Hardware-system unit
Motherboard
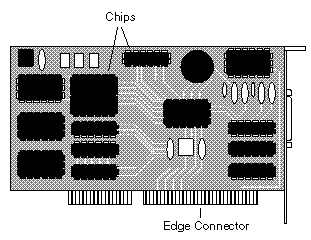 circuit
board
circuit
board
The main part of a personal computer. The system unit includes the chassis, microprocessor, main memory, bus, and ports, but does not included the keyboard or monitor, or any peripheral devices. A system unit is sometimes called a box or main unit.
Processor
The processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), interprets and carries out basic instructions that operate the computer. The processor significantly impacts overall computing power and manages most of a computer's operation. Some computer and chip manufactures use the term microprocessor to refer to the personal computer processor chip. Processors contain a contain unit and arithmetic logic unit, for example Intel.
Memory
Internal storage areas in the computer. The term memory identifies data storage that comes in the form of chips, and the word storage is used for memory that exits on tapes or disks. Moreover, the term memory is usually used as shorthand for physical memory, which refers to the actual chips capable of holding data. Some computers also use virtual memory which expands physical memory onto a hard disk.
Every computer comes with a certain amount of physical memory, usually refer to as main memory or RAM .You can think of main memory as an array of boxes, each of which can hold a single byte of information. A computer that has 1 megabyte of memory, therefore, can hold about 1 million bytes ( or characters) of information.
There are several different types of memory
-
RAM (random- access memory) :This is the same as main memory. When used by itself, the RAM refers to read and write memory; that is ,you can both write data into RAM and read data from RAM.
-
ROM (read-only memory): computers almost always contain a small amount of read-only memory that holds instructions for starting up the computer. Unlike RAM, ROM cannot be written to.
-
PROM (programmable read-only memory) :A PROM is a memory chip on which you can store a program. Like ROMs, P ROMs are non-volatile
-
EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory): An EPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to ultraviolet light.
CACHE

Pronounced cash, a special high-speed storage mechanism. It can be either a reserved section of main memory or an independent high-speed storage device. Two types of cashing are commonly used in personal computer: memory cashing and disk caching
A memory cache, sometimes called a cache store or RAM cache, is a portion of memory made of high-speed static RAM( SRAM) instead of the slower and cheaper dynamic RAM (DRAM) used for main memory. Memory caching is effective because most programs access the same data or instructions over and over. By keeping as much of this information as possible in SRAM, the computer avoids accessing the slower DRAM.
Disk caching works under the same principle as memory cashing, but instead of using high-speed SRAM, a disk cache uses conventional main memory Disk caching can dramatically improve the performance of applications, because accessing a byte of data in RAM can be thousands of times faster than accessing a byte on a hard disk.
When data is found in the cache, it is the cache hit, and the effectiveness of a cache is judged by its hit rate.
Port
An interface on a computer to which you can connect a device. Personal computers have various types of ports. Internally, there are several ports for connecting disk drives, display screens, and keyboard. Externally , personal computers have ports for connecting modems, printers, mice, and other peripheral devices.
The several popular type of port
-
SUB port-short for universal Serial Bus, an external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps. A single SUB port can be used to connect up to 127 peripheral devices.
-
Fire wire Port-A very fast external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of up to 400Mbps (in 1394a) and 800Mbps (in 1394b). Products supporting the 1394 standard go under different names, depending on the company. Apple, which originally developed the technology, uses the trademarked name Fire Wire.
Bus
A collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another. You can think of a bus as a highway on which data travels within a computer. When used in reference to personal computer, the term bus usually refers to internal bus. This is a bus that connects all the internal computer components to the CPU and main memory. There's also an expansion bus that enables expansion boards to access the CPU and memory
Every bus has a clock speed measured in MHz. A fast allows data to be transferred faster, which makes application run faster. On PCs, the old ISA bus is being replaced by faster buses such as PCs.
Nearly all PCs made today include a local bus for data that requires especially fast transfer speeds, such as video data. The local bus is a high-speed pathway that connects directly to the processor.
Bay
Short for drive bay, this refer to site in a site in a personal computer where a hard or floppy disk drive, CD-ROM drive or tape drive can be installed. Thus, number of drive bays in a computer determines how many mass storage devices can be internally installed
For PCs, bays come in two basic sizes: 3.5-inch and 5.25-inch, which represents the bay's height. In addition, bays are described as either internal or exposed. An internal bay cannot be used for removable media, such as floppy drives. Some manufactures use the terms hidden and accessible in place of internal and expose.