OVERVIEW : THE BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY
Eggs develop and are stored and matured in the ovaries. The fallopian tubes carry the eggs that are released from the ovaries during ovulation to the
uterus. Fertilization of an egg by a sperm usually occurs in the fallopian tube. If an egg is fertilized, it will develop into a fetus in the uterus. The uterus has a specialized lining called the endometrium that allows an embryo to implant into the wall providing the developing baby with nutrients and support.


MENSTRUAL CYCLE AND OVULATION
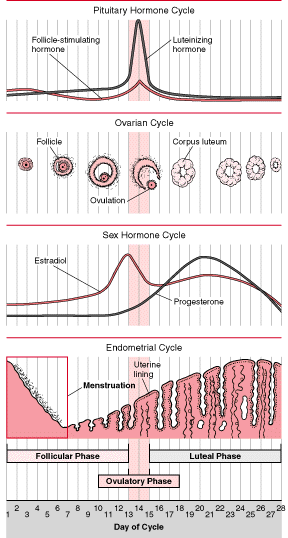
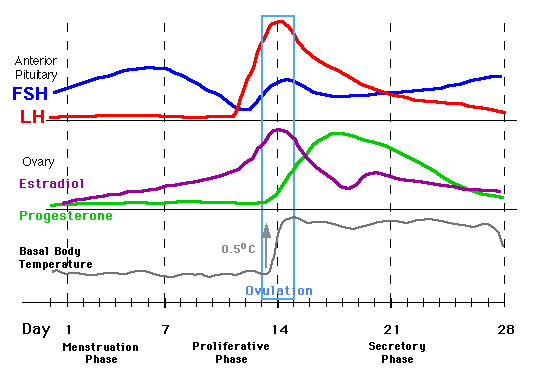
The entire menstrual cycle is controlled by the brain in concert with the ovaries. There are five main hormones involved in reproduction. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and prolactin are produced by the pituitary gland in the brain. FSH stimulates the growth of the egg within the ovary, while LH stimulates ovulation or the release of the egg. Estrogen and progesterone are produced in the ovary and help prepare the lining of the uterus so it will accept a fertilized egg. The menstrual cycle is measured in days, starting with Day 1 as the first day of the menstrual period. Ovulation usually occurs at approximately Day 14. If the released egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) is sloughed off as the menstrual period. Although a 28 day cycle is shown in the picture above, most women’s cycles vary in length.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY
Millions of sperm are produced every day in the testes. It takes approximately 2 months for sperm to develop and mature. The vas deferens carry the sperm from the testicles to the urethra where the seminal vesicles and prostate gland add fluid to form semen. Semen moves out of the body through the urethra in the penis. Although approximately 40 million sperm are released at ejaculation, sperm are very small and most of the semen consists of fluid that provides nutrients and enzymes to nourish the sperm.

MEN OR WOMEN?
Infertility problems are associated equally with both men and women. (Female 35%, Male 35%, Male and Female 25%, unexplained infertility 5%).
MALE FACTORS
Men are most likely to have a problem with their sperm (volume, count, shape, movement). Sometimes infertility can also be due to problems with testicles, prostate, varicocele (large vein), illness, medications, or hormones.
FEMALE FACTORS
Infertility can be caused by egg quality, ovulation factors, cervical factors, tubal factors, pelvic factors, or even weight. Both hormone functioning and reproductive anatomy must be "normal" for fertilization and fetal growth to occur.