

|
Capacitors are components which have capacitance (stores free electrons)
storage devices for which store a reservoir of potential current flow.
This stored current can be released in a controlled way or discharged
quickly in response to the needs of the circuit. In its simplest form
a capacitor is made up of two metal surfaces with the same area, The metal
surface is usually aluminium foil which is separated by a dielectric (insulating
material such as glass).
If the capacitor is inserted into a dc circuit, see fig 10 and a battery is connected to it a voltage potential is created across both plates of the capacitor. At first the capacitor appears to be a short circuit and current from the battery flows at maximum for a few milliseconds until the charge begins to build up and the current flow reduces rapidly until it ceases. Electrons from the plate connected to the battery positive terminal are attracted to the positive terminal of the battery and the plate becomes positively charged. At the same time electrons are drawn from the negative plate of the battery to the other plate of the capacitor which gathers a negative charge. In between these two charged plates there is a sheet of insulating glass, which under normal circumstances will prevent current flow from the negative to the positive terminal of the battery. The build up of this charge will continue until the it reaches a point where there is no voltage potential between the battery terminal and the capacitor plates. |
Since the sheet of glass prevents the flow of electrons from the negative battery terminal to the positive battery terminal the capacitor builds up a voltage potential across the plates This charge will build up until it equals the voltage potential created by the battery.  Fig 10 If the battery is disconnected from the circuit, the charge will remain in the capacitor until it leaks away over a period of time or until it is physicaly discharged. The animation below illustrates a capacitor charging up to a maximum voltage level before being disconnected from the circuit and the discharge resistor inserted. 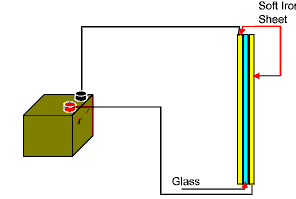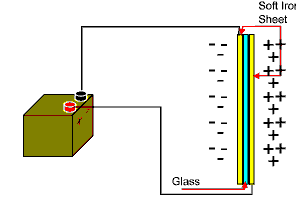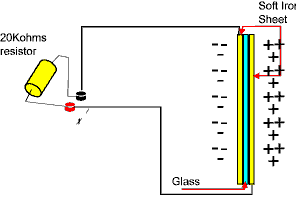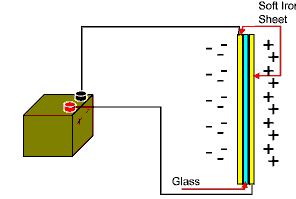 Fig 10b A resistor is connected across the capacitor to discharge it before reconnecting the capacitor back into circuit and the cycle repeats |