg, ip). On the test day, one group of rats (n = 7) was treated with methylcellulose followed by rat recombinant IL-1 beta (1.0 µg/kg, ip). Another group (n = 7) was injected with the CCK-A receptor antagonist (L-364,718, 500 µg/kg, ip) followed by IL-1. Injections were made 10 min apart at dark onset. All recording sessions started at and lasted for 23 h. The amounts of NREMS, REMS, and the delta activity of EEG during NREMS (slow-wave activity, SWA) were measured. Results: During
the first four hours after injections, IL-1-treated rats showed sta
Conclusions: Intraperitoneal injection of 500 \mu g/kg L-364,718 completely blocks the somnogenic action of exogenously administered CCK (1) and increased feeding (2). CCK-A receptor antagonist did not affect IL-1-induced sleep suggesting that the somnogenic effects of IL-1 are independent of CCK-A receptors. References: Chang, H.-Y. and L. Kapás. L-364,718, a cholecystokinin (CCK)-A receptor antagonist, inhibits the sleep-inducing effects of CCK. Sleep Res. 26:138, 1997. Shemyakin, A. and Kapás, L. A CCK-A receptor antagonist inhibits sleep responses to feeding in rats. Sleep 23 (suppl. 2), A121, 2000. Support: Research
supported by NIH (NS-30514).
|