The solpugids, or sunspiders, are arachnids of a considerable size (10 to 70 mm) with the body provided with large erect hairs. They colonize the hot and dry areas of both hemispheres. They look fierce and agressive but are totally inoffensive since they have no poisonous glands.
They present both cephalothorax and abdomen segmented. The chelicerae are large and strong, formed by two parts with a grabbing function. The pedipalps are ended by a cupping-glass and their function is prehensile and adherent. The first pair of legs has a tactile function and the others are walkers. The fourth pair has some characteristic organs: the rackets, situated under the first segments and formed by some quitinose disks united to the appendix by a thin pedicel. They have a tactile function.

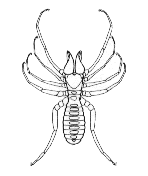
The solifuges live for many years and build a tubular nest, considerably deep, that they abandon during the night to look for food. During the mating season the males walk in search for the females nests. The spiderlings stay for a certain period of time in their mother's nest until they reach a stage when they can build their own and look for food. In the Iberian Peninsula is found only one species belonging to this order: Glubia dorsalis.