COMPUTERIZED TABLE OF ISOTOPES
“NUCKLIDE TRACK” (NT)
COMPUTERIZED TABLE OF ISOTOPES
Nuclide properties represented in program’s
“Nuclide Track” Data Base (NTDB)
Nuclide data representation types in “Nuclide Track” program
About “Nuclide Track Manager” window
Table of isotopes – “Nuclide track” window
Nuclide Track Program’s complement and other information
It is computerized
interactive program, which represents most essential propeties of atomic nuclei
(nuclides, isotopes) in dependence of number of protons Z, number of neutrons N
and mass number A=Z+N on tables and graphs. Nuclide data is retrieved from nuclide
database, reordered due to users requirements and represented in convenient
form.
Investigated nuclide
propeties are saved in Nuclide Data Bases (NDB) . Most representative of those
are in Nuclear Data Center... Most essential
and popular propeties of nuclei from those data bases are copied to our
“Nuclide Track” database in MS Access format.
Table of isotopes,
where column number is equal to neutron number N in nucleus and row number is
equal to proton number Z of nucleus is most natural interface to represent and
retrieve propeties of nucleus from nuclide database. Every nucleus is
represented in this table by separate box. But not every box corresponds to
(represents) really existing nucleus. Totality of known existing nuclides is represented in table of isotopes by an
area which form resembles some track. That’s why our program and its interface
to nuclide data is called “Nuclide
Track.” (NT) .
Let us begin a tour
along nuclide track
Example of
“Nuclide Track interface” to our Nuclide
Track Data Base
(NTDB) is shown below in
figure 1. and on the figure on table of homepage.
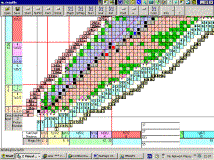
Figure 1. Table of isotopes “Nuclide Track” , its initial part.
Columns in our table of
nuclides NT are numbered from left to right, from N=0 to N=165 according to
number of neutrons N in nucleus. Rows are numbered upward from Z=0 to Z=112 in
correspondence with the number of protons Z in nucleus. Nuclides whose
propeties are known very roughly are not compiled in our NTDB.
Particles bound in
atomic nucleus, neutrons and protons are called nucleons
Neutrons and protons in
nucleus are bound by attractive short ranged nuclear forces of saturative type.
Range of those forces is within the radius of nucleus.
While long ranged
repulsive insaturative Coulomb forses between protons are known better. Proton repulsion force strength outside nucleus
is roughly proportional to ~(Z-1)*e2/r2, where e is
elementary charge and r – the mean distance between proton and residual protons
of nucleus. Those are the main reasons
why there are no nucleus with large difference between proton and neutron
numbers in nucleus and why there are no nucleus with Z~>118 and N~>170.
All nuclides in table of isotopes are arranged nearby so called nuclide
stability track, from both sides of it (Fig 1.).
Each box, representing
stabile nuclide in our table on Fig 1.,
is composed of two rectangles: of black
and grey color. Percent of width of black rectangle with respect to full
table box width represents natural percental abundance of this isotope in
element.
Nuclide properties represented in
program’s
“Nuclide
Track” Data Base (NTDB)
In main NTDB table
every record (table row) represents propeties of separate nuclide. Number of
records is equal to 2934, the number of nuclides in nuclide track.
Every column of the
table (NTDB field) represents one specified parameter in all nuclides.
Properties of nuclides may be represented together with dispersions (in the
case of numeric parameters), referencies and remarks.
The next properties of
nuclei are represented in Nuclide Track Data Base.
1.
atomic number Z, neutron number N, mass number A=Z+N of nuclide;
2.
atomic mass, mass defect, bind energy;
3.
abundance of isotope in element;
4.
concentracion of nuclide in earth’s surface, meteorites and cosmos in
absolute units or in logarithmic scale;
5.
lifetime of unstable isotope in
absolute units or in logarithmic scale;
6.
spin and parity of nuclide ground state;
7.
decay type and its probability for :
isomeric transition;
beta+ decay;
beta- decay;
electron capture;
alpha decay;
proton emission;
neutron emission;
beta- decay and simultaneous neutron emission;
spontaneous decay;
8.
neutron separation energy;
9.
proton separation energy;
10.
alpha particle separation energy;
11.
separation energy of other particles;
12.
magnetic moment of ground state;
13.
quadruple moment of ground state;
14.
deformation of nucleus;
15.
energy levels of nuclides;
Data of more than 40
parameters of all nuklides are represented in “Nuclide Track” data base. This
information can be got and represented with the aid of interface of “Nuclide Track” program.
Nuclide data representation types in “Nuclide Track” program
There are few types of windows, where nuclide data
information and management buttons are located:
1. main information
window Table of isotopes – “Nuclide track” as shown in Fig. 1. ;
2. nuclide data
table window;
3. graphics window;
4. nuclide ordering
window;
5. window of
selected nuclide with all its parameters shown;
6. movable control
panel window “Nuclide Track Manager”;
About “Nuclide Track Manager” window
Movable “Nuclide
Track Manager” window is u
Movable “Nuclide Track Manager” window is shown
together with current information window and is used: 1) to select information
window, 2) to select data representation type,
3) to form
selected parameter list and 4) to show selected parameters of specified nucleus
on special table in Manager’s window for quick view.
This window contains:
1. panels of command buttons, used to select information window and data representation type in our program;
2. parameter name list box, used to make “selected parameters list” whose values will be shown:
1) on selected
parameters names and values table of specified nucleus (look 3.);
2) on graphics, which represent selected parameters values in dependence of nuclide number in selected nuclide chain;
3. table of selected parameters names and values of specified nucleus together with histogram.
All nuclides on tables and graphs can be scanned by
their number in nuclide chain automatically with selected speed or by hand.
Table of isotopes – “Nuclide track” window
Example of this
window is shown in Fig. 1.
Visible part of
NT can be changed by pressing left mouse button on free Table space and
drugging in needed direction.
There is another
way to locate needed part of NT on the screen: 1-push “Pos” on “Manager”, 2-select N and Z, 3-push
”Okay” . N,Z box of NT will be located
on the center of a screen.
The size of NT
table boxes can be changed in NT Manager window: 1) with the aid of special Size
buttons 2) by specifying box width and height.
NT boxes are sensitive to mouse marker. When marker is over nuclide box, corresponding selected parameters are shown in table on NT Manager window and are fixed after mouse click and boxes become insensitive to mouse marker. Another mouse click over NT box will renew sensitivity of boxes.
After double click over nuclide box all parameter names and values of corresponding nucleus are shown in special table.
User can make his own Table of isotopes with selected parameters set on NT boxes with the aid of special button on NT manager window. User himself must reset the size of nuclide box.
Graphs
With the aid of
NT graphical means we can represent values of selected parameters on graphs in
dependence of nuclide position in some specified nuclide chain. It may be
Element’s isotopes Z-chain, isotones N-chain or isobars A-chain.
For example, in
element’s Z-chain You can represent nuclide’s proton separation energy in
dependence on neutron number of isotope and compare it with the resembling
dependence in the case of neutron separation energy.
Dependencies may
be shown on ordinary graphs, where abscise axe is nuclide’s order number in
chain, while ordinate axe represents parameter values.
Dependencies may be shown directly on the
table of isotopes, on selected nuclide chain, while line drawn through chain
boxes serves as an axe of a graph, representing nuclide’s order number in chain, while another,
special drown axe, represents numeric values of parameters.
Nuclide Track Program’s complement and other information
In programs
description on separate booklet user will find the main information about “Nuclide Track” program, what can it
do, how to install and use program. Additionally user will find here the minimal
and most essential information about nuclear structure and properties, needed
in order to understand what is about.
Programs ”Nuclide
Track” installation package is written on CD and may be installed on computers
with windows based systems: WINDOWS 95, 98, Millennium, XP, 2000, NT.
Programs ”Nuclide Track” algorithm size is about 0.7MB,
programs size on CD together with data base and other dependencies – about 70
MB.
February 25, 2004 Rimgaudas
Ţirgulevičius