



POINTERS
The previous program can be rewritten to
make it easier to read, understand and maintain. To do this, we will use
a dedicated pointer to maintain and initialise the list, rather than get
into the long notation that we used in the previous program, eg,
startrecord^.nextrecord^.nextrecord^.number := 30;The modified program now looks like,
program PointerRecordExample2( output );
type rptr = ^recdata;
recdata = record
number : integer;
code : string;
nextrecord : rptr
end;
var startrecord, listrecord : rptr;
begin
new( listrecord );
if listrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('1: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
startrecord := listrecord;
listrecord^.number := 10;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the first record';
new( listrecord^.nextrecord );
if listrecord^.nextrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('2: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
listrecord := listrecord^.nextrecord;
listrecord^.number := 20;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the second record';
new( listrecord^.nextrecord );
if listrecord^.nextrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('3: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
listrecord := listrecord^.nextrecord;
listrecord^.number := 30;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the third record';
listrecord^.nextrecord := nil;
while startrecord <> nil do
begin
listrecord := startrecord;
writeln( startrecord^.number );
writeln( startrecord^.code );
startrecord := startrecord^.nextrecord;
dispose( listrecord )
end
end.
The lines of code
new( listrecord );
if listrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('1: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
startrecord := listrecord;
listrecord^.number := 10;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the first record';
creates the first record and initialises it, then remembers where it is
by saving it into startrecord. Pictorially, it looks like,

The lines of code
new( listrecord^.nextrecord );
if listrecord^.nextrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('2: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
listrecord := listrecord^.nextrecord;
listrecord^.number := 20;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the second record';
add a new record to the first by linking it into listrecord^.nextrecord,
then moving listrecord to the new record. Pictorially, it looks
like,
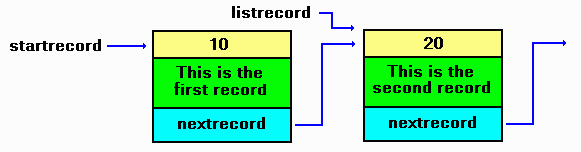
The lines of code
new( listrecord^.nextrecord );
if listrecord^.nextrecord = nil then
begin
writeln('3: unable to allocate storage space');
exit
end;
listrecord := listrecord^.nextrecord;
listrecord^.number := 30;
listrecord^.code := 'This is the third record';
listrecord^.nextrecord := nil;
add the last record to the previous by linking it into listrecord^.nextrecord,
then moving listrecord to the new record. Pictorially, it looks like,



