Thanks to the modern Euro currency,
in most parts of Europe, including Rome, now the same
coins and banknotes may be used, but no more than 150 years ago, when the
city still belonged to the Papal State, things were completely different.
In those days, not only each country had its own
system, but often cities belonging to the same state used different coins,
and according to their weight, the values of some units could vary.
In fact, the purchasing power of a coin, especially if made of gold, basically
depended on its value as raw metal. Therefore, only coins were used, made
of gold, silver, billon (an alloy containing various percentages of silver, copper
and other metals) and copper; banknotes
had not been invented yet, although forerunners of the modern cheques called
"letters of credit" already existed: they were documents signed by the
debtor, which the creditor then produced at a given bank to obtain cash. |
 |
All trades were subject to the risk of an unfavourable exchange rate, and to
the slyness of the many money-changers, whose complicated lists
enabled to calculate how much any foreign coin was worth in one's own city.
Furthermore, most systems were based on a combination
of decimal and non-decimal coinage, and to figure out even the simplest
calculation, i.e. how much change was due after a purchase, would appear today
rather complicated.
The one in Rome was probably the weirdest among the systems found in Europe.
This was due to the very old age of some monetary units, whose value in time
had somewhat changed; newer ones, issued by the following popes,
usually did not replace old units, but were simply added to the preexisting ones.
On top of this, Rome's people gave nicknames to some popular coins, some
of which were alternatively referred to with two, three or sometimes four
different names.
This page takes into consideration the period between the 16th and
the 19th century. |
The following list briefly describes each of the main units of this system,
with a few sample pictures that show coins in their actual size.
GIULIO · PAOLO · DOPPIO GROSSO
One of the oldest units in Rome was the giulio,
named after Julius II, who had introduced it in 1504.
Soon after, Paul III (1534-49) wanted a unit of his own, and called it paolo,
slightly modifying the value of the old giulio so to make the two coins perfectly match.
The two names were used as synonyms, although giulio was preferred for
official purposes, while the common people called it more often paolo. |
 |
 |
Both of them were worth 10 baiocchi (see below). But since
5 baiocchi also made a grosso (see below), a third name for
the paolo a.k.a. giulio was doppio grosso
("double grosso").
Some popes also struck a doppio giulio (double piece, worth 20 baiocchi). |
1 giulio (paolo) = 2 grossi = 10 baiocchi = 50 quattrini
3 giuli (paoli) = 1 testone
GROSSO
Its name comes from the Latin grossus, "thick",
although the papal grosso had completely lost
this feature. It was a name also found in other countries, e.g. the English
groat. The roman people popularly referred to it as
grossetto ("small grosso"), or
lustrino ("little shiny"), as it was the
smallest silver coin of the system, worth 5 baiocchi, or ½ giulio. |
 |
1 grosso = 5 baiocchi = 25 quattrini
6 grossi = 3 giuli = 1 testone
BAIOCCO
 |
This is another unit of ancient origin, whose name was
probably borrowed in the Middle Ages from a Merovingian coin, that bore the text
BAIOCAS CIVITAS ("city of Baiocas").
Originally struck in silver,
its value was gradually reduced, until in 1725 Benedict XIII changed
its metal to copper. The same name baiocco also became a generic term
for "small coin". |
Nevertheless, smaller coins did exist (see below).
Several multiples and submultiples of this unit were struck
in the 18th-19th centuries; Pius VI issued eleven different baiocchi
pieces: 60, 25, 12, 8, 4, 2, 5, 2 ½, 2, 1, and ½ baiocco.
The 2 and 4 baiocchi pieces were sometimes called
muraiola (from muro = "wall",
of uncertain meaning), while Pius VI's 5 baiocchi
was also known as madonnina ("small Madonna"),
and the same pope's 2 ½ baiocchi was nicknamed
sampietrino ("small St.Peter").
The smaller coins (up to 5 baiocchi) were in copper, all the others
were in billon.
|
 |
Curiously, by the time of
Pius VI, a silver
grosso coin, worth 5
baiocchi,
coexisted with coins of lesser metallic value (billon), but of higher
nominal value (8, 12, 25 e 60
baiocchi).
1 baiocco = 5 quattrini
30 baiocchi = 6 grossi = 3 giuli = 1 testone
QUATTRINO
 |
Despite the name clearly derived from
quattro ("four"), suggesting the quarter of a unit, in the roman
system this was the fifth part of a baiocco, thus it represented the smallest
coin, made of copper.
Also the term quattrino became a synonym for "penny, small coin",
(i.e. in expressions such as "pennyless", and so on), and a generic word
for "money". |
150 quattrini = 30 baiocchi = 3 giuli = 1 testone
TESTONE
The name testone, literally meaning "big head",
alludes to the pope's bust featured on some of the early issues.
This name, though, was maintained for later issues in which the head was
replaced by the pope's coat of arms. The coin was in silver.
As of the reign of Pius VI (1775-1791), 10 testoni made a
doppia d'oro (see below).
|
 |
1 testone = 3 giuli= 6 grossi = 30 baiocchi = 150 quattrini
10 testoni = 1 doppia d'oro
SCUDO
 |
Another old unit found in many lands, whose name
derived from the crest or shield (scudo) with the arms of the pope, or
king. Some issues, though, have the pope's head. Another name for this coin
was piastra.
|
At first the popes struck it in two
different metals, gold and silver. The former
(scudo d'oro)
weighed about 3.30-3.35 gr. The one in silver was obviously much larger,
to counterbalance the gold coin's intrinsic value.
As a unit, its value considerably varied in time, until it
was finally fixed at 10 paoli, or 100 baiocchi.
The last golden scudo was issued in 1738, and gradually replaced by the
zecchino (see below). All the following scudi were only in
silver. |

|
1 scudo = 10 giuli = 100 baiocchi
3 scudi = 1 doppia d'oro
CARLINO
 |
The name of this old unit derived
from Charles I of Anjou, who first issued it in 1278. After Julius II's monetary reform, in the early
16th century, it had been completely abandoned. But over two centuries
later, in 1747, Benedict XIV retrieved it; among his own issues
are ½ carlino, 1 carlino and 2 carlini, all in
billon. The rate of the unit was fixed at 7 ½ baiocchi. Instead, the
cross rate with 1 giulio was unpractical (1.333), unless calculating
it in a ratio of 3 paoli = 4 carlini.
|
The 2
carlini piece became rather popular in the early 19th century;
Rome's poet G.G.Belli referred to it as "the real roman Lira", i.e. the most
handy among the many existing units. Since it originally featured Benedict XIV's head,
the popular nicknames for the 2
carlini piece were
papetto ("small pope"),
Prospero Lambertini (actual name of the
pope), or in short
Prospero, or
Lambertini. Puns based on these nicknames were
rather frequent; even among Belli's verses, a commoner comments about
Gregory XVI in the following way:
Er Zantopadre, pe diograzzia, è l'asso,
È un testone, è un papetto de giudizzio:
E ssi ariviè ssan Pietro a ffà st'uffizio,
Lui se ne frega, e se lo porta a spasso. |
|
Thanks god, the Holy Father is a great man,
He's got brains (=testone), he is a wise pope (=papetto):
And should St.Peter come back again for doing this duty,
He wouldn't care, he would make him do what he wants.
|
1 carlino (½ papetto) = 1 ½ grossi = 7 ½ baiocchi
4 carlini (2 papetti) = 3 giuli = 1 testone
QUARTINO
 |
The name means "small quarter",
referring to the fourth part of the golden zecchino.
Introduced by Clement XII (1730-40), the piece weighed 0.69 gr, and
it was worth 5 paoli; but turning a quartino into
testoni was unpractical: the latter would have to be broken into decimals. |
1 quartino = 5 giuli = 50 baiocchi
4 quartini = 1 zecchino
ZECCHINO
This used to be a popular gold coin in
many parts of Italy (especially around Venice);
Rome's own zecchino was introduced by
Benedict XIII rather late, in 1728. Its size and weight was almost identical to the gold
scudo (3.40 gr versus 3.30-3.35 gr, respectively), but its
conventional exchange rate was fixed at 20 giuli, i.e. twice as a
gold scudo. Therefore, in a short while the latter coin was replaced
by the zecchino, and only the silver scudo was maintained. |
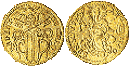 |
One year after the roman
zecchino had been introduced, the quality
of this coin was so much appreciated by the market, that it had been
completely "absorbed", so the pope issued it again, slightly reducing its
weight.
1 zecchino = 4 quartini = 20 giuli = 200 baiocchi
3 zecchini = 2 doppie d'oro = 1 quadrupla d'oro
DOPPIA D'ORO
The "golden double" was introduced by Pius VI (1775-99).
Despite its name, it was not the exact double of any of the units.
It weighed 5.39-5.49 gr, and was worth 3 scudi.
|
 |
1 doppia d'oro = 3 scudi = 10 testoni = 30 giuli = 300 baiocchi
2 doppie d'oro = 1 quadrupla d'oro
QUADRUPLA D'ORO
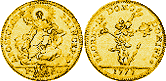 |
The "quadruple", also called 2 doppie,
was the coin of highest value ever issued in Rome. Only Pius VI
struck it, and only once, in 1777. It weighed 10.90 gr, and it was worth
6 scudi (60 giuli or paoli),
although we may think that such a precious piece
did not circulate very much, being mainly used for the storage of large sums of money,
or for major transactions, as nowadays it happens with banknotes such as 500 Euro, or
1.000 US$, etc. |
1 quadrupla d'oro = 2 doppie d'oro = 6 scudi = 20 testoni = 60 giuli = 600 baiocchi
The following diagram summarizes the main units of this system, showing
their rate.

This other diagram, instead, lists the various pieces that were issued and
actually circulated, although many of them did so only for limited
periods. For each of them the equivalent in
quattrini (the smallest subunit)
is shown, as an easier reference of their value.


Except the baiocchi pieces, that came from the mint in Gubbio (central Italy, once
belonging to the Papal State), all the others were stricken at Rome's own
mint, located in Ponte district, not far from Sant'Angelo Castle in which,
at the end of the 16th century, Sixtus V had moved the Papal State's treasury.
This neighborhood was full of banks, as the names of the nearby
streets, still in use today, clearly suggest: via dei Banchi Vecchi ("old banks street"),
via dei Banchi Nuovi ("new banks street"), via del Banco di Santo Spirito
("Santo Spirito bank street"). Banco ("desk") was the actual table
where the money-changer weighed the coins and calculated the exchange rates,
which later became the name of the same commercial activity.
|

Rome's old mint |
The reason for such a concentration of
banks near the mint was Julius II's attempt of turning this area into Rome's new commercial
district, a goal partially failed when expensive projects for
the making of many important buildings caused the pope to run out of funds
(see also
The 22 Rioni,
Ponte).

via del Banco di Santo Spirito
and Sant'Angelo Castle |
But what was the power of purchase of the old roman coins? A comparison with
today's currencies would be extremely difficult, and likely imprecise. However,
also in this case G.G.Belli is a valuable source of information, as
many of his sonnets mention both money and the purchased goods. So, for instance,
we learn that, sold by the pound, the price of bread was about 2 baiocchi,
and beef was ½ grosso. A pound of anchovies was 9 baiocchi
but cod was 10 ½, turbot 2 carlini, and bass, sea bream and other
fine fish 1 papetto.
Twenty artichokes costed 1 giulio (paolo), while at the inn
wine was 2 quattrini for half litre. However, in some taverns
it was possible to pay by the time, i.e. 6 or 7 quattrini each hour,
for drinking as much as one liked.
Household goods were unexpensive, but good quality had its cost:
for a drinking vessel of fine glass, one could have spent about 20 baiocchi
(a papetto), and the price of a "cane" of good cloth
(roman measure, 2 m 23 cm) would have been no less than
2 testoni.
For 1 giulio one could go to the theatre, while those who went bathing
in the river could hire a closed hut for 1 carlino
(but Belli remarked that most people would choose the open ones, for no more
than 1 lustrino, i.e. 1 grosso).
|
And for the same price of 1
grosso one could buy a monthly magazine: print was
still expensive in those days! Instead, who preferred other forms of ...leisure, would
have found Rome's prostitutes rather cheap: 1
giulio or
1
papetto ("you'll always get back some change from
a
testone", wrote Belli).
Having to do with bureaucracy was expensive: only the stamp placed on
a paper to make it official would have costed 1
giulio.
The fee for the licence to carry a hunting rifle was 3
giuli.
But if you wanted to marry your cousin (or another second-third grade relative)
you would have needed a special permit from the religious authorities, which
costed almost 700
scudi!! This was indeed a large sum of money,
considering that a cardinal, second in rank only to the pope-king,
received a yearly appanage called
piatto, ("dish") of 4,000
scudi.
In 1831 Gregory XVI raised it to 4,500
scudi: a promise he had
made in order to be elected pope, somebody said.

engraving by B.Pinelli (detail) featuring a
tavern: food,
wine and gambling were among the most frequent expenses |
In Belli's verses we also find how
the poor families rented their children to "professional" beggars
for 1 grosso a day per kid, while the expenses for a burial
included 9 scudi for the marble slab, 6 scudi for the
letters in relief and the cross, etc.
This clever sonnet by Belli, dated August 30, 1835, about a
father settling an account with his son, almost contains a full summary of the coinage of
those days; it is said to have been inspired by a real discussion once
occurred between Bartolomeo Pinelli, famous roman engraver and painter,
and his son Achille, a painter as well. |
|
ER CONTO TRA PPADRE E FFIJO
Che? Stammatina t'ho dato uno scudo,
E già stasera nun ciài più un quadrino?!
Rennéte conto, alò, sor assassino:
Qua, perch'io nu li zappo: io me li sudo.
Sù, tre ppavoli er pranzo, dua de vino
Tra giorno; e questi già non ve l'escrudo.
Avanti. Un grosso p'er modello ar Nudo.
Bé: un antro ar teatrin de Cassandrino
So ssei pavoli. E ppoi? Mezzo testone
De sigari: un lustrino er pan der cane...
E er papetto c'avanza, sor cojone?
No, pranz'e vino ve l'ho messo in cima
Dunque? Ah, l'hai speso per annà a pputtane.
Va bene, via: potevi dillo prima.
|
|
THE ACCOUNT BETWEEN FATHER AND SON
What? This morning I gave you a scudo,
And this evening you are already left without a quattrino?!
Give account of it right now, you squanderer:
Come here, 'cause I don't grow money: I earn it working hard.
Come on, three paoli for the lunch, two for wine
During the day; and I'm not complaining about these.
Well then. One grosso for the nude model at the Academy.
What else: another one for the theatre of Cassandrino
Makes six paoli. And then? Half testone
For cigars: one lustrino the bread for the dog...
And what about the spare papetto, you blockhead?
No, I counted food and wine as first,
So then? Ah, you spent it on prostitutes.
Well, it's OK: you should have told me before.
|
The currency system described in this page was
only discontinued in 1866, four years before the Papal State
came to an end. The last pope-king Pius IX, introduced the
more practical decimal currency (1 Lira = 20 soldi = 100 centesimi)
that was already being used in other parts of Italy.