 |
| Horizontal Well Applications in the Coalinga Field, Case History and Best practice review with Optimization of Placement with 3D/4D Seismic E. L. von Dohlen, C.W. Simonson Chevron Reservoir Characterization/Horizontal Well Forum April, 2000 Stanford University Petroleum Engineering Seminar February, 2001 |
| Application of Horizontal Wells is problematic in the stratigaphically diverse thermal processed sands in the Coalinga Field. Complicating factors as sand connectivity, steam injection support, geometry of well placement, and sand control has limited this application. The technology did not demonstrate its forecasted productivity and sapped field resources. With 3D seismic visualization of thermal processing in reservoir bodies to assist placement and cost improvement in the drilling design, application of horizontal producers now holds significant potential for performance improvement in realignment of drives. |
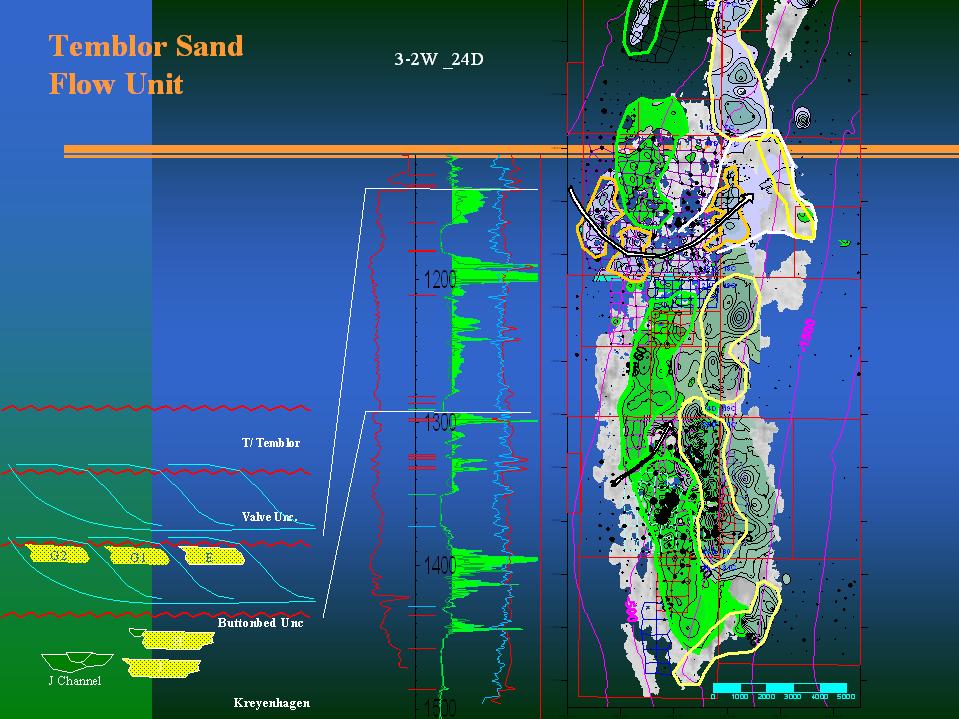
| Stratigraphic mozaic of Temblor shorefront sand packages defining regressive sequence. Flow units are defined by a combination of net sand and seismic amplitude bodies. Sequential shorefront elements are breached with constructure of the next package. |
| Seismic data serves as backdrop in horizontal well planning, reinforcing interpretation for continuity of sand units. |
| Sand zone temperature map derived from 4D seismic amplitude difference analysis. Fiber Optic temperature survey of the horizontal well corresponds closely to the temperature map. Timing of the survey was about 1 year prior to the drilling of the well. |
| Completion of the two Coalinga horizontal producers significantly improved the financial performance of the project. Production increased 500 BOPD over forecast with a steamdrive Steam/Oil ratio drop to 4. |