Exam Review
Exam Review
Date: Tuesday Jan 23
Room --> ????
Date of revision: Jan 24 2006
Contributors to this file: R. Brown, G. Kavaungh , R. Warren
Exam Format
Exam prepared by Mr. R. Warren
- Multiple choice 60 marks
- Short answers 69 marks
Multiple choice on Scantron so make sure you have a pencil, ruler, calculator, and eraser.
Short answers will be answered in the booklet provided.
A formula sheet will be provided.
It is a 2 hour exam.
Bring your text book to the exam site for collection.
All four strands will be questioned, so don't ignore any of them.
The exam is broken into the four separate strands; multiple choice section for each and a written response section for each.
How's about a look at the 2P exam review; you should know all this stuff too!

Pages to look at: ignore at your own risk:
18, 32, 54, 61, 67, 74, 75, 77, 173, 174, 186, 190, 296, 346, 410, 426, 501, 506, 511, 517.
Glossary of Terms to KNOW!
Similar terms will be grouped
- albedo
- weather & climate
- food chain, food web; know what they are with examples of each and all the various terms related to chains & webs
- consumer, producer, decomposer scavenger etc.
- biodiversity
- carrying capacity
- MSDS
- how to recognize a balanced equation
- covalent, ionic bonds
- the five reaction types
- acid , base & neutral solutions
- uniform speed & velocity & acceleration
- conduction, convection, and radiation
- Coriolus effect
- dew point and humidity
- ions
- catalyst
- pH and indicators
- significant digits for multiplication/division adn addition/subtraction
- average & instantaneous speed/velocity
- scalar & vector
- niche & habitat consumer & producer
- energy transfer
- the atmosphere, lithosphere & hydrosphere
- cells and wind types
- clould types and fronts
- extreme weather conditions
Concepts that must be KNOWN! from all strands
- Area under a curve, whats it mean and for what type of graph is it used
- Periodic table and information that can be determined from it such as
- metals from nonmetals
- where the reactive elements are found
- how many electrons, protons, and neutrons in any element
- identifying chemical families
- shell structure
- how many valence electrons in an atom
- Bonding -- ionic and covalent
which elements do which
- Identifying reaction types
- Balancing equations
- Acids and bases, what are they?
- Be able to manipulate algebraic equations based on velocity and acceleration
- Be able to read a graph
- Be able to read a weather map; know the symbols listed and be aware that there are three types.
- Vector analysis, know your directions N, W, S, E, be able to construct a vector triangle and make the appropriate angle and displacement readings.
- Parts of the atmosphere
- Cloud types
- Catalysts with examples
- Chemical nomenclature; naming and writing formula, usually in a chart
- Indicator colour changes, what do they prove
- Solve motion problems using required formula
- Work with a vector diagram, using ruler and protractor, to obtain the resultant vector answer
- Reading a food web diagram, be able to interpret the various tropic levels
- The three main cycles studied: carbon, water, and nitrogen
- What are phosphates used for
- Factors the effect the rate of a chemical reaction, with examples
- Severe weather conditions, be able to list them and discuss them
- Factors effecting wind patterns
- Population growth and patterns of population growth, steady state
- The gas tests
And now for some specific material on each strand
Biology Strand
Define the following words
autotrophs
abiotic
biotic
acid rain
artificial ecosystems
biomass
biome
biodiversity
biomagnification/bioaccumulation
carnivore
carrying capacity
community
consumer
community
decomposer
denitrification
|
detritus
ecology
ecosystems
ecological pyramid – energy and number
ecotone
endangered
extinct
environment
food chain
food web
leaching
habitat
individual
heterotrophs
herbivores
|
niche
nitrogen fixation
producer
pesticide
secondary consumer
omnivore
water pollution
population
trophic level
primary consume
percolation
pests
sustainable ecosystem
|
- What is meant by the term biodiversity?
- Explain the pathway of energy through an ecosystem?
- Define photosynthesis. Write the word equation for it. What effect does it have on the carbon cycle? Why is it the most important reaction in the world?
- Define respiration. Write the word equation for it. How is it related to photosynthesis? What effect does it have on the carbon cycle?
- Why are the carbon cycles (e.g. carbon cycle, water cycle, nitrogen cycle phosphorus cycle) important in the environment?
- Although the atmosphere is mostly nitrogen (79%), many plants suffer from lack of nitrogen. Explain how this is possible. What are the ways that plants can get their supply of nitrogen?
- List the biomes studied and give two physical (abiotic) characteristics of each biome as well as list two plants and/or organisms (biotic) that live there.
- Draw a labelled diagram showing all the different layers of soil.
- Draw a food chain using any of the following organisms: chicken, corn, human and fox. Use the same list to construct a food web.
Be able to interput a food web of trophic pyramid. Energy transfer in each.
- What is the source of energy for all ecosystems?
- What is the difference between a vulnerable species, a threatened species an extinct species?
- What is a pesticide? What is the problem with them?
- List the four factors that affect a population growth and explain how each one affects the population i.e. increase or decrease population size.
- Know what trophic levels are and a species position: ie, first order consumer, top carnivor, etc.
- Problems caused by acid rain, how can it be corrected
- Factors effecting population growth and how to predict a population from these values
- What is a closed versus an open population
- When does a steady state population growth occur and what is carrying capacity
- Know you endanger species terms
Chemistry Strand
Define the following words
periodic table
family/group
element
compound
metal
non-metal
metalloids
chemical formula
ions
word equation
chemical equation
balanced equation
pH
oxides
acids
|
base/alkaline
neutralization
hydrocarbon
pure substance
product
reactants
incomplete combustion
complete combustion
synthesis
decomposition
single displacement
double displacement
precipitate
alkali metals
halogen
|
noble gases
ionic compounds
molecular compounds
atom
molecule
polyatomic ions
catalyst
binary compounds
covalent bond
ionic bond
alkaline earth metals
alkali metals
halogens
indicator
reaction rate
|
- For each of the following groups state the group number, the group name, how many valence electrons there are, how many electrons it gains or loses to form an ion, and the ionic charge it will have:
Alkali metal alkaline earth metals halogens noble gases
- What is a pure substance?
- Explain the collision model of reaction rates.
How does a catalyst effect the rate of a reaction.
- List the elements that exist as diatomic gases and know their formulas.
- Name the following compounds:
Li2S, CuCl, CuCl2, KNO3, CCl4
- Give the chemical formula for the following compounds: barium chloride, tin (IV) oxide, dinitrogen pentoxide, iron (III) sulfate, zinc nitrate, and magnesium sulphate. Please note that these are just examples and would not be directly on the exam as such.
- State the law of conservation of mass. Be able to do the math that would be found in an experiment.
- Balance the following reactions:
- Mg + HCl -----> MgCl2 + H2
- C3H8 + O2 --------> CO2 + H2
- Al2(SO4)3 + Ba(NO30)2 --------->
Al(NO3)3 + BaSO4
You should also be able to name each compound and give the reaction type.
- List the four factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction. Explain each using the particle theory ie. collision theory of molecules in motion.
- List four types of chemical reactions. Give an example of each. And be able to pick them out from a list of reactions.
- Write the word equation for the complete and incomplete combustion of butane (C4H10, for example.
- What is the range of the pH scale? What is the range for an acid, a base and a neutral substance?
- What would you expect to have a higher pH value, vinegar or an antacid? Explain.
- How can you make a base from an element? Pick an element and show the chemical reactions involved.
Should be able to do the same for the making of an acid.
- Write the general word equation for neutralization reaction. What type of reaction is this?
- What causes ionic bonds? covalent bonds?
- Be able to count the number of elements in a formula
- Distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion, endothermic and exothermic reactions
- Know how to count electrons in ions and neutral atoms
Physics
Here's the equations you are suppost to know
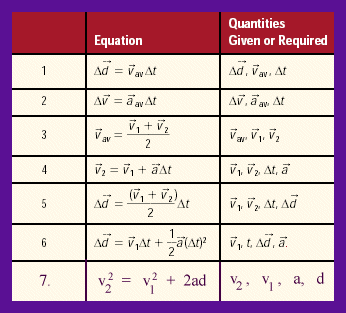
- be able to solve word problems using the seven formulae given; be careful of using v = d/t since it is very restrictive in its application. Ntte that this formula is not even listed up above.
- you must be able to analyze a graph and recognize the various shapes for d vs t and v vs t and what slope of these graphs mean.
- you must be able to construct a vector scale diagram and use it to determine a displacement or a velocity.
- know the difference between distance and displacement, scaler and vector, velocity and speed.
- know the difference and how to calculate or determine average speed and instantaneous speed. Note: speed and veleocity are often used interchangably when the direction of the motion is not relevant.
- know what the acceleration due gravity is (it is a vector). Remember, what goes up must come down!
- Negative acceleration means that the the direction of the velocity and acceleration are opposite. The object is slowing down.
- know how to determine the distance travelled from a velocity time graph.
- be able to work with velocity as a vector
- On a velocity time graph can you find or determine:
a)speed, b)acceleration, c) distance travelled
- A car is speeding down a highway at a velocity of 120 km/h [E] when he spots a police car and begins to decelerate to s speed of 80 km/h. In what direction is the car accelerating? If the change in speed takes 20 s, what distance is require for the car to slow down to 80 km/h?
- A student runs for 120s at a velocity of 4.2 m/s [N40oE]. She then changes direction to [N30oW], staying at the same speed for another 90 s. What is her displacement?
- An object is dropped off a tall building and falls for 2.6 s. How high is this building?
If this same object was thrown downward from this height and it takes only 1.8 s to reach the ground, what was the initial velocity of this object?
Weather
- Parts of the atmophere in their correct order.
- How does atmospheric change with altitude?
- Which part of the Earth receives the most heat energy ? the least amount of energy? And how does this effect weather patterns?
- Explain how heat is spread throughout the Earth's atmosphere and in the hydrosphere?
- What is dew point and what does it tell you about relative humidity?
- List the different types of precipitation and explain how they are formed.
- What type of weather is associated with a high-pressure system? a low pressure system?
- Be able to sketch with proper direction and properly label, wind patterns across the globe.
- What are weather cells, where are they located and what are they called?
- Difference between climate and weather and what causes or drives each.
- Winds: causes, directions across the globe, three main wind cells (Hadley cells).
Local winds such as sea breeze; be able to explain.
- Ocean currents, wind patterns, the Coriolis effect
- Name three ways that clouds can form.
- Explain the jet stream and how does the Coriolis effect influence prevailing wind patterns.
- cloud types and position found in the atmosphere based on altitude
- Bernouilli's principle and pressure effects
- Extreme weather events; hurricanes, tornadoes, blizzards, floods and droughts, temperature extremes.
- The three types of weather maps
Reading weather maps and their symbols.
When reporting the weather what variables are described?
- The various different cloud types
- Compare and contrast:
- Gulf stream & Labrador current
- dew & frost
- tornado & hurricane
- cold front & warm front
- stationary front & occluded front
- sea breeze & land breeze
- barometer & psychrometer
- relative humidity & absolute humidity
Sample Exam Questions
Prepared Jan 21 2004, "... with a little help from my friends"
These question are designed as multiple choice question but the selections are missing, you determine what would be a correct answer and try to invent some wrong answers.
Chemistry
- Which of the following is a sulfite? Question can be used for any radical
- Which of these atoms has the greatest valance?
- Given this equation which number completes the balancing?
- Given this equation what type of reaction is this?
- Which reaction is exothermic?
- Which atom/ion is isoelectronic with:
- Which of these indicators turns blue?
- Which of these indicators turns yellow?
- Bases always have PH's that are:
- Which of these compounds is a(n) base/acid?
Name or formulas can be given.
- Ionic substances are formed from:
- In order to speed up a reaction you could:
- The sequence of electron shells is:
- Hydrogen (other examples are oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.) gas can be tested by:
- Which of these compounds forms covalent bonds:
- Which of these molecules/compounds is/are an organic molecule(s)?
- Which of these compounds is named by a prefix:
- Using the law of conservation of mass. Not multiple choice.
Motion; Physics
- The formula for acceleration is:
- Vector "A" equals 5cm North. Vector "B" is 4cm East. Vector "A" plus "B" is:
- Which of the following is a vector quantity:
- Which graph represents an increase in velocity for acceleration:
- Given a VT graph how do you find the distance travelled?
- There are "simple, dummy" questions. Using simple formulas.
- How do you find the slope?
- The difference between instantaneous and average speed is:
OR instantaneous speed can be found by:
-
Ecology
- Which of these animals is a 1st order consumer?
- Mushrooms are considered to be a
- The southern most biome in Canada is
- A food chain is defined as a
- Hogs, cows and horses in a barnyard would be considered a
- A major cause of acid rain is
- Ecology is a study of:
- BIosphere consists of:
- The main source of acid rain is:
- pH can be increased by adding: (For land or water)
- The correct ordering of soil layers is:
- There are ______ number of biomes in Canada: Can you name them?
- Bioamplification is the process by which:
- An exotic species is one that:
- In this food chain the second order consumer is or the hetrotrop/autotrop is:
- A pyramid of energy describes:
- In order to put nitrogen into the environment or soil:
- An ecotone may be defined as:
- Any species that no longer exists in one part of Canada but can be found in others is classified as:
- In a food web mushrooms would be considered to be:
- Plants and animals need nitrogen to make:
- Population size is affected by:
- Which of these factors affect biotic potential: (lists)
- A biome is determined by:
- The littoral zone is:
- Eutrophic lakes are usually:
- Which of the following are abiotic:
- The greatest danger of a pesticide is:
- Respiration and photosynthesis are opposites, explain, with equations
Weather
- explain how clouds are formed
- how can you measure relative humidity
- list all four fronts; explain the difference between and occlude front and a stationary front with diagrams etc.
- draw weather symbols for the following: see page 683 and station map symbols page 684
- Air pressure depends on altitude, explain and what effects result because of this
- relationship between prevailing wind patterns and ocean currents and the Coriolis effect
- be able to compare and contrast the following:
- occulude and stationary fronts
- warn and cold fronts
- rain and snow
- convection and advection
- frost and dew
- humidity and relative humidity
- hurricanes and tornadoes
- sea and land breezes
- convective clouds and orographic clouds and frontal clouds
- prevailing or global winds and local winds
- heat sink and albedo
- What type of weather do you get when a front passes through.
- What are the different types of clouds and how does each form.
- What instruments are used to make weather measurements.
- What are the differences between a hurricane and a tornado?
- Do you the different air masses and where they come from? and the type of weather conditions they produce?
- Can you name the layers of the atmosphere in order?
- How is energy transfered and what experiments where done to show these methods.
- What is the difference between the "prevailing winds" and the "local winds"?
- Can you describe &/or name the different cloud types?
- What are the different types of precipitation?
- What is humidity and what is its relation to dew point?
- Do you know the various "weather map symbols"?
- What instruments are used in weather forcasting, be able to name them & state what are they used for?
Exam Comments from last June's finals. These are general comments from several courses, but applicable to this program as well. 



