|
A symbol of concentric circles and 33 rays -Created by Charles R Henry. This is our
symbol as sign of honoring a friend. |
A key to unlockThe mystery on aGeometrical Nazca Marking. Part-2
T.L. Subash Chandira Bose and Jack
Andrews. |
With the
modern technology of CAD design we begin our study by drawing in our home
PC (computer).
“Orientation”(Marking the
Cardinal and Ordinal Directions)
Chapter 6 –
Orientation, Maya Mata describes the ancient geometrical method to find out the
directions.
6.1-2a: Now I give the
method of determining the cardinal points with the help of gnomon. (One should
proceed) at sunrise during a month when the solar path is towards the north
during a bright fortnight when sunrise is beautiful, when there are no spots in
the solar disc and when the sun is in the asterism of the appropriate
fortnight.
6.2b- 3a: First of all
a piece of ground in the middle of the chosen site should be leveled by the
water method; this must be square one square pole in the center in the center
of which the gnomon should be set.
6.3b- 5: Herewith the
dimensions of the gnomon (Sanku): the largest kind is one cubit long, its
diameter at is one digit at the top and five at the bottom, it is perfectly
circular and without irregularities; one of medium size (has a length of)
eighteen digits and a small one a length of twelve or nine digits, their
diameter at the top and bottom being (in all case) proportionate to their
length.
6.6- 7a: The materials
prescribed for the making the gnomon are as follows: Ivory, sandalwood, wood of
khadira, kadara, sami, saka or tinduka or other hard wood; its tip should be
perfectly circular.
6.7b- 8a: When
the gnomon has been made it is set up in the chosen place at sunrise, then a
circle is drawn of which the gnomon is the center and which the diameter is
double the length of the gnomon.
6.8b-11a: The line
which join the two points where the shadow (of gnomon) has touched the circle
in morning (A) and in the evening (B), gives the east - west direction. The
line which passes through the space between these two points and (which is like that which) connects the head
and tail of a carp, is the north - south axis; the sage should draw these two
lines, Then the circles which have their centers at the east and west points should
be drawn.

Apacchaya
6.11b- 13: (When the
sun) is in Taurus or Virgo there is apaccya; when it is in Aries, Gemini, Leo
or Libra the (east-west axis) must be put back two digits; when it is in
Cancer, Scorpio or Pisces it must be adjusted by four digits, when it is in
Sagittarius or Aquarius (it must be adjusted) by six digits and when it is in
Capricorn by eight digits. The east-west line is to be fixed after it has been
moved to the right or to left of the shadow.
Apacchaya – Contd.
6.27: (The east=west
line) should be established with adjustments of the following numbers of digits
for each ten day period of each month: (Aries) two, one, zero, (Taurus) zero,
one, two, (Gemini) two, three, four, (Cancer) four, three, two, (Leo) two, one,
zero, (Virgo) zero, one, two, (Libra) two, three, four, (Scorpio) four, five,
six, (Sagittarius) six, seven, eight, (Capricorn) eight, seven, six, (Aquarius)
six, five, four, (Pisces) four, three, two.
6-28: When the course of the sun has been taken into consideration in relation to the constellations, the indicated adjustment should be made, when necessary; the correction once made, the line is drawn from the stake and the ground can be prepared.
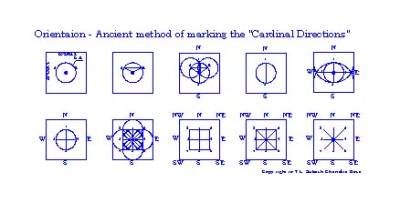
With
refer to “Mayamata: Chapter-6”, an ancient method of marking Cardinal direction
and four cardinal (lines) four directions N-S and then E-W were marked. On the basis of ancient geometry “Bodhayana
Sulpasutra: 1.22-23” a square was drawn and four ordinals directions (NE, SE, SW
and NW) are marked.
Plus + (cross) mark or “KA”
In the
above diagrams of marking the cardinal directions; the E, W, N and S directions
forms a symbol of a Plus + (cross)
mark.
When we
studied various ancient manuscripts and we are surprised to know that “KA” is
the first number. “The One” in ancient number system and also represents
unity. Since it is part of all numbers it represents the ideal symbol of
deity. It is the origin, the elementary.
Interestingly
we find in Mayamata, Diagrams - Chapter: 7. 57, the word “Ka” represent “The Supreme”. In the ancient Puranas we
find many names for Sun (Surya) one among those name is “Arka” (Ar + Ka) –“The
Radiant One”. We also find the word “KA
or CA” in Inca (In + ca).
The
ancient numerical system were initially originated in India, and during the
third Tamil Sangam period and also in post Indus (Brahmi) numerals; the number
“one” was symbolized as a plus (cross) + mark. We have found many ancient
inscriptions in Tamil Nadu, in which the Tamil Letter “KA” was used for, number
“one”. The plus
(cross) + mark or “KA” will further discussed in part 3.

A:
Pre Second Tamil Sangam Period or early Indus Numerals. B: Pre-Third Tamil
Sangam Period or mature Indus Numerals. C: Third Tamil Sangam or post Indus
(Brahmi) numerals.
Thanks
to: “Indus Scripts Among Dravidian Speakers”- Dr. R. Mathivanan.

Thanks to: S.Ganesan and R.Jayaraman –Jr.
Epigrapher, Department of Archeology, Tamil Nadu, India.
For additional information regarding ancient
numerals please visit the web site:
http://www.oocities.org/rmlyra/hindi.html
http://www.oocities.org/rmlyra/Numbers.html.

Above
Left: A marking of the Plus + mark with in the square, which also represents
four directions.
Above
right: The symbol at right with eight directions. Below: The symbols showing
the Plus + mark (cross) found in Tamil Nadu, India.

© T. L. Subash Chandira Bose 2003.
Interested persons to use these pictures for reference with the exact location of the symbols in Tamil Nadu are requested to get the written permission from :(lscbose@eth.net)
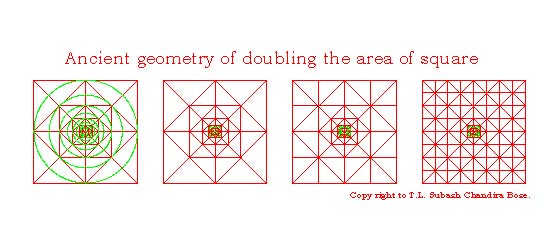
Doubling the area of Square: The famous “Pythagorean
theorem, which states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is
equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.”
The
above “Pythagorean theorem” is applicable to a right angled triangle but we
find in
Bodhayana Sulpasutra: 1.46-47(theorem of
rectangle) the steps by set, we can go up to the square with area =na˛, which is also indicated in Katayana
Sulpasutra.II.8-9.
The first area of the square is doubled and three circles are also drawn {refer the below diagram squares (red) and the circles (Green)}.

The area of square further doubled and nine circle all drawn as shown in the below diagrams. The square was divided into sixteen parts (squares) and finally into sixty-four parts (squares).
Sixteen Directions
or rays: In the book “Hidden Treasure of Vastu Shilpa Shastra and
Indian Traditions” - Derebail Muralidhar Rao, Page 23.) We find: It is a common knowledge that the direction
where the sun rises is known as East - Poorva or Puurab, where it sets as
west-Paschima, the North- Uttara and South- Dakshina. The corners where two
directions meet obviously is more significant since it combines the forces
emanating from both the directions. Northeast corner is called as Eeshanya,
Southeast corner as Aagneya, Southwest corner as Nairuthrya and Northwest corner
as Vaayavys. The every corner has been further divided into two sides each such
as:
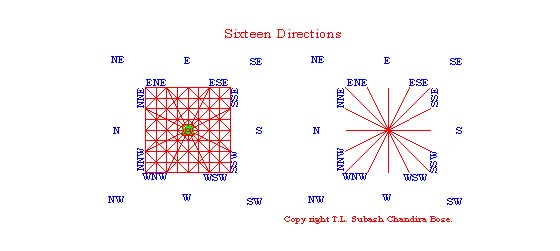
North
–East 1.
East North East - Eastern side of
North-East.
2. North
East - Northern side of North- East.
South-East 1. East South East - Eastern side of South –East.
2. South
East- Southern side of South-East.
South-West 1. South West- Southern side of
South=west.
2. West
South West – Western side of South West.
North-west 1. West North West - Western side of North West.
2. North
North West – Northern side of North-west.
Interestingly
we observe in the diagrams of orientation of cardinals directions, only a
circle “One”, circle with divided into with North and South cardinal line,
which divide the circle into ”Two”, with four cardinal directions (E, W, N and
S) divide the circle/square in to four and with eight directions divide the
square into eight triangles. With the above sixteen directions, form a square
with sixteen parts.

Thanks
to Madam Kathy Doore, ©
Labyrinthina.com.
1,2, 4, 8 and 16 directions, It is amazing to
know the “MU” symbol found in Peru have sixteen rays. Also we have observed
there are sixteen rays in the center of the Geometrical Nazca Marking or GGF.
“The Surprise is the
beginning of understanding the Mystery ”.
(Part – 3 shall continue.)
