AMTK10003
Acela Inspection Car

AMTK10003Acela Inspection Car |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

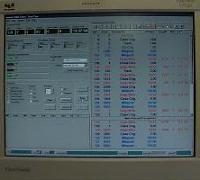
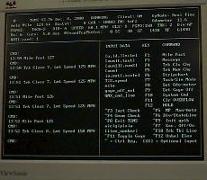
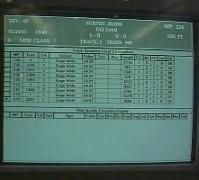
| The system's computers are housed in two 6 foot high industrial component racks. All but one of the computers are dual processor pentiumII machines. Four use a windows operating system while three use QNX, a real time based unix-like operating system used for data acquisition and also Global Positioning Satellite tracking of the car. The tall racks also house analog to digital signal conditioning equipment and the controls for the KLD lasers. |
|
|
|

|

|