CHAPTER 9 HOMEWORK
1. (p.231 Ex.4) A 145-g baseball, moving along the x-axis with speed 30.0m/s, strikes a fence at a 45° angle and rebounds along the y-axis with unchanged speed. Give its change in momentum using unit vector notation.
2. (p.232 Ex.13) A child in a boat throws a 5.40-kg package out horizontally with a speed of 10.0m/s, Fig. 9-36. Calculate the velocity of the boat immediately after, assuming it was initially at rest. The mass of the child is 26.0kg and that of the boat is 55.0kg.
3. (p.233 Ex.26) A 140-kg astronaut (including space suit) acquires a speed of 2.50m/s by pushing off with his legs from a 1800-kg space capsule. (a) Whaat is the change in speed of the space capsule? (b) If the push lasts 0.500s, what is the average force exerted by each on the other? As the reference frame, use the position of the capsule before the push. (c) What is the kinetic energy of each after the push?
4. (p.233 Ex.33) A 0.450-kg hockey puck, moving east with a speed of 4.20m/s, has a head-on collision with a 0.900-kg puck initially at rest. Assuming a perfectly elastic collision, what will be the speed and direction of each object after the collision?
5. (p.234 Ex.42) An 18-g rifle bullet traveling 180m/s buries itself in a 3.6-kg pendulum hanging on a 2.8-m-long string, which makes the pendulum swing upward in an arc. Determine the horizontal component of the pendulum's displacement.
6. (p.234 Ex.54) Two billiard balls of equal mass move at right angles and meet at the origin of an xy coordinate system. One is moving upward along the y axis at 2.0m/s, and the other is moving to the right along the x axis with speed 3.7m/s. After the collision (assumed elastic), the second ball is moving along the positive y axis (Fig. 9-42). What is the final direction of the first ball, and what are their two speeds?
7. (p.235 Ex.66) Determine the CM of a thin, uniform, semicircular plate.
8. (p.235 Ex.70) Two 35-kg masses have velocities (in m/s) of v1 = 12i - 16j and v2 = -20i + 14j. Determine the velocity of the center of mass of the system.
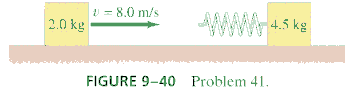
*9. (p.233 Ex.41)A 2.0-kg block slides along a frictionless tabletop at 8.0m/s toward a second block (at rest) of mass 4.5kg. A coil spring, which obeys Hooke's law and has spring constant k = 850N/m, is attached to the second block in such a way that it will be compressed when struck by the moving block. Fig. 9-40. (a) What will be the maximum compression of the spring? (b) What will be the final velocities of the blocks after the collision? (c) Is the collision elastic?

*10 (p.235 Ex.67) Determine the CM of a machine part that is a uniform cone of height h and radius R, Fig 9-45. [Hint: Divide the cone into an infinite number of disks of thickness dz, one which is shown.]
