KEYWORDS
HDTV
HIGH DEFINITION TELEVISION
-
-
-
Digital
Television (DTV) refers to transmitting a broadcast
signal by encoding it as zeroes and ones, the digital
code used in computers. DTV has many advantages. It can
be compressed to provide four, five or more channels in
the same bandwidth required for one channel of NTSC
television (the current standard). Digital television
provides a crystal clear, "snow-free" picture
to all TVs that can receive a minimum level signal.
-
-
Standard-Definition
Television (SDTV) is a digital television system that is
similar to current standards in picture resolution and
aspect ratio. The picture and sound will be clearer than
NTSC, and its digital base will allow more than one
program to be broadcast over the same bandwidth at the
same time.
-
-
Abbreviation
of National Television Standards Committee. The NTSC is
responsible for setting television and video standards in
the United States (in Europe and the rest of the world,
the dominant television standards are PAL and SECAM). The
NTSC standard for television defines a composite video
signal with a refresh rate of 60 half-frames (interlaced)
per second. Each frame contains 525 lines and can contain
16 million different colors. The NTSC standard is
incompatible with most computer video standards, which
generally use RGB video signals. However, you can insert
special video adapters into your computer that convert
NTSC signals into computer video signals and vice versa.
A new digital television standard being developed is
called HDTV (High-Definition Television ).
- http://webopedia.internet.com/TERM/N/NTSC.html
-
-
To
translate into a digital form. For example, optical
scanners digitize images by translating them into bit
maps. It is also possible to digitize sound, video, and
any type of movement. In all these cases, digitization is
performed by sampling at discrete intervals. To digitize
sound, for example, a device measures a sound wave's
amplitude many times per second. These numeric values can
then be recorded digitally.
-
-
-
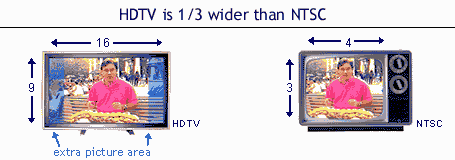
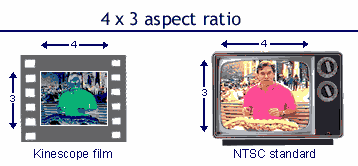
The
ratio of screen width to screen height. Example: 16x9,
4x3
- http://www.cybercollege.com/tvp009.htm
-

A word
derived from Picture Elements. This is the smallest
unique point of a digital video image. In a Digital
Video, a picture is divided up into thousand of Pixels,
each specified by Luminance, Chrominance, and position
information.
-
-
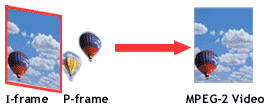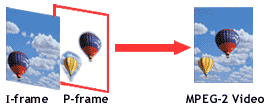
Video
on digital TV will be compressed using a scheme called
MPEG-2. It takes advantage of how the eye perceives color
variations and motion. Inside each frame, an MPEG-2
encoder records just enough detail to make it look like
nothing is missing. The encoder also compares adjacent
frames and only records the sections of the picture that
have moved or changed. If only a small section of the
picture changes, the MPEG-2 encoder only changes that
area and leaves the rest of the picture unchanged. On the
next frame in the video, only that section of the picture
is changed. MPEG-2 has some problems, but it's a good
compression scheme and it's already an industry standard
for digital video for DVD-Videos and some satellite
television services. One problem with MPEG-2 is that it's
a "lossy" compression method. That means that a
higher compression rate gives a poorer picture. There's
some loss in picture quality between the digital video
camera and what you'll see on your television. However,
the quality is still a lot better than an average NTSC
image. And using these compression schemes, MPEG-2 can
reduce the amount of bits by about 55 to 1! With that
ratio, there's a lot of information that get's thrown
away, but there's still enough to look like everything is
still there. The human ear isn't as easy to fool, though.
It's much more sensitive to subtle changes in sound.
Digital TV is going to improve the sound over today's
television using advances in digital sound developed over
the last two decades.
- http://www.pbs.org/opb/crashcourse/digital_v_analog/mpeg2.html
-
-
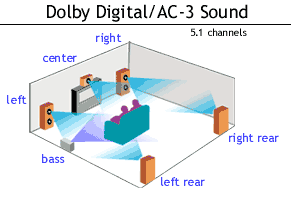
Audio
AC-3digital audiodigital video DVDGive Us YourFeedbackA
standard for high-quality digital audio that is used for
the sound portion of video stored in digital format,
especially videos stored on DVD-ROMs. Dolby Digital
delivers 6 channels in the so called "5:1"
configuration: left, right, and center screen channels,
separate left and right sounds, and a subwoofer channel.
This is sometimes called surround sound or 3D sound.
- http://www.cybercollege.com/tvp042.htm
-
-
A
technique for changing the field of view of a motion
picture or down converted HDTV images that has been
transferred to a smaller viewing format.
-
-
A
phosphor is any material that, when exposed to radiation,
emits visible light. The radiation might be ultraviolet
light or a beam of electrons. Any fluorescent color is
really a phosphor - fluorescent colors absorb invisible
(to us) ultraviolet light and emit visible light at a
characteristic color. In a CRT, phosphor coats the inside
of the screen. When the electron beam strikes the
phosphor, it makes the screen glow. In a black-and-white
screen there is one phosphor that glows white when
struck. In a color screen there are three phosphors
arranged as dots or stripes that emit red, green and blue
light. There are also three electron beams to illuminate
the three different colors together. There are thousands
of different phosphors that have been formulated. They
are characterized by their emission color and the length
of time emission lasts after they are excited.
- http://www.cybercollege.com/gloss_p.htm
-






