CHAPTER 5 HOMEWORK
1. (p.125 Ex.7) A 1.50-kg box is released on a 30° incline and accelerates down the incline at 0.30m/s2. Find the friction force impeding its motion. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction?
2. (p.125 Ex.15) Piles of snow o slippery roofs can become dangerous projectiles as they melt. Consider a chunk of snow at the ridge of a roof with a pitch of 30°. (a) What is the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction needed to keep the snow from sliding down? (b) As the snow begins to melt the coefficient of static friction decreases and the snow finally slips. Assuming that the distance from the chunk to the edge of the roof is 5.0m and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20, calculate the speed of the snow chunk when it slides off the roof. (c) If the edge of the roof is 10.0m above ground, what is the speed of the snow when it hits the ground?
3. (p.126 Ex.24) In Fig. 5-29 the coefficient of static friction between mass m1 and the table is 0.40, whereas the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. (a) What maximum value of m1 will keep the system from starting to move? (b) What value(s) of m1 will keep the system moving at constant speed?
4. (p.128 Ex.41) A coin is placed 12.0cm from the axis of a rotating turntable of variable speed. When the speed of the turntable is slowly increased, the coin remains fixed on the turntable until a rate of 50rpm is reached, at which point the coin slides off. What is the coefficient of static friction between the coin and the turntable?
5. (p.128 Ex.47) A 1000kg sports car moving at 20m/s crosses the rounded top of a hill (radius =100m). Determine (a) the normal force on the car, (b) the normal on the 70-kg driver, and (c) the car speed at which the normal force is zero.
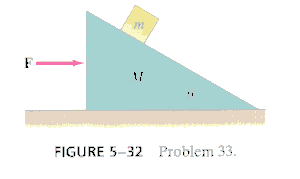
*6. (p.127 Ex.31) A bicyclist can coast down a 7.0° hill at a steady 9.5km/h. If the drag force is proportional to the square of the speed v so that FD = cv2, calculate (a) the value of the constant c and (b) the average force that must be applied in order to descend the hill at 25km/h. The mass of the cyclist plus bicycle is 80.0kg. Ignore other types of friction.*7. (p.127 Ex.33) A small block of mass m rests on the rough, sloping side of a triangular block of mass M which itself rests on a horizontal frictionless table as shown in Fig-5-32. If the coefficient of static friction is m, determine the minimum horizontal force F applied to M that will cause the small block m to start moving up the incline.
