CHAPTER 22 HOMEWORK
1. (p.587 Ex.3) A cube of side l is placed in a uniform field E = 6.50 x 103N/c with edges parallel to the field lines. What is the net flux through the cube? What is the flux through each of its six faces?
2. (p.588 Ex.7) In a certain region of space, the electric field is constant in direction (say horizontally, in the x direction), but its magnitude decreases from E = 560N/C at x = 0 to E = 410N/C at x = 30m. Determine the charge within a cubical box of side l = 30m, where the box is oriented so that four of its sides are parallel to the field lines (Fig. 22-27).
3. (p.588 Ex.11) A long thin wire, hundreds of meters long, carries a uniformly distributed charge of -2.8mC per meter of length. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at points (a) 5.0m and (b) 2.0m from the wire?
4. (p.588 Ex.15) A spherical cavity of radius 4.50cm is at the center of a metal sphere of radius 18.0cm. A point charge Q = 5.50mC rests at the very center of the cavity, whereas the metal conductor carries no net charge. Determine the electric field at a point (a) 3.0cm from the center of the cavity and (b) 6.0cm from the center of the cavity.
5. (p.589 Ex.28) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of radius Ro and length L (Ro << L) posses a uniform volume charge density rE(C/m3), Fig.22-33. Determine the electric field at points (a) outside the cylinder (r < R0). Do only for points far from the ends and for which r << L.
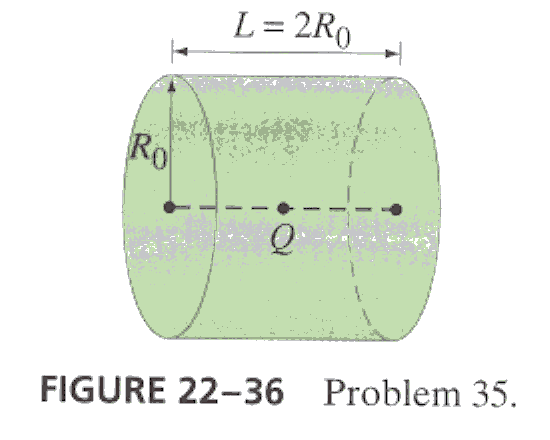
6.* (p.589 Ex.35) A point charge Q is on the axis of a cylinder at its center. the diameter of the cylinder is equal to its length L (fig. 22-36). What is the total flux through the curved sides of the cylinder? [Hint: First calculate the flux through the ends.]

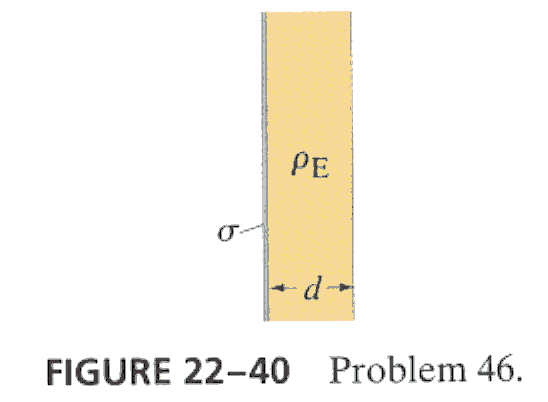
7.* (p. 590 Ex.46) A very large thin plane has uniform surface charge density s, Touching it on the right (Fig. 22-40) is a long and wide slab of thickness d with uniform volume charge density rE. Determine the electric field (a) to the left of the plane, (b) to the right of the slab, and (c) everywhere inside the slab.