

| INSTRUCTIONS |
1. Question 1 is compulsory.
2. Choose any other 2 questions to make up a total of 3 questions.
3. Each question carries 20 marks.
4. DO NOT answer more than 3 questions in total.
5. Please start every questions in a new page.
6. Answers will not be marked if it is illegible.
7. Enter the question number (in the order you have attempted) in the boxes provided
below:
Question |
Total | |||||
|
QUESTION 1
a) Define the following terms using drawings where appropriate:
i) Abstract Data Type [2 marks]
Abstract Data Type refers to the combination of a data object with its operators.
ADT normally comprises of two paths: its specifications and its implementation.
ii) Data Abstraction [2 marks]
Where the implementation of the Data Type and its physical qualities are more important
than its method of implementation.
For example, an ADT such as stack behaves the same way with the same principles of PUSH
and POP no matter how the stack was created (array, records, pointers etc).
iii) Queue [2 marks]
Data strcuture which allows new elements to be added at one end (rear) and elements are
removed from the queue at the other end (front).
b) For each of the following strucutres, give an example problem situation in which they
would be appropriate for the programmer writing a program to solve the problem. Explain
how each data structure could be used in solving the problem and explain why it would be a
good choice. Your examples may be drawn from external application programs, or may be
drawn from algorithms used by operating systems or compilers to implement external
application programs.
i) Queue [2 marks]
Suitable for problems where earliest requests are serviced first.
example: a program which maintains a queue of passengers waiting to see a ticket agent.
ii) Binary Search Tree [2 marks]
Useful fror storage of records that have to be ordered and need to be searched.
example: program which maintains a sorted airline passenger list

Key values on Left subtree of node 1 is less than Key value in the root.
Key values on Right subtree of node 1 is more than the Key value in the root.
iii) Stack [2 marks]
- suitable where a Last-in, First-Out type of processing is needed.
example: program which accepts a string and displays in reverse area
(diagram)
iv) List (implemented with links) [2 marks]
useful for storing a list of items that are ordered and are subjected to having new
elements added and existing elements being removed frequently.
example: list of outstanding orders sorted by order number.
(diagram)
c) A text editor program needs to use a data structure that looks like the following:
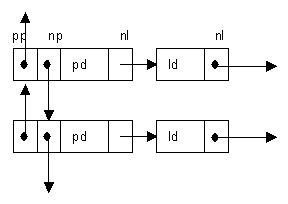
where ‘pp’ and ‘np’ are pointers to the previous and next pages,
‘pd’ is a page number, ‘nl’ is a pointer to the next line and
‘ld’ contains the details of that line.
Declare the structure using Pascal. [6 marks]
PagePtr=^PageNode;
LinePtr=^LineNode;
LineNode=Record
ld : String[80;
nl: LinePtr;
END;
PageNode=RECORD
pp: PagePtr;
np: PagePtr;
pd: Integer;
nl:LinePttr;
End;
QUESTION 2
Examine the following Pascal code segment :-
Procedure Unknown (First, Second : Integer; VAR Third: Integer);
Var
Temp : Integer;
BEGIN
Temp := First - Second;
If Temp < 0 Then
Third := 1
Else
If Temp = 0 Then
Third := 0
Else
Third := 1;
END;
a) i) Identify the purpose of Procedure ‘Unknown’. [2 marks]
ii) Write a more efficient Pascal Function called ‘Check’ that performs the same
task as Procedure ‘Unknown’. [8 marks]
iii) Write a statement that can ve used to invoke the routine ‘Check’.
(Assume that all needed variables are declared and initialized.) [2 marks]
b) i) Explain 3 differences between Functions and Procedures. [6 marks]
ii) Is it better to use a Function or a Procedure for the task of Procedure
‘Unknown’ above ? Why? [2 marks]
QUESTION 3
a) Explain why the use of functions and procedures assist in program design [4 marks]
allows codes to be reused
breaks down a large complex problem into smaller and more manageable modules
ensures that each module perform a specific task only - simplifies overall program design.
allows top-down or bottom up design strategies to be employed
b) Identify the purpose of the function UNKOWN given below.
main purpose :
to determine iif an array ‘A’ containing ‘Length’ number of
elements is sorted in ascending order or not.
details:
accepts twp input parameters - A and length
uses 2 local variables I and OK
loop is repeated as long as counter ‘I’ is within the range of 1 to Length and
OK has the value of TRUE
OK’s value is se based on the comparison of the adjacent elements in A
should the elements be in ascending order, OK is set to TRUE
should the elements be not sorted, OK is set to FALSE
in any events, the result of the comparisons is sent back to the calling point
Function Unknown (A : List; Length:Integer) : Boolean;
VAR
I : Integer;
OK : Boolean;
Begin
I := 1; OK := TRUE;
While ((I<Length) and OK) do
begin
OK := (A[I] < A[I+1]);
I := I + 1;
end;
Unknown:= OK;
end; [8 marks]
c)
i) Explain what is ‘Recursion’. [2 marks]
Recursion is a method used to repeat the execution of program statements through letting
functions and procedures invoking themselves, until there is no more need to.
ii) Write a recursive function to compute the following sum for any value of N (where N
>=0).
2N + 2N-1 + 2N-2 +...+22 + 21 + 20
[6 marks]
function cal(n:integer) : integer;
var
power : integer;
count : integer;
begin
if n=0 then
cal := 1
else
begin
power := 1;
for count := 1 to N Do
power := power *2;
cal:=power+cal(n-1);
end;
end;
QUESTION 4
a) Convert the following infix expression into their Prefix and Postfix form.
i) (A^B)/(C*D) [2 marks]
QUESTION 5
Given a tree :-

i) Give the expression in :
a. infix [2 marks]
A+C+F^G*E
b.prefix [2 marks]
++AC*^FGE
c.postfix [2 marks]
AC+FG^E*+
ii) Write a recursive procedure DestroyAll that will remove all nodes in the tree
(assume the data type in question 4b is used)
[10 marks]
Procedure DestroyAll (VAR R : TreePtr);
BEGIN
if R<> NIL THEN
begin
Destroy(R^.Left);
Destroy(R^.Right);
Dispose(R);
end;
END;
iii) Name 2 usage of a binary tree. [4 marks]
Binary Search Tree - for record indexing and fast searching
Dynamic data storage