home | our design | design code | software | firewire | resources | design team | contact us
FIFO is used by the three modules:
i. The transmitter module,
ii. Receiver module and
iii. The Transaction Control Logic.
The data that is to be transferred to other module is saved in FIFO by the TCL. It is also used by the Receiver to put data that it has received from other node, and now has to be transferred to the Transaction Layer.
The FIFO is quadlet aligned. The size of FIFO is 16 quadlets.
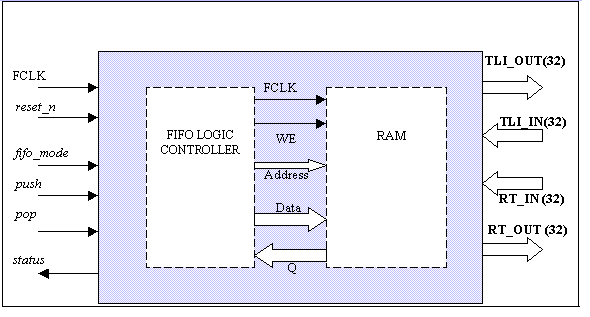
Figure 9.1: The
FIFO module pin diagram
 |
Table 9.1: Port description of the FIFO
module
Signal |
Name and Description |
| |
|
| Status |
This signal shows whether the FIFO is empty or not. HIGH=not empty, LOW=empty. |
| TCL_OUT[31:0] |
Output lines to the Transaction Control Logic. |
| RT_OUT[31:0] |
Output lines to the Receiver and Transmitter modules. |
| Internal
Signals |
Name
and Description |
| WE |
Signals the RAM to strobe data. |
| Address[3:0] |
Address of the RAM. |
| Data[31:0] |
Used for data transfer to RAM. |
| Q[31:0] |
Data output from RAM |
· The FIFO is capable of performing the push and pop operations simultaneously.
· The external modules don’t need to check for the availability of FIFO.
· This facilitates the simultaneous use of FIFO by the Transaction Control Logic and Receiver/Transmitter.
· Excellent speed performance is achieved by allowing simultaneous use of FIFO.
· The technique employed is the Time-Slicing Technique.
It is obvious that read and write operations can not be performed on a memory unit at the same time. An attempt to do so will result in data contention ie failure. To achieve concurrent read and write operations and to avoid failure, Time Slicing technique is used.
In this design if both push and pop operations occur simultaneously, pop operation is performed before push. For external modules it seems that both operations occur simultaneously. This technique is implemented with the use of an external clock with frequency twice as that of the BCLK.
|
The waveform describes all possible combinations of the push and pop signals. First only push operation is performed. Before this the FIFO was empty as shown by the status signal. After push the status signal is HIGH.
At 1.2ms. Both push and pop operations are performed. The pop operation is performed first and the push operation is delayed. Disabling the WE signal that guides the push operation, introduces the delay.