NEPAL-
In WORLD MAP ( Find ASIA)
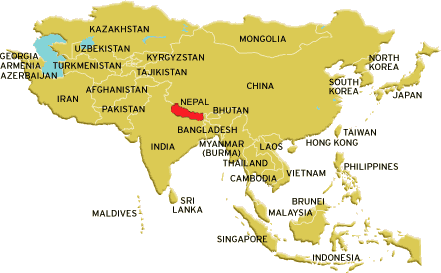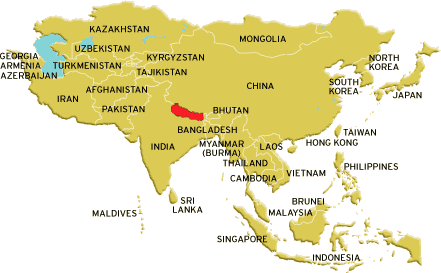
ASIA ( See the RED AREA)
This is NEPAL you are searching
Nepal Geographical Information
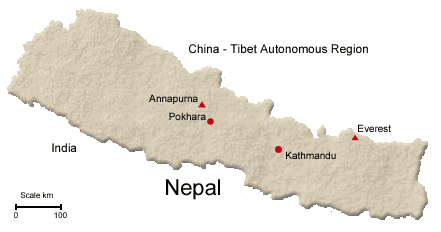
Nepal, a sovereign Independent Kingdom, lies between
80 degree 12' east longitude and 26 degree 22' and 30 degree 27' north
latitude. It is bounded on the north by the Tibet Autonomous Region of the
People's Republic of China; on the east by Sikkim and West Bengal of the
Indian Union on the south by Indian States of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh and
on the west by Uttar Pradesh of Indian Union. The length of the Kingdom is
885 kilometers east-west and its breath varies from 145 to 241 kilometers
north-south. Climatically, it lies in the temperate zone with the added
advantage of altitude.
The country can be divided into three main geographic regions :
.Himalayan Region: The altitude of this region ranges between 4877 meters and 8848 meters with the snow line running around 48848 meters. It includes 8 of the existing 14 summits in the world which exceed an altitude of 8000 meters. They represent. (1) Sagarmatha (Mt. Everest) 8848 m, (2) Kangchenjunga - 8586 m, (3) Lhotse - 8516m, Makalu - 8463m, (5) ChoOyo- 8201 m, (6) Dhaulagiri - 8167m, (7) Manaslu - 8163m, and Annapurna- 8091 m.
Mountain Region: This region accounts for about 64 percent to total land area. It is formed by the Mahabharat range that soars upto 4877 meters. To its south lies the lower Churia range whose altitude varies from 610 meters to 1524 meters.
Terai Region: The low-land Terai region which has a width of about 26 to 32 kilometers and a maximum altitude of 305 meters, which occupies about 17% of total land area of the country. Kechanakawal the lowest point of the country with an altitude of 70 meters lies in Jhapa District of the eastern Terai