1. ![]() The diagram below shows
some of the lines of electrical force around a positive point charge.
The diagram below shows
some of the lines of electrical force around a positive point charge.
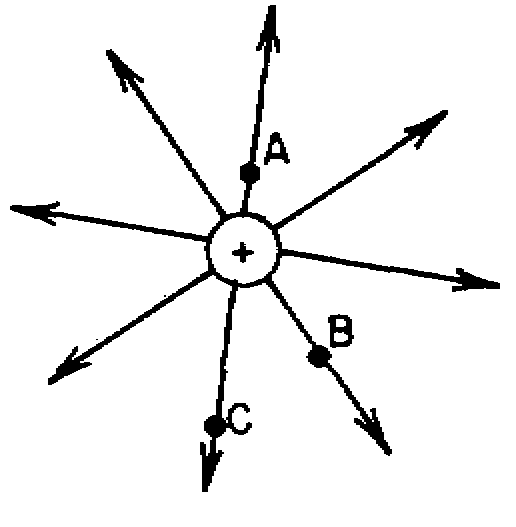
![]() The strength of the electric
field is
The strength of the electric
field is
![]() greatest at point A
greatest at point A ![]() greatest at point B
greatest at point B ![]() greatest at point C
greatest at point C ![]() equal at points A, B, and C
equal at points A, B, and C ![]()
2. ![]() Two charged spheres are
shown in the diagram below. Which polarities will produce the electric field shown ?
Two charged spheres are
shown in the diagram below. Which polarities will produce the electric field shown ?
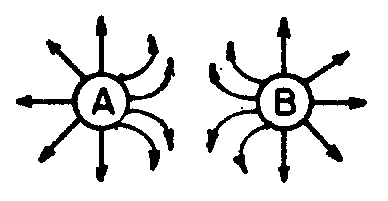
![]() A and
B both negative
A and
B both negative ![]() A and B both positive
A and B both positive ![]() A positive and B negative
A positive and B negative ![]() A
negative and B positive
A
negative and B positive ![]()
3. ![]() As shown in the diagram
below, a charged rod is held near, but not touching, a neutral electroscope.
As shown in the diagram
below, a charged rod is held near, but not touching, a neutral electroscope.
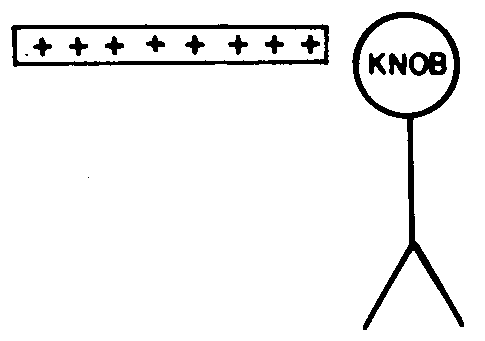
![]() The charge on the knob is
The charge on the knob is
![]() + and leaves +
+ and leaves + ![]() + and leaves -
+ and leaves - ![]() - and leaves +
- and leaves + ![]() - and the leaves -
- and the leaves - ![]()
4. ![]() The diagram
below represents two small identical charged spheres located 2.00 meters apart.
The diagram
below represents two small identical charged spheres located 2.00 meters apart.

![]() The force between
these spheres is
The force between
these spheres is
![]() 1.80 x 10-2 N
1.80 x 10-2 N ![]() 3.60 x 10-2 N
3.60 x 10-2 N ![]() 4.50 x 10-2 N
4.50 x 10-2 N ![]() 9.00 x 10-2 N
9.00 x 10-2 N ![]()
5. ![]() How many
electrons are contained in a charge of 8.0 x 10-19 C ?
How many
electrons are contained in a charge of 8.0 x 10-19 C ?
![]() 5
5 ![]() 2
2 ![]() 8
8 ![]() 4
4 ![]()
6. ![]() After a neutral object loses 2
electrons, it will have a net charge of
After a neutral object loses 2
electrons, it will have a net charge of
![]() -2
elementary charges
-2
elementary charges ![]() +2
elementary charges
+2
elementary charges ![]() -3.2 x
10-19 elementary charges
-3.2 x
10-19 elementary charges ![]()
![]() +3.2 x
10-19 elementary charges
+3.2 x
10-19 elementary charges ![]()
7. ![]() What is the amount of energy
gained by a proton accelerated through a potential difference of 50 V ?
What is the amount of energy
gained by a proton accelerated through a potential difference of 50 V ?
![]() 1 eV
1 eV
![]() 10 eV
10 eV
![]() 50 eV
50 eV
![]() 100 eV
100 eV
![]()
8. ![]() How much work is done in
moving 6 electrons through a potential difference of 2.0 V ?
How much work is done in
moving 6 electrons through a potential difference of 2.0 V ?
![]() 6.0 eV
6.0 eV
![]() 2.0 eV
2.0 eV
![]() 3.0 eV
3.0 eV
![]() 12 eV
12 eV
![]()
9. ![]() The Millikan oil drop
experiment showed the existence of
The Millikan oil drop
experiment showed the existence of
![]() an
elementary charge
an
elementary charge ![]() a
photon
a
photon ![]() an
atomic nucleus
an
atomic nucleus ![]() an
atom
an
atom ![]()
10. ![]() A charge of 100. elementary
charges is equivalent to
A charge of 100. elementary
charges is equivalent to
![]() 1.60 x
10-21 C
1.60 x
10-21 C ![]() 1.60 x
10-17 C
1.60 x
10-17 C ![]() 6.25 x
10-16 C
6.25 x
10-16 C ![]() 6.25 x
1020 C
6.25 x
1020 C ![]()
11. ![]() If 6.0 J of work is done to
move 2.0 C of charge between two points, what is the potential difference
If 6.0 J of work is done to
move 2.0 C of charge between two points, what is the potential difference
![]() between these two points ?
between these two points ?
![]() 6.0 V
6.0 V
![]() 0.33 V
0.33 V
![]() 3.0 V
3.0 V
![]() 12 V
12 V
![]()
12. ![]() In the diagram below, a
cloth is brought near, but does not touch a neutral electroscope.
In the diagram below, a
cloth is brought near, but does not touch a neutral electroscope.
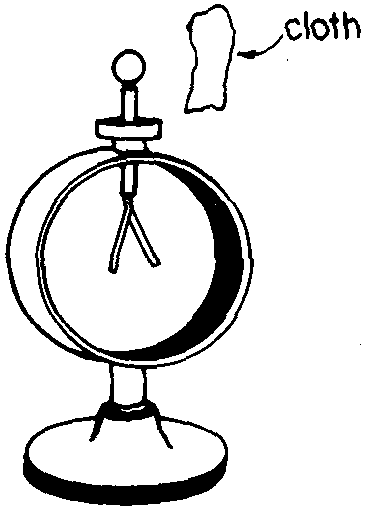
![]() The electroscope leaves
separate.What charge, if any, does the cloth have ?
The electroscope leaves
separate.What charge, if any, does the cloth have ?
![]() positive
positive
![]() negative
negative
![]() unknown
unknown
![]() no
charge
no
charge ![]()
13. ![]() Which electric charge is
possible ?
Which electric charge is
possible ?
![]() 8.0 x
10-20 C
8.0 x
10-20 C ![]() 2.4 x
10-19 C
2.4 x
10-19 C ![]() 3.2 x 10-19
C
3.2 x 10-19
C ![]() 6.32 x
10-18 C
6.32 x
10-18 C ![]()
14. ![]() As the distance between two
point charges is tripled, the electostatic force between the charges will become
As the distance between two
point charges is tripled, the electostatic force between the charges will become
![]() 1/9 as
great
1/9 as
great ![]() 1/3 as
great
1/3 as
great ![]() 3
times as great
3
times as great ![]() 9
times as great
9
times as great ![]()
15. ![]() When an object is brought
near the knob of a positively charged electroscope, the leaves initially diverge.
When an object is brought
near the knob of a positively charged electroscope, the leaves initially diverge.
![]() The charge on the object
The charge on the object
![]() must
be zero
must
be zero ![]() must be
positive
must be
positive ![]() must
be negative
must
be negative ![]() cannot
be determined
cannot
be determined ![]()
16. ![]() The electronvolt is a unit of
The electronvolt is a unit of
![]() charge
charge
![]() energy
energy
![]() potential
difference
potential
difference ![]() current
current
![]()
17. ![]() After two neutral solids, A
and B, were rubbed together, solid A acquired a net negative charge.
After two neutral solids, A
and B, were rubbed together, solid A acquired a net negative charge.
![]() Solid B, therefore, experienced a
net
Solid B, therefore, experienced a
net
![]() loss
of protons
loss
of protons ![]() increase
of protons
increase
of protons ![]() loss of
electrons
loss of
electrons ![]() increase
of electrons
increase
of electrons ![]()
18. ![]() If it takes 12 J of energy to
move 2.0 C of charge through a lamp filament, the potential difference across
If it takes 12 J of energy to
move 2.0 C of charge through a lamp filament, the potential difference across
![]() the filament is
the filament is
![]() 6.0 V
6.0 V
![]() 10 V
10 V
![]() 14 V
14 V
![]() 24 V
24 V
![]()
19. ![]() If the charge on each of two
positively charged objects is halved, the electrostatic force between the
If the charge on each of two
positively charged objects is halved, the electrostatic force between the
![]() objects will
objects will
![]() decreased
to 1/2
decreased
to 1/2 ![]() decrease
to 1/4
decrease
to 1/4 ![]() decrease
to 1/16
decrease
to 1/16 ![]() remain
the same
remain
the same ![]()
20. ![]() An object with +10 elementary
charges is grounded and becomes neutral. What is the best explanation
An object with +10 elementary
charges is grounded and becomes neutral. What is the best explanation
![]() for this occurrence ?
for this occurrence ?
![]() The
object gained 10 electrons from the ground
The
object gained 10 electrons from the ground ![]() The object lost 10 electrons to the ground
The object lost 10 electrons to the ground
![]()
![]() The object gained 10 protons from the ground
The object gained 10 protons from the ground ![]() The
object lost 10 protons to the ground
The
object lost 10 protons to the ground ![]()
21. ![]() The diagram below shows two
identical metal spheres. Sphere A has a charge of +12 C. Sphere B is neutral.
The diagram below shows two
identical metal spheres. Sphere A has a charge of +12 C. Sphere B is neutral.

![]() When spheres A and B are in
contact, the total charge of the system is
When spheres A and B are in
contact, the total charge of the system is
![]() neutral
neutral
![]() +6 C
+6 C ![]() +12
C
+12
C ![]() +24 C
+24 C
![]()
22. ![]() Two identical metal spheres
with charges of -2 elementary charges and +6 elementary charges come in
Two identical metal spheres
with charges of -2 elementary charges and +6 elementary charges come in
![]() contact and then are separated.
What is the charge left on both spheres ?
contact and then are separated.
What is the charge left on both spheres ?
![]() -2
elementary charges
-2
elementary charges ![]() +2
elementary charges
+2
elementary charges ![]() -4
elementary charges
-4
elementary charges ![]() +4
elementary charges
+4
elementary charges ![]()
23. ![]() What is the energy gained
by an electron through a potential difference of 100 V ?
What is the energy gained
by an electron through a potential difference of 100 V ?
![]() 100 eV
100 eV
![]() 100 J
100 J
![]() 100 C
100 C
![]() 100 V
100 V
![]()
24. ![]() If a negative rod is
brought near the knob of an uncharged electroscope, the leaves will become
If a negative rod is
brought near the knob of an uncharged electroscope, the leaves will become
![]() positive
and diverge
positive
and diverge ![]() negative
and diverge
negative
and diverge![]() positive
and fall
positive
and fall![]() negative
and fall
negative
and fall
25. ![]() An electron is between two
oppositely charges parallel metal plates. As the electron moves from the
An electron is between two
oppositely charges parallel metal plates. As the electron moves from the
![]() negative plate to the positive
plate, the electron's potential energy
negative plate to the positive
plate, the electron's potential energy
![]() decreases
decreases
![]() increases
increases
![]() remains
the same
remains
the same ![]()
26. ![]() What is the magnitude of
the electric force acting on an electron located in an electric field with an
What is the magnitude of
the electric force acting on an electron located in an electric field with an
![]() intensity of 5.0 x 103
N/C ?
intensity of 5.0 x 103
N/C ?
![]() 3.2 x
10-23 N
3.2 x
10-23 N ![]() 8.0 x 10-16
N
8.0 x 10-16
N ![]() 5.0 x
103 N
5.0 x
103 N ![]() 3.2 x
1022 N
3.2 x
1022 N ![]()
27. ![]() Most metals are good
electrical conductors because
Most metals are good
electrical conductors because
![]() their
molecules are close together
their
molecules are close together ![]() they
have high melting points
they
have high melting points ![]()
![]() they
have many intermolecular spaces
they
have many intermolecular spaces ![]() they have a large number of free electrons
they have a large number of free electrons
28. ![]() An alpha particle with a
charge of +2 elementary charges is accelerated in a vacuum through a
An alpha particle with a
charge of +2 elementary charges is accelerated in a vacuum through a
![]() potential difference of 10,000 V.
What is the energy acquired by the particle ?
potential difference of 10,000 V.
What is the energy acquired by the particle ?
![]() 3.2 x
10-15 eV
3.2 x
10-15 eV ![]() 2.0 eV
2.0 eV
![]() 20,000
eV
20,000
eV ![]() 40,000
eV
40,000
eV ![]()
29. ![]() A charged particle is
placed in an electric field E. If the charge on the particle is doubled, the
A charged particle is
placed in an electric field E. If the charge on the particle is doubled, the
![]() force exerted on the particle by
the field E is
force exerted on the particle by
the field E is
![]() unchanged
unchanged
![]() doubled
doubled
![]() halved
halved
![]() quadrupled
quadrupled
![]()
30. ![]() An elementary charge is
accelerated by a potential difference of 9.0 V. The total energy acquired
An elementary charge is
accelerated by a potential difference of 9.0 V. The total energy acquired
![]() by the charge is
by the charge is
![]() 9.0 eV
9.0 eV
![]() 12 eV
12 eV
![]() 3.0 eV
3.0 eV
![]() 27 eV
27 eV
![]()
31. ![]() What happens to the
electric field intensity between two oppositely charged parallel plates as you
What happens to the
electric field intensity between two oppositely charged parallel plates as you
![]() move from the positive to the
negative plate ?
move from the positive to the
negative plate ?
![]() it
decreases
it
decreases ![]() it
increases
it
increases ![]() remains
the same
remains
the same
32. ![]() Identical spheres A and B,
charged as shown in the diagram below, are brought in contact and then separated.
Identical spheres A and B,
charged as shown in the diagram below, are brought in contact and then separated.
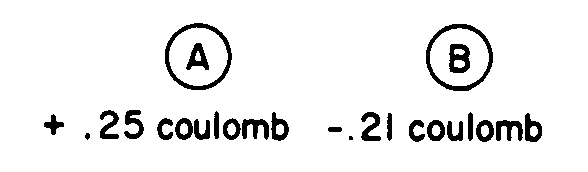
![]() What is the charge that remains
on sphere A ?
What is the charge that remains
on sphere A ?
![]() 0 C
0 C
![]() +0.02 C
+0.02 C
![]() -0.02
C
-0.02
C ![]() -0.04 C
-0.04 C
33. ![]() In the diagram below a
neutral pith ball is suspended on a string. A positively charged rod approaches the ball.
In the diagram below a
neutral pith ball is suspended on a string. A positively charged rod approaches the ball.
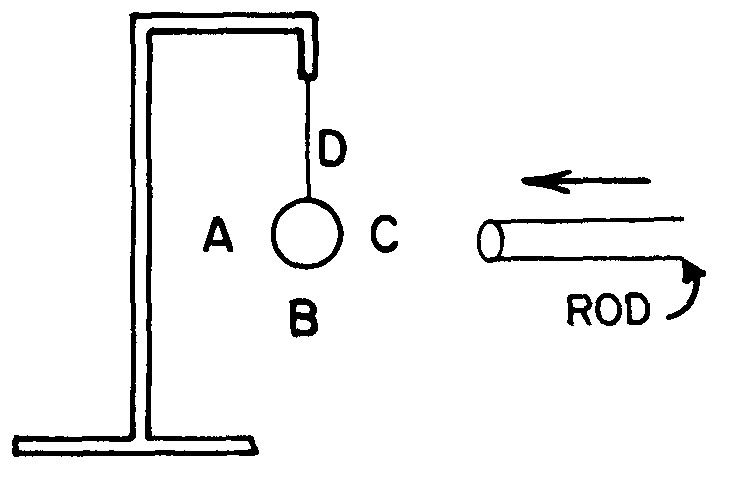
![]() The ball will first move toward
The ball will first move toward
![]() A
A ![]() B
B ![]() C
C ![]() D
D ![]()
34. ![]() Two large metal plates are
charged to a potential difference of 100 V.
Two large metal plates are
charged to a potential difference of 100 V.
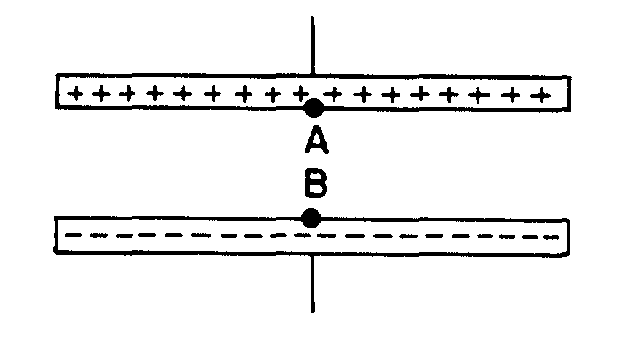
![]() How much work is needed to move 1
C of negative charge from point A to point B ?
How much work is needed to move 1
C of negative charge from point A to point B ?
![]() 1 J
1 J ![]() 100
J
100
J ![]() 1 eV
1 eV
![]() 100 eV
100 eV
![]()
35. ![]() Four electric charges, A,
B, C, D are arranged as shown.
Four electric charges, A,
B, C, D are arranged as shown.
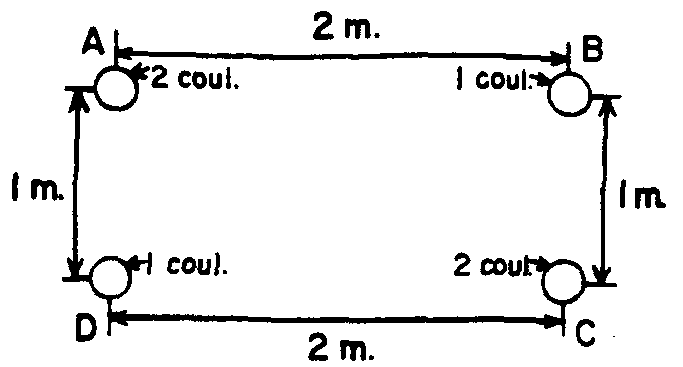
![]() The electric force will be least
between charges
The electric force will be least
between charges
![]() A and B
A and B ![]() A and C
A and C ![]() A and D
A and D ![]() B
and D
B
and D ![]()