|
DATABASE
A large collection of information
manipulated by a computer.
More Detailed Definition:
(1) Often abbreviated DB. A
collection of information organized in such a way that a computer
program can quickly select desired pieces of data. You can think
of a database as an electronic filing system.
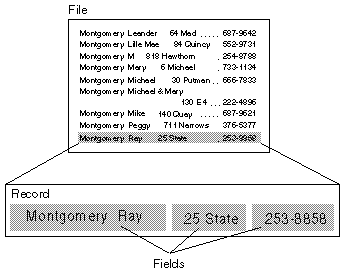
Traditional databases are organized by fields, records, and files.
A field is a single piece of information; a record is one complete
set of fields; and a file is a collection of records. For example,
a telephone book is analogous to a file. It contains a list of
records, each of which consists of three fields: name, address,
and telephone number.
An alternative concept in database design is known as Hypertext.
In a Hypertext database, any object, whether it be a piece of
text, a picture, or a film, can be linked to any other object.
Hypertext databases are particularly useful for organizing large
amounts of disparate information, but they are not designed for
numerical analysis.
To access information from a database, you need a database
management system (DBMS). This is a collection of programs that
enables you to enter, organize, and select data in a database.
(2) Increasingly, the term database is used as shorthand for
database management system.
|
