Biology Revision cells and osmosis
Cells


Cell membrane
controls movement in and out. Thin membrane, holds the cell together.
Nucleus controls processes in cell. Contains
chromosomes
Cytoplasm produces energy, makes things,
stores food
Cell wall made of cellulose, a rubbery
material makes cell strong
Sap vacuole has watery fluid (sap), pushed
cytoplasm sideways
Chloroplast contains chlorophyll which is
used for photosynthesis
Mitochondrion releases energy for the cell
Glycogen stored animal food, mostly glycogen
Starch plants food storage, equivalent to
glycogen
Turgid
when a plant cell is full of water (firm)
Flaccid limp (no water)
The
characteristics of living things
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion
Nutrition
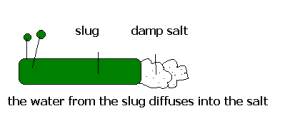
Osmosis
Diffusion
this is the movement of molecules or atoms from an area of their
high concentration to their low concentration.
Osmosis
this is a special kind of diffusion involving only water. Water moves from
an area of its high concentration (weak solution) to its low concentration
(strong solution) across a selectively permeable membrane

Two ways of investigating osmosis -1) using selectively permeable visking
tubing, or
2) Using dyed agar jelly cubes.
Diffusion
is fastest when there is a larger surface area.
A
potato left in strong sugar solution will go flaccid as the water inside it will
go by osmosis into the lower concentration of water in the sugar solution. A
potato left in water will go turgid as the water will go by osmosis into the
potato, as there is a lower concentration of water there.
Examples: