|
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE An organized system of commands that enables a computer user to create programs. More Detailed Definition:
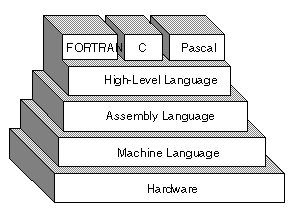
A vocabulary and set of grammatical rules for instructing a computer to perform specific tasks. The term programming language usually refers to high-level languages, such as BASIC, C, C++, COBOL, FORTRAN, Ada, and Pascal. Each language has a unique set of keywords (words that it understands) and a special syntax for organizing program instructions. High-level programming languages, while simple compared to human
languages, are more complex than the languages the computer
actually understands, called machine languages. Each different
type of CPU has its own unique machine language.
The question of which language is best is one that consumes a lot
of time and energy among computer professionals. Every language
has its strengths and weaknesses. For example, FORTRAN is a
particularly good language for processing numerical data, but it
does not lend itself very well to organizing large programs.
Pascal is very good for writing well-structured and readable
programs, but it is not as flexible as the C programming language.
C++ embodies powerful object-oriented features, but it is complex
and difficult to learn. |