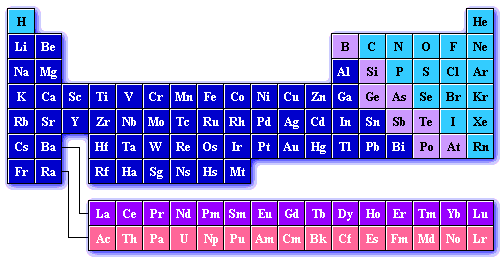
The periodic table is a chart of all the elements based on increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus). Elements with similar physical and chemical properties are listed in columns. This is why the table is refered to as periodic. Chemicals in these columns are refered to as families of elements.

There are five "common-named" families of elements
All atoms are made up of protons, neutrons (found in the nucleus) and electrons (found in shells surrounding the nucleus).
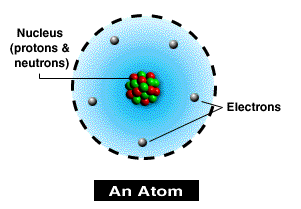
| Particle | Mass | Charge | Where Found |
| Proton | |||
| Neutron | |||
| Electron |
Bohr diagrams you should be familiar with. I would expect you to be able to sketch a Bohr diagram for the the first twenty elements.
Isotopic symbolism is used to show and indicates the mass number (written on top) and the number of protons (found on the bottom).

If the atomic number is subtracted from the mass number the number of nuetrons can be calculated.
What is an ion? An ion is formed when an atom either gains or losses an electron(s). If an electron is gained the charge on the atom decreases. For example, when the hydrogen atom gains one electron its charge changes from 0 (zero) to -1 (negative one); an algebraic decrease. When the sodium atom loses 1 electron its charge changes from 0 to +1 and increase in charge. Atoms that lose electrons have their postive charge value increased.
Which class of elements gain electrons? Answer == nonmetals
Which class of elements lose electrons? Answer == metals.
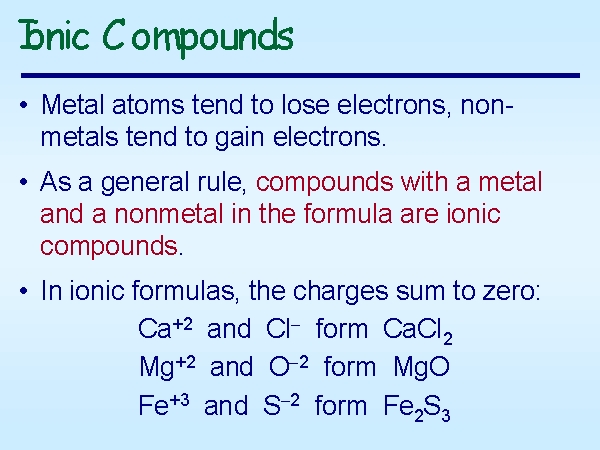
Metalloids have the ability do go both ways, in other words they can behave as either a metal or a nonmetal depending on the chemical enviroment.
> The ionic charge of an atom is the numerical value of the electric charge eithr plus or minus.
Cations
Atoms that have lost an electron(s) and are positive are called cations

Anions
Atoms that gain electron(s) and become negative are called anions
