Chapter 16
Light and Sound
- Light and Sound are the two major ways that we receive information about the world. A Ray represents the
path of a very narrow beam of light. It was concluded by the Danish astronomer Ole Roemer that light took less that one second to
cross Earth. He was wrong! It takes 22 minutes.
- American physicist Albert Michelson developed Earth-based techniques of measuring the speed
of light. He measured the time required to make a round trip through a pipe within the California mountains.
 Albert
Albert

sources
- A luminous body emits light waves. The light bulb is a luminous body because, electrical
energy heats a thane tungsten wire in the bulb and causes it to glow.
An illuminated body reflects light waves. The moon is an illuminated body. The illuminance on a
surface varies inversely as the square of its distance from a light source. The amount of light
produced per unit of time is called the luminous flux, P. The unit for this is the lumen, lm.
If we only want to know the amount of light produced by a source on a specific object (table,
chair), we have to use the formula for illuminance, E. This formula tells us the amount of light per meter square at a
certain distance.
b> E = P/4(pi)d²
Thus, the illuminance is just the luminous flux divided by the area of a sphere. Why a sphere?
For example, lets put two objects in different places, both of them two meters away from a source of light. As you
can see the illuminance on these objects is the same. This is because almost every source of
light emits light in all directions and two objects within the same radius receive the same amount of light.

Light and Matter
- Materials that transmit light waves are transparent. Others that transmit light but do
not permit objects to be seen clearly are translucent. They are also opaque.
Colors
- Red, green and blue are known as primary colors, because when they are added together
white light is formed. By mixing primary colors in pairs we obtain secondary colors. Red and
green produce yellow. Blue and red produce magenta, and blue and green produce cyan.

Polarization
- A polarizer produces polarized light.
- A polarizer will permit only light of one polarization to be transmitted.
- Light can be polarized by reflection and by scattering.
Chapter 17
Reflection
- Total international reflection occurs when light is incidence on a boundary from the
medium with the larger index or
refraction. If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angel, no light leaves; it is all reflected.
The Law of Reflection
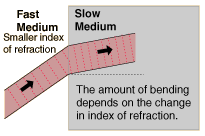
- When a ray of light passes from one medium to another, it bends. Depending of the new medium the light will travel faster or slower.
If the light travels faster in the second medium, then this medium is called the rarer medium.
On the other hand, the medium in which the light travels slower, in this case the first one, is
called the denser medium.
When a ray of light enters a denser medium, it is bent towards the normal.
When a ray of light enters a rarer medium, it is bent away from the normal.
 OR
OR 
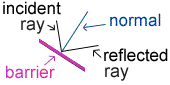
- Refraction occurs only when the incident ray strikes the boundary at an angle. A light ray
incident upon a reflective
surface will be reflected at an angle equal to the incident angle. Both angles are typically
measured with respect to the normal to the surface.

Snell's Law
Medium n Medium n
======= ====== =========== ====
vacuum 1.00 crown glass 1.52
air 1.0003 quartz 1.54
water 1.33 flint glass 1.61
ethanol 1.36 diamond 2.42
- A ray of light bends in such a way that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence
to the sine of the angle of
refraction is a constant.
- The refractive index can be determind by measuring angels of incidence and refraction.

Speed of Light
- The index of refraction is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed in
the medium.
n water=c/v water
Applications of
Reflected
and Refracted Light
- Total internal reflection occurs if light is incident on a boundary from the medium with
the larger index of refraction. If the angel of incidence is greater than the critical angel,
no light leaves; it is
all reflected.
- Light waves of different wave lenths have slightly differnt refractive indices. Thus
they are refracted at differnt angels into a spectrum of colors.
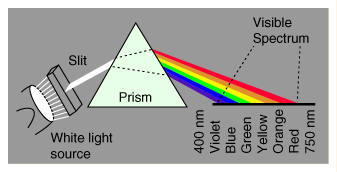
Dispersion
- Dispertion is the seperation of light into a spectrum by refracton.
- Dispersion in a priam is used to analyze the spectrum of light soure.
- The separation in a raindrop.
References
Links
Hyper Physics
Physics Cental
Physics Today
Wikipedia Encyclopedia
Easy physics
Magazine Articles/Text book
Light By R.W.Ditchiourm
Physics By James Walker
Manipulating Light: Reflection, Refraction and Absorption By Darlene R. Stille
New experiments strike a blow against time travel By Laura Wright
Phsics Text Book chapters 6 & 17
 Albert
Albert





 OR
OR 

