Javadaki tüm
girdi çıktı programlaması veri akış (stream) kavramına dayanır. Veri akışını
bir su akışı veya bir kablolu sistem üzerinden bilgi akışı gibi düşünebiliriz.
Javada sadece dosya değil yazıcı, scanner gibi herhangi bir kaynağa veri
iletmek istediğimizde bu veri akış sistemini kullanırız. Javada oldukça
geniş bir veri akış kütüphanesi bulunmaktadır.
java.io kütüphanesinde
yer alan girdi çıktı programlama sınıfları şunlardır :
InputStream
FilterInputStream
LineNumberInputStream
BufferedInputStream
DataInputStream
PushbackInputStream
ByteArrayInputStream
FileInputStream
ObjectInputStream
PipedInputStream
SequenceInputStream
StringBufferInputStream
OutputStram
ByteArrayOutputStream
FileOutputStream
FilterOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream
DataOutputStream
PrintStream
ObjectOutputStream
PipedOutputStream
ObjectStreamClass
StreamTokenizer
Reader
FileReader
BufferedReader
LineNumberReader
CharArrayReader
FilterReader
PushbackReader
InputStreamReader
FileReader
PipedReader
StringReader
Writer
BufferedWriter
CharArrayWriter
FilterWriter
OutputStreamWriter
PipedWriter
PrintWriter
StringWriter
File
FileDescriptor
RandomAccessFile
Bu sınıfların
hepsinin genel görevi javaya girdi sağlamak ve çıktı almaktır. Burada bunlardan
bir kısmının işlevlerini ve nasıl çalıştıklarını inceleyeceğiz. Önce temel
ana sınıfların bazılarının tanımlarına daha detaylı
bakalım. InputStream
sınıfı byte türü yazı okuma sınıfıdır. Tüm byte türü bilgi akış kanalı
sınıflarının ana sınıfıdır. Tanımı :
public abstract
class InputStream extends Object
{
public
InputStream();
public int
available() throws IOException;
public void
close() throws IOException;
public
synchronized void mark(int readlimit);
public boolean
markSupported();
public abstract
int read() throws IOException;
public int
read(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public int
read(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
public
synchronized void reset() throws IOException;
public long
skip(long n) throws IOException;
}
InputStream
sınıfının byte türü yazma pareleli olan OutputStream sınıfının tanımı ise
:
public abstract
class OutputStream extends Object
{
public
outputStream();
public void
close() throws IOException;
public void
flush() throws IOException;
public abstract
void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void
write(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public void
write(byte b[],int başlamanoktası,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
}
Abstract sınıf
Reader, InputStream sınıfına olduça yakındır, yalnız data transferinde byte
yerine char kullanır, böylece girdi çıktıda unicode stream kullanabilme
olasılığı yakalar.
public abstract
class Reader extends Object
{
protected
Reader();
protected
Reader(Object o);
public abstract
void close() throws IOException;
public
void mark(int readlimit) throws IOException;
public boolean
markSupported() ;
public abstract
int read() throws IOException;
public int
read(char c[]) throws IOException;
public int
read(char c[],int başlamanoktası,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public boolean
ready() throws IOException;
public
void reset() throws IOException;
public long
skip(long n) throws IOException;
}
Abstract sınıf
Writer da Output straem sınıfına eşdeğerdir. Fakat aynı readerda olduğu
gibi bu sınıf da veri akışında char ve string kullanır.
public abstract
class Writer extends Object
{
public
outputStream();
public void
close() throws IOException;
public void
flush() throws IOException;
public abstract
void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void
write(char c[]) throws IOException;
public void
write(char c[],int başlamanoktası,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public void
write(String s) throws IOException;
public void
write(String s,int başlamanoktası,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
}
Bu sınıflar temel sınıflardır. Bunların altında yer alan çeşitli sınıflara
aşağıdaki bölümlerde daha detaylı bakacağız.
File sınıfı
girdi çıktı işlemlerini sağlarken, dosya isimleri ve bulundukları dizin
ile ilgili bilgi verir.
File sınıfının
tanımı :
Public class
File extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable
{
public
static final String pathSeperator;
public
static final char pathSeperatorChar;
public
static final String seperator;
public
static final char seperatorChar;
public
File(String dosya_ismi);
public File(String dizin_ismi, String dosya_ismi);
public File(File file_tipi_nesne,String dosya_ismi);
public
boolean canRead();
public
boolean canWrite();
public
boolean compareTo(Object o);
public
boolean compareTo(File başkabirdosya);
public
boolean createNewFile();
public
static File createTempFile(String isim) throws IOException;
public
static File createTempFile(String isim,File dosya) throws IOException;
public
boolean delete();
public
void deleteOnExit();
public
boolean equals(Object o);
public
boolean exists(Object o);
public
File getAbsooluteFile();
public
File getAbsoolutePath();
public
File getCanonicalFile() throws IOException;
public
File getCanonicalPath() throws IOException;
public
String getName();
public
String getParent();
public
File getParentFile();
public
String getPath();
public int
hashCode();
public
boolean isAbsolute();
public
boolean isDirectory();
public
boolean isFile();
public
boolean isHidden();
public
long lastModified();
public
long length();
public
String[] list();
public
String[] list(FilenameFilter filitrefonksiyonu);
public
static File[] listRoots();
public
boolean mkdir();
public
boolean mkdirs();
public
boolean renameTo(File yeniisim);
public
boolean setLastModified(long nezaman);
public
boolean setReadOnly();
public
String toString();
public URL
toURL() throws MAlformedURLException;
}
Kurucu metotların
çağırılmasına örnek olarak :
File f1=new File(/);
File f2=new File(/,autoexec.bat);
File f3=new File(f1,autoexec.bat);
tanımlarını verebiliriz. File sınıfında tanımlanmış olan Metotlardan
bazılarının tanımları şunlardır. canRead()
Tanımlanan dosyadan bilgi okunulabilirliğini test eder.
canWrite()
Tanımlanan dosyaya bilgi yazılabilirliğini test eder.
delete()
Dosyayı siler
equals(Object)
Dosya ismini Object te verilen dosya ismiyle karşılaştırır.
exists()
Dosyanın mevcut olup olmadığını kontrol eder.
getAbsolutePath()
Dosyanın tam dizin ismini ve dosya ismini verir( co/java/prog/Hosgeldiniz.java).
getName()
Dosyanın ismini verir.(Hosgeldiniz.java)
getParent()
Dosyanın içinde bulunduğu dizinin ismini verir.(prog)
getPath()
dosyanın ismini ve içinde bulunduğu dizinin ismini verir.(prog/Hosgeldiniz.java)
isAbsolute()
Dosya isminin mutlak isim olup olmadığını kontrol eder.(Eğer dosya ismi
co/java/prog/Hosgeldiniz.java olarak verilmişse true değeri verir.)
isDirectory()
verilen isimin bir dizin ismi olup olmadığını kontrol eder.
isFile()
verilen isimin birdosya isimi olup olamdığını kontrol eder.
lastModified()
Dosyanın en son değiştirildiği tarihi verir
length()
Dosyanın boyutunu Byte olarak verir.
list()
Verilen dizinin içindeki dosyaların listesini verir.
list(FilenameFiltre)
Verilen dizinin içindeki Filtre nesnesindeki tanıma uyan dosyaların listesini
verir.
mkdir()
Yeni bir dizin oluşturur.
mkdirs()
O anda tanımlı olan dizinin içine bir alt dizin oluşturur.
renameTo(File)
Dosyanın ismini değiştirir.
toString()
Dosya ve dizin isimleri topluluğunun String değişkeni eşdeğerini verir.
File(dosya) sınfındaki metodlardan da görülebileceği gibi bu sınıf dosyadan
okuyup yazma gibi bir işlem yürütmez. File sınıfının temel işlevi girdi
çıktı dosyasının adlandırılması ve isimle ilgili fonksiyonlara ulaşılmasıdır.
File sınıfının bazı metotlarını ufak bir program içinde kullanalım.
Program
10.1 . FileTestiSW.java programı
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.filechooser.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
public class FileTestiSW
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
//önce JFileChooser kullanarak dosyayı seç, sonra dosya özelliklerini
göster.
File f=new File("Hosgeldiniz.java");
JFileChooser dosyasec=new JFileChooser();
int onay = dosyasec.showOpenDialog(null);
//veya kayıt için int onay = dosyasec.showSaveDialog(null);
if(onay==JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION)
{
f=dosyasec.getSelectedFile();
}
String s="";
s+="Dosya ismi : "+f.getName()+"\n";
s+="Dizin ismi : "+f.getPath()+"\n";
s+="Mutlak Dizin ismi : "+f.getAbsolutePath()+"\n";
s+="Üst Dizin ismi : "+f.getParent()+"\n";
s+=f.exists() ? "Mevcut " : " Mevcut değil "+"\n";
s+=f.canWrite() ? "Yazılabilir " : " Yazılamaz"+"\n";
s+=f.canRead() ? "Okunabilir " : " Okunamaz"+"\n";
s+=f.isDirectory() ? "Dizin " : " Dizin degil"+"\n";
s+=f.isFile() ? "Dosya " : " Dosya degil"+"\n";
s+=f.isAbsolute() ? "Mutlak dizin ismi " : " Mutlak dizin ismi değil"+"\n";
s+="Son Degisiklik : "+f.lastModified()+"\n";
s+="Dosya boyutu : "+f.length()+" Byte"+"\n";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,s,"Dosya testi",JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
}
10001.JPG
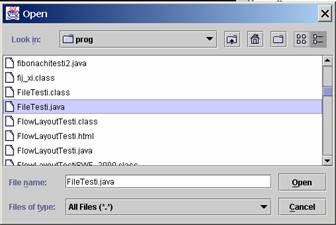
Şekil 10.2
FileTesti.java programının içindeki dosya seçim penceresi
10002.JPG
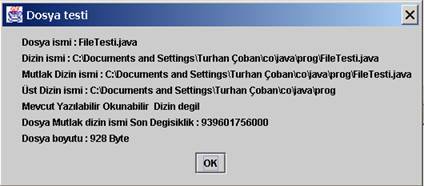
Şekil 10.2
FileTesti.java programının sonucları
Burada swing
hazır dosya seçme programı
JfileChooser kullanılarak dosya ismi seçilmiş, sonar bu dosya ile ilgili
çeşitli bilgiler JoptionPane grafik ortamında aktarılmıştır.
Java bilgi
dosyalarını birbiri ardısıra gelen byte veya char (unicode) akışı olarak
görür. Her dosya dosya-bitiş işaretiyle sonlanır. Yeni bir dosya açıldığında
bu dosyayla ilgili bir nesne oluşturulur. Yeni bir java programı açıldığında
üç akış nesnesi otomatik olarak açılır. Bunlar System.in , System.out,
System.err nesneleridir. Eğer kendimiz bir girdi veya çıktı akış nesnesi
oluşturmak istersek FileInputStream veya FileOutputStream
sınıfı bir nesne tanımlıyabiliriz. Akısın içindeki değişkenleri sadece
byte olarak okumak yerine direk olarak double veya integer gibi değişkenler
türünden okumak istersek DataInputStream ve DataOutputStream sınıflarını
kullanabiliriz. Genel olarak FileOutputStream ve DataOutputStream sınıflarını
aşağıdaki gibi bir arada kullanabiliriz:
DataOutputStream ciktiakimi;
try{ ciktiakimi=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(isim.dat));}
catch(IOException e) {System.err.println(Dosya acilamadi\n+e.toString());}
Bu deyim bize isim.dat isimli dosyadan bir fileOutputStream aracılığıyla
açılan dosyayı DataOutputStreame çevirip gerçek değişkenler cinsinden akış
kanalı açar. DataOutputStream ve FileOutputStream sınıflarının tanımları
:
public class DataOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream implements
DataOutput
{
public DataOutputStream(OutputStram o);
protected int written
public void flush()
public final void size()
public synchronized void write(byte[],int baslangıçnoktası,int uzunluk);
public synchronized void write(int);
public final void writeBoolean(boolean b);
public final void writeBytes(String s)
public final void writeChar(int)
public final void writeChars(String)
public final void writeDouble(double)
public final void writeFloat(float)
public final void writeInt(int)
public final void writeLong(long)
public final void writeShort(int)
public final void writeUTF(String)
}
FileOutputStream ise dosya sınıfı File ile DataOutputStream sınıfı arasındaki
gerekli tanımları sağlar
public class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream
{
public FileOutputStream(File file) throws IOException;
public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fd) throws IOException;
public FileOutputStream(String s) throws IOException;
public FileOutputStream(String s, boolean b) throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
protected void finalize() throws IOException;
public void getFD() throws IOException;
public void write(byte[]) throws IOException;
public void write(byte[], int, int) throws IOException;
public void write(int) throws IOException;
public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException;
}
Kanal açıldıktan sonra DataOutputStream sınıfının metodlarını
kullanarak dosyaya yazı yazabiliriz. Yazma metodlarının işlevlerine bir
göz atarsak :
write(byte B[] )
byte tipi boyutludeğişkeni açılmış olan DataOutputStream kanalına yazar.
write(byte B[], int baslangıcindeksi, int indeksboyutu)
byte tipi boyutludeğişkeni açılmış olan DataOutputStream kanalına yazar.
Baslangiç indeksinden baslar ve indeksboyutu uzunluğundaki kısmı yazar.
write(int B) int datayı data output streame yazar.
writeBoolean(boolean B) Boolean değişkeni DataOutputStreame yazar.
writeByte(int) int değişkeni byte olarak DataOutputStreame yazar.
writeBytes(String) String değişkeni byte boyutlu değişken olarak
DataOutputStreame yazar.
writeChar(int) int değişkeni char değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeChars(String) String değişkeni Char değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeDouble(double) double değişkeni double değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeFloat(float) float değişkeni float değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeInt(int) float değişkeni float değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeLong(long) long değişkeni long değişken olarak DataOutputStreame
yazar.
writeShort(int) int değişkeni short (short integer) değişken olarak
DataOutputStreame yazar.
writeUTF(String) String değişkeni unicode UTF-8 formatı karekter
boyutu olarak yazar.
Bu şekilde
yazdığımız bir veri akışın okumak için ise :
DataInputStream girdiakimi;
try{
girdiakimi=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(isim.dat"));
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
tanımını kulanabiliriz.
Buradaki DataInputStream sınıfının tanımı :
public class
DataInputStream extends FilterInputStream implements DataInput
{
public DataInputStream(InputStream
in);
public DataInputStream(InputStream
in);
public final
int read(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public final
int read(byte b[], int başlangıçdeğeri, int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public final
void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public final
void readFully(byte b[],int başlangıçdeğeri, int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public final
int skipBytes(int n) throws IOException;
public final
boolean readBoolean() throws IOException;
public final
byte readByte() throws IOException;
public final
int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException;
public final
short readShort() throws IOException;
public final
int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException;
public final
char readChar() throws IOException;
public final
int readInt() throws IOException;
public final
long readLong() throws IOException;
public final
float readFloat() throws IOException;
public final
double readDouble() throws IOException;
public final
String readLine() throws IOException;
public final
String readUTF() throws IOException;
public final
static String readUTF(DataInput in) throws IOException;
}
şeklindedir.
FileInputStream ise :
public FileInputStream(File
file) throws FileNotFoundException
{
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj);
public int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[],int başlangıçnoktası,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public long skip(long n) throws IOException;
public int available() throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException;
protected void finalize() throws IOException;
}
şeklinde tanımlıdır. DataInputStream metdunun alt okuma metodlarına
biraz daha detaylı göz atarsak:
read(byte[])
byte veri
akışını direk okur.
read(byte[], int başlangıçnoktası,
int boyut)
byte veri
akışını başlangıçnoktası
indeksinden boyut uzunluğuna kadar okurdirek okur.
readBoolean()
boolean değişken
(true veya false) okur.
readByte()
8-bit byte integer okur
readChar()
unicode karecter(char) okur
readDouble()
double okur
readFloat()
float okur
readFully(byte[])
byte boyutlu değişkenini, byte[] boyutlu girdi değişkeninin boyutuna
göre okur.
readFully(byte[], int, int)
readInt()
Integer okur
readLine()
Bir satırı satırbaşı yap komutuna kadar okur. Java 1.0 komutudur. 1.1
ve üzerinde bazı okuma hataları yaptığı görüldüğünden kullanılmaması tavsiye
edilir.
readLong()
Long tamsayı değişkeni okur.
readShort()
Short tamsayı değişkeni okur
readUnsignedByte()
8-bitlik işaretsiz tamsayı değişkeni okur.
readUnsignedShort()
16-bitlik işaretsiz tamsayı değişkeni okur.
readUTF()
Unicode karekteri okur.
readUTF(DataInput)
Unicode Karakterini (Character) DataInput girdi akışından okur.
skipBytes(int n)
n byte değeri okumadan atlar.
Şimdi bir örnek
problem ile bu yazma ve okuma işlemine daha yakından bir göz atalım. Program
10.2 de yeni bir dosya açılmakta, ve dosyaya veri girilmektedir. Program
10.3 de aynı programın swing kullanılarak yazılmış versiyonu mevcuttur. Program
10.4 de ise yaratılan dosyaya girilen veriler okunmaktadır.
Program 10.2 ardisikDosyaYarat.java programı
import
java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class ardisikDosyaYarat extends Frame implements ActionListener
{
private TextField hesapIsmiKutusu,isimKutusu,soyIsimKutusu,hesapKutusu;
private Button enter,done;
private DataOutputStream cikti;
private Label H,I,S,P;
public ardisikDosyaYarat()
{
super("Musteri dosyasi Ac");
try{
cikti=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("musteri.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{ System.err.println("Dosya dogru acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
setSize(300,150);
setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
H=new Label("Hesap numarasi :");
add(H);
hesapIsmiKutusu=new TextField();
add(hesapIsmiKutusu);
I=new Label("isim : ");
add(I);
isimKutusu=new TextField(20);
add(isimKutusu);
S=new Label("Soyisim : ");
add(S);
soyIsimKutusu=new TextField(20);
add(soyIsimKutusu);
P=new Label("Hesaptaki para : ");
add(P);
hesapKutusu=new TextField(20);
add(hesapKutusu);
enter=new Button("Gir");
enter.addActionListener(this);
add(enter);
done=new Button("Cikis");
done.addActionListener(this);
add(done);
setVisible(true);
}
public void hesapEkle()
{
int accountNumber=0;
Double d;
if(!hesapIsmiKutusu.getText().equals(""))
{
try{
accountNumber=Integer.parseInt(hesapIsmiKutusu.getText());
if(accountNumber0)
{
cikti.writeInt(accountNumber);
cikti.writeUTF(isimKutusu.getText());
cikti.writeUTF(soyIsimKutusu.getText());
d=new Double(hesapKutusu.getText());
cikti.writeDouble(d.doubleValue());
}
hesapIsmiKutusu.setText("");
isimKutusu.setText("");
soyIsimKutusu.setText("");
hesapKutusu.setText("");
}
catch(NumberFormatException nfe)
{
System.err.println("Hesap numarasi tamsayi degisken olamalidir");
}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosyaya yazarken hata olustu\n"+io.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
hesapEkle();
if(e.getSource()==done)
{
try{ cikti.close();}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosya kapatilamadi\n"+io.toString());
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
new ardisikDosyaYarat();
}
}
10003.JPG

Şekil 10.3 ArdisikDosyaYarat.java
programı ve sonuclarının Frame çıktısında görülmesi
Program
10.3 ardisikDosyaYaratSWF_200.java
programı
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ardisikDosyaYaratSWF_2000 extends JFrame implements
ActionListener
{
private JTextField hesapIsmiKutusu,isimKutusu,soyIsimKutusu,hesapKutusu;
private JButton enter,done;
private DataOutputStream cikti;
private JLabel H,I,S,P;
Container c;
public ardisikDosyaYaratSWF_2000()
{
super("Müşteri dosyasi Aç");
c=getContentPane();
try{
cikti=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("musteri.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{ System.err.println("Dosya doğru açılamadı\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
c.setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
H=new JLabel("Hesap numarasi :");
c.add(H);
hesapIsmiKutusu=new JTextField();
c.add(hesapIsmiKutusu);
I=new JLabel("isim : ");
c.add(I);
isimKutusu=new JTextField(20);
c.add(isimKutusu);
S=new JLabel("Soyisim : ");
c.add(S);
soyIsimKutusu=new JTextField(20);
c.add(soyIsimKutusu);
P=new JLabel("Hesaptaki para : ");
c.add(P);
hesapKutusu=new JTextField(20);
c.add(hesapKutusu);
enter=new JButton("Gir");
enter.addActionListener(this);
c.add(enter);
done=new JButton("Cikis");
done.addActionListener(this);
c.add(done);
setVisible(true);
}
public void hesapEkle()
{
int accountNumber=0;
Double d;
if(!hesapIsmiKutusu.getText().equals(""))
{
try{
accountNumber=Integer.parseInt(hesapIsmiKutusu.getText());
if(accountNumber>0)
{
cikti.writeInt(accountNumber);
cikti.writeUTF(isimKutusu.getText());
cikti.writeUTF(soyIsimKutusu.getText());
d=new Double(hesapKutusu.getText());
cikti.writeDouble(d.doubleValue());
}
hesapIsmiKutusu.setText("");
isimKutusu.setText("");
soyIsimKutusu.setText("");
hesapKutusu.setText("");
}
catch(NumberFormatException nfe)
{
System.err.println("Hesap numarasi tamsayi degisken olamalidir");
}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosyaya yazarken hata olustu\n"+io.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
hesapEkle();
if(e.getSource()==done)
{
try{ cikti.close();}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosya kapatilamadi\n"+io.toString());
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ardisikDosyaYaratSWF_2000 pencere= new ardisikDosyaYaratSWF_2000();
pencere.setSize(300,150);
pencere.addWindowListener(new BasicWindowMonitor());
pencere.setVisible(true);
}
}
10004.JPG
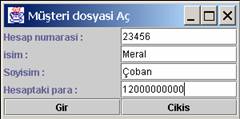
Şekil 10.4 ArdisikDosyaYaratSWF.java
programı ve sonuclarının Frame çıktısında görülmesi
Program
10.4 ardisikDosyaOku.java programı
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class ardisikDosyaOku extends Frame implements ActionListener
{
private TextField accountField,firstNameField,lastNameField,balanceField;
private Button next,done;
private DataInputStream input;
public ardisikDosyaOku()
{
super("Musteri dosyasini oku");
try{
input=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("musteri.dat"));
} catch(IOException e) { System.err.println("Dosya acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
setSize(300,150);
setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
add(new Label("Hesap Numarasi :"));
accountField=new TextField();
add(accountField);
add(new Label("isim : "));
firstNameField=new
TextField(20);
add(firstNameField);
add(new Label("soyisim : "));
lastNameField=new TextField(20);
add(lastNameField);
add(new Label("Hesaptaki para : "));
balanceField=new TextField(20);
add(balanceField);
next=new Button("bir sonraki hesap");
next.addActionListener(this);
add(next);
done=new Button("cikis");
done.addActionListener(this);
add(done);
setVisible(true);
}
public void readRecord()
{
int account;
String first,last;
double balance;
{
try{
account=input.readInt();
first=input.readUTF();
last=input.readUTF();
balance=input.readDouble();
accountField.setText(String.valueOf(account));
firstNameField.setText(first);
lastNameField.setText(last);
balanceField.setText(String.valueOf(balance));
}
catch(EOFException eof)
{
closeFile();
}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosyay� okurken hata olustu\n"+io.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if(e.getSource()==next)
readRecord();
else
closeFile();
}
private void closeFile()
{
try{
input.close();
System.exit(0);
}
catch(IOException
e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya Kapama Hatası oluştu\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
new ardisikDosyaOku();
}
}
10004.JPG

Şekil 10.4
ArdisikDosyaOku.java
programı ve sonuclarının Frame çıktısında görülmesi
ArdisikDosyaYarat.java
programında musteri.txt dosyası
try{
cikti=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("musteri.txt"));
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya dogru acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
gurubunu kullanarak
açılmıştır. Bu gurubu File sınıfını da kullanarak
File f=new
File(musteri.txt);
f=f.getAbsolutePath(f);
try{
cikti=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
}
catch(IOException e)
{ System.err.println("Dosya dogru acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
şeklinde de yaratabilirdik. İkinci şekilde dosyayı tanımlarken tam dizin
ismini de otomatik olarak tanımlamış olurduk.
Dosyanın okunması
içinse
try{
input=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("musteri.dat"));
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
gurubunu kullandık.
Eğer dosya ismi de değişkende dışarıdan okuduktan sonra ismi File sınıfına
yükleyip sonra akış kanalı açabiliriz.
Dosya ile işlemler
bittikten sonra dosya kapanır.
private
void closeFile()
{
try{
input.close();
System.exit(0);
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya Kapama Hatası oluştu\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
closeFile()
metotu dosya akışını
kapatmak amacıyla oluşturulmuştur.
Bu örnekte
kullandığımız, DataOutputStream, FileOutputStream, DataInputStream,
FileInputStream girdi çıktı akış kontrolları temel olarak daha önce
tanımlarını vermiş olduğumuz OutputStream ve InputStream sınıflarından
türetilmiş sınıflardı. Ve temel olarak byte değişken türü üzerinden veri
akışını sağlamaktadırlar.
Yine yukarıda
tanımlanmış olan Reader ve Writer sınıfları ise aynı işlemi char sınıfı
veri akışı üzerinden yapmaktadır ve char sınfı direk olarak unicode olarak
tanımlandığından herhangibir hataya sebep vermeden daha iyi bir veri akışı
sağlar. Bu sınıfın alt sınıfları olarak tanımlanan ve yazma işleminde kullanılan
sınıfların kullanılmasına bir göz atalım.
Genel olarak
Writer sınıfından türetilen ve en çok kullanılan Yazma kanalı PrintWriter
, BufferedWriter, FileWriter veya OutputStreamWriter
sınıflarının beraber kullanılmasıyla gerçekleştirilebilir. Bu sınıfların
birlikte kulanılmalarını şu deyimlerle örnekleyebiliriz :
dosya "a.txt"
e yazdırmak için :
PrintWriter
cfout=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt")));
tanımı kullanılabilir.
PrintWriter
sınıfının tanımı :
public class PrintWriter extends Writer
{
public PrintWriter(OutputStream o) ;
public PrintWriter(OutputStream o, boolean b) ;
public PrintWriter(Writer w) ;
public PrintWriter(Writer w, boolean b);
public void flush();
public void close();
public boolean checkError();
protected void setError();
public void write(int c);
public void write(char buf[]);
public void write(String s,int baslamaindeksi,int uzunluk);
public void write(String s);
public void print(boolean b);
public void print(char c);
public void print(int i);
public void print(long l);
public void print(float f);
public void print(double d);
public void print(Object obj);
public void println();
public void println(boolean x);
public void println(char x);
public void println(int x);
public void println(long x);
public void println(float x);
public void println(double x);
public void println(char x[]);
public void println(Object x);
}
PrintWriter
sınıfının mevcut metotlarının işlevleri şunlardır :
checkError()
Tüm veriyi gönderir ve hata kontrolu yapar.
close()
veri akış kanalını kapatır.
flush()
veri akış kanalındaki tüm veriyi gönderir (ve bufferi yeni veri için boşaltır).
print (boolean)
boolean değişken yazar.
print (char)
character değişken yazar.
print (char[])
boyutlu chracter değişkenleriyazar.
print (double)
double yazar.
print (float)
float yazar.
print (int)
integer yazar.
print (long)
long yazar.
print (Object)
object sınıfının tanımladığı çıktıyı (object türüne göre değişebilir) yazar.
print(String)
String yazar
println ()
satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (boolean)
boolean yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (char)
character yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (char[])
boyutlu character değişkenleri yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (double)
double yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (float)
float yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (int)
Print an integer, and then finish the line.
println (long)
long yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println (Object)
object sınıfının tanımladığı çıktıyı (object türüne göre değişebilir) yazar
ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
println(String)
String yazar ve satır sonu yapar alt satıra geçer.
setError()
bir hata oluştuğunu gösterir
write (char[])
boyutlu character değişkenlerini yazar
write (char[],
int, int) boyutlu character değişkenlerini birinci integer(tamsayı) boyutundan
ikinci integer boyutuna kadar yazar.
write (int)
tek bir character yazar.
write (String)
string yazar
write(String,
int, int) string değişkenini birinci integer(tamsayı) boyutundan ikinci
integer boyutuna kadar yazar.
BufferedWriter sınıfının tanımı :
public class BufferedWriter extends Writer
{
public BufferedWriter(Writer cikti);
public BufferedWriter(Writer cikti,int boyut);
public void write(int c) throws IOException;
public void write(char c[],int başlamaindeksi,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public void write(String s, int başlamaindeksi,int uzunluk) throws
IOException;
public void newLine() throws IOException;
public void flush() throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
}
şeklindedir. Yazma verimini arttırmak için akışa ilave edilmektedir.
FileWriter sınıfı ise File sınıfı ile bağlantımızı kuran (dosyayı tanımlayan
sınıfımızdır.). Writer sınıfının altında yer alan OutputStreamWriter Sınıfının
alt sınıfıdır. tanımı :
public class FileWriter extends OutputStreamWriter
{
public FileWriter(String fileName) throws IOException;
public FileWriter(String fileName,boolean append) throws IOException;
public FileWriter(File file) throws IOException;
public FileWriter(FileDescriptor fd);
}
OutputStreamWriter sınıfının tanımı :
public class OutputStreamWriter extends Writer
{
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream o,String enc) throws UnsupportedEncodingException;
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream o);
public String getEncoding();
public void write(int c) throws IOException;
public void write(char c[],int başlamaindeksi,int uzunluk) throws IOException;
public void write(String str,int başlamaindeksi,int uzunluk) throws
IOException;
public void flush() throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
}
Bu sınıfları
kullanarak bir yazma kanaı açmak istersek :
PrintWriter cfout=new PrintWriter(new
BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("a.txt")));
cfout.println("hello");
Komutunu
kullanabiliriz. Bu komut
hello string
değişkenini a.txt dosyasına yazdırır.
Dosya veya
ekrandan okumak için ise paralel olarak BufferedReader, FileReader ve
InputStreamReader sınıflarını kullanabiliriz. BufferedReader sınıfının
tanımı :
public class
BufferedReader extends Reader
{
public
BufferedReader(Reader giriş,int boyut);
public
BufferedReader(Reader giriş);
public int
read(char c[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
public int
read() throws IOException;
public String
readLine() throws IOException;
public long
skip(long n) throws IOException;
public boolean
ready() throws IOException;
public boolean
markSupported();
public void
mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException;
public void
reset() throws IOException;
public void
close() throws IOException;
}
BufferedReader
ve FileReader sınıflarını birarada kullanarak bir okuma kanalı açabiliriz.
örneğin a.txt dosyasından okumak için :
BufferedReader
cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
deyimini
kullanabiliriz.
Bu terimleri kullanarak dosyaya yazma ve okumayla ilgili ufak bir örnek
verelim
Program
10.5 : YazOku.java programı
import java.io.*;
class YazOku
{
public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException
{
String s1="ilk deger";
String s2="ilk deger";
String s3="ilk deger";
PrintWriter cfout=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new
FileWriter("a.txt")));
cfout.println("Merhaba");
cfout.println("isminiz nedir");
cfout.println("sizinle tanistigima memnun oldum");
cfout.close();
BufferedReader cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
s1=cfin.readLine();
s2=cfin.readLine();
s3=cfin.readLine();
cfin.close();
System.out.println("s1 = "+s1);
System.out.println("s2 = "+s2);
System.out.println("s3 = "+s3);
}
}
Program çıktısı
:
s1 = Merhaba
s2 = isminiz nedir
s3 = sizinle tanistigima memnun oldum
dosya a.txt
:
Merhaba
isminiz nedir
sizinle tanistigima memnun oldum
Şeklinde olacaktır.
Programımız a.txt dosyasını oluşturup, üç string değerini yazdıktan sonra
okuma kanalı açarak bu veriyi okudu.
Benzer bir
okuma sınıfı olarak şu ana kadar kullandığımız Text sınıfını da verebiliriz.
Aslında Text sınıfının içeriğine baktığımızda yukarıda verilen sınıfların
organize bir şekilde kullanılmasından ibaret olduğunu rahatlıkla görebiliriz.
Text sınıfının listesi :
Program
10.6 Text.java programı
//============================================
// Java nümerik analiz paketi
// Class Text to read data from screen or file
// and write (by using print) to screen or file
// formatted c printf like comand structure
// Dr. Turhan Coban
//============================================
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Text
{
BufferedReader in;
/*
---------------------------------------------------
Static routines provided are:
---------------------------------------------------
public static void prompt(String s);
public static int readInt(DataInputStream in);
public static int readInt(BufferedReader in);
public static double readDouble(DataInputStream in);
public static double readDouble(BufferedReader in);
public static String readString(DataInputStream in);
public static String readString(BufferedReader in);
public static char readChar(DataInputStream in);
public static char readChar(BufferedReader in);
----------------------------------------------------
Dynamic routines provided are :
----------------------------------------------------
public void Text()
public void Text(String s1)
public void Text(File f1)
public int readInt();
public double readDouble();
public String readString();
public char readChar();
Sample use :
--------- reading a double--------------
DataInputStream cin=new DataInputStream(System.in);
double number;
number=Text.readDouble(cin);
veya
BufferedReader cin=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double number;
number=Text.readDouble(cin);
veya
double number;
Text cin=new Text();
number=cin.readDouble();
------ reading data from a file "datafile.dat"------
DataInputStream fin=new DataInputStream
(new FileInputStream("datafile.dat"));
double number;
number=Text.readDouble(fin);
veya
double number;
BufferedReader fin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("datafile.dat"));
double number;
number=Text.readDouble(fin);
veya
double number;
Text cin=new Text("dataFile.dat");
number=cin.readDouble();
------ printing data into a file "printfile.dat"----
PrintStream fout=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("printfile.dat"));
String a="turhan";
fout.println(a);
veya
BufferedWriter fout=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("datafile.dat"));
String a="Turhan");
fout.println(a);
----------------------------------------------------
*/
private
static StringTokenizer T;
private static String S;
public Text()
{
in=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public Text(String s1) throws IOException
{
in=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s1));
}
public static void prompt (String s) {
System.out.print(s
+ " ");
System.out.flush();
}
public static int readInt (DataInputStream in) throws IOException
{
if (T==null) refresh(in);
while (true)
{
try {
String item = T.nextToken();
return Integer.valueOf(item.trim()).intValue();
}
catch (NoSuchElementException e1) { refresh (in);}
catch(NumberFormatException e2)
{ //System.err.println("Error in number, try again.");
}
}
}
public int readInt() throws IOException
{
return Text.readInt(in);
}
public String readStringLine() throws IOException
{
return Text.readStringLine(in);
}
public double readDouble() throws IOException
{
return Text.readDouble(in);
}
public String readString() throws IOException
{
return Text.readString(in);
}
public char readChar() throws IOException
{
return Text.readChar(in);
}
public static int readInt (BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
if (T==null) refresh(in);
while (true)
{
try {
String item = T.nextToken();
return Integer.valueOf(item.trim()).intValue();
}
catch (NoSuchElementException e1) { refresh (in);
} catch(NumberFormatException e2)
{ //System.err.println("Error in number, try again.");
}
}
}
public static char readChar (DataInputStream in) throws IOException
{
if (T==null) refresh(in);
while (true)
{
try {
return T.nextToken().charAt(0);
}
catch(NoSuchElementException e1) {refresh (in);}
}
}
public static char readChar (BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
if (T==null) refresh(in);
while (true)
{
try {
return T.nextToken().charAt(0);
}
catch(NoSuchElementException e1) {refresh (in);}
}
}
public static double readDouble(DataInputStream in) throws IOException
{
if(T==null) refresh(in);
while (true) {
try {
String item = T.nextToken();
return Double.valueOf (item.trim()).doubleValue();
} catch(NoSuchElementException e1) {
refresh (in);
} catch(NumberFormatException e2)
{
//System.err.println("Error in number, try
again.");
}
}
}
public static double readDouble(BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
if(T==null) refresh(in);
while (true)
{
try {
String item = T.nextToken();
return Double.valueOf (item.trim()).doubleValue();
} catch(NoSuchElementException e1) {
refresh (in);
} catch(NumberFormatException e2)
{
//System.err.println("Error in number, try
again.");
}
}
}
// this method is deprecated, but still kept for historical reasons
// prefer BufferedReader version
public static String readString(DataInputStream in) throws
IOException
{
if(T==null) refresh (in);
while (true) {
try {return T.nextToken();}
catch (NoSuchElementException e1) {
refresh (in);
}
}
}
public static String readString(BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
if(T==null) refresh (in);
while (true) {
try {return T.nextToken();}
catch (NoSuchElementException e1) {
refresh (in);
}
}
}
public static String readStringLine(DataInputStream in) throws IOException
{
//reads a line of strings from DataInputStream in
int ch;
String r = "";
boolean done = false;
while (!done)
{ try
{ ch = in.read();
if (ch < 0 || (char)ch == '\n' || (char)ch == '\0')
done = true;
else
r = r + (char) ch;
}
catch(java.io.IOException e)
{ done = true;
}
}
return r.substring(0,(r.length()-1));
}
public
static String readStringLine(BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
//reads a line of strings from BufferedReader in
int ch;
String r = "";
boolean done = false;
while (!done)
{ try
{ ch = in.read();
if (ch < 0 || (char)ch == '\n' || (char)ch == '\0')
done = true;
else
r = r + (char) ch;
}
catch(java.io.IOException e)
{ done = true;
}
}
return r.substring(0,(r.length()-1));
}
private static
void refresh (DataInputStream in) throws IOException
{
String s = in.readLine();
if (s==null) throw new EOFException();
T = new StringTokenizer(s);
}
private static
void refresh (BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
String s = in.readLine();
if (s==null) throw new EOFException();
T = new StringTokenizer(s);
}
}
Text sınıfını
kullanarak sequential bilgiyi dosyadan okuyan YazOku1.java programı altta
verilmiştir.
Program
10.7 YazOku1.java programı
import java.io.*;
import Text;
class YazOku1
{
public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException
{
String s1="bos String";
String s2="bos String";
String s3="Bos String";
String s4="Bos String";
PrintWriter cfout=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new
FileWriter("a.txt")));
cfout.println("Merhaba");
cfout.println("isminiz nedir");
cfout.println("Hosgeldiniz");
cfout.close();
Text cfin=new Text("a.txt");
s1=cfin.readString();
s2=cfin.readString();
s3=cfin.readString();
s4=cfin.readString();
System.out.println("s1 = "+s1);
System.out.println("s2 = "+s2);
System.out.println("s3 = "+s3);
System.out.println("s4 = "+s4);
}
}
bu programın
çıktısı :
s1 = Merhaba
s2 = isminiz
s3 = nedir
s4 = Hosgeldiniz
şeklindedir. Burada görüldüğü gibi her kelime ayrı bir string olarak
algılanmıştır. Bu yapıyı gerçekleştiren Text sınıfı içerisinde kullanılan
StringTokenizer sınıfıdır.
String item = T.nextToken();
ifadesiyle okunmakta olan Stringi cümlelere böler.
Ardışık dosya okuma örneği olarak Atom.java, AtomTest.java, Atom.txt,
gurubunu verebiliriz. Atom.java Atomların bazı fiziksel özelliklerini tanımlayan
bir programdır. Program atomlarla ilgili veriyi Atom.txt dosyasından okumaktadır.
Program 10.8 Atom.java programı
//======================================================
// Thermodynamic Package in java
// Class Atom
// Properties of single atom
// -----------------------------------------------------
// Programmer : Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBITAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Reasearch Institute
// turhan@mam.gov.tr
// -----------------------------------------------------
// File Name : Atom.java
// This file contains the atom class
// this class sets basic properties of requested atom
// required data is read from atom.txt
// atom.txt should be copied to the same directory as your
// atom.java
file
// =====================================================
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import Text;
class Atom
{
public int number; // atomic number
public String name; // name of the the atom
public String symbol; // symbol of the atom
public double mass; // mass of the atom
public double N; // number of the atoms
BufferedReader
fina;
public Atom()
{
//empty constructor
number=0;
symbol="";
name="";
mass=0;
N=1;
}
//=================================================================
public Atom(int anumber,double NN) throws IOException
{
//this constructor will load Atom data from a given atomic number
//and number of atoms
//type
String atom_name;
String atom_symbol;
double atom_mass;
int atom_number;
try{
fina=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Atom.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File Atom.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try {
while(fina != null)
{
atom_number=Text.readInt(fina);
atom_name= Text.readString(fina);
atom_symbol= Text.readString(fina);
atom_mass=Text.readDouble(fina);
if(atom_number==anumber)
{
N=NN;
number=atom_number;
name=atom_name;
symbol=atom_symbol;
mass=atom_mass*N;
break;
}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof) {fina.close(); }
}
public Atom(String
st1,double NN) throws IOException
{
// this constructor will load Atom data from a given atom name
// or atom symbol and number of atoms
// type
String atom_name;
String atom_symbol;
double atom_mass;
int atom_number;
try{
fina=new
BufferedReader(new FileReader("Atom.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File Atom.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try {
while(fina != null)
{
atom_number=Text.readInt(fina);
atom_name= Text.readString(fina);
atom_symbol= Text.readString(fina);
atom_mass=Text.readDouble(fina);
if(st1.equals(atom_name)
|| st1.equals(atom_symbol))
{
N=NN;
number=atom_number;
name=atom_name;
symbol=atom_symbol;
mass=atom_mass*N;
break;
}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof) {fina.close(); }
}
public Atom(String
st1) throws IOException
{
// this constructor will load Atom data from a given atom name
// or atom symbol and number of atoms
// type
double NN=1;
String atom_name;
String atom_symbol;
double atom_mass;
int atom_number;
try{
fina=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Atom.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File Atom.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try {
while(fina != null)
{
atom_number=Text.readInt(fina);
atom_name= Text.readString(fina);
atom_symbol= Text.readString(fina);
atom_mass=Text.readDouble(fina);
if(st1.equals(atom_name) || st1.equals(atom_symbol))
{
N=NN;
number=atom_number;
name=atom_name;
symbol=atom_symbol;
mass=atom_mass*N;
break;
}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof) {fina.close(); }
}
public Atom(Atom
a)
{
number=a.number;
name=a.name;
symbol=a.symbol;
mass=a.mass;
N=a.N;
}
public Atom(Atom
a, double NN)
{
number=a.number;
name=a.name;
symbol=a.symbol;
mass=a.mass;
N=NN;
}
//=================================================================
public void assign(Atom a)
{
number=a.number;
name=a.name;
symbol=a.symbol;
mass=a.mass;
N=a.N;
}
//=================================================================
//boolean equals logical comparisons
public boolean equals(String s)
{
boolean b;
if(name.equals(s) || symbol.equals(s))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean
equals(int n)
{
boolean b;
if(number==n)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//=================================================================
public String toString()
{
String st=symbol;
if(N != 1.0)
if(N==Math.floor(N)) st = st + (int)N;
else st = st + N;
return st;
}
}
//=================================================================
Program 10.9 AtomTest.java programı
//======================================================
// Thermodynamic Package in java
// Class Atom Test//Properties of single atom
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// File Name : AtomTest.java
// This file contains the atom class
// this class sets basic properties of requested atom
// required data is read from atom.dat.
// =====================================================
import java.io.*;
class AtomTest
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Atom n2=new Atom("N",2);
System.out.println(n2.toString());
int n=8;
Atom o2=new Atom("O",n);
System.out.println(o2.toString());
}
}
//=================================================================
Atom.txt girdi dosyası
Program AtomText.java
çıktısı :
N2
O8
Burada hemen
şunu kaydedelim. Programdan da anlaşılacağı gibi Atom.java javayı öğretme
amacıyla hazırlanmamıştır. Gazların termodinamik özelliklerini hesaplayan
bir program gurubunun parçası olarak hazırlanmıştır.
Raslantısal
Ulaşım Dosyasının (Random Access File) Ardışık Dosya sisteminden temel farkı,
Teyp kaydıyla CD kaydı arasındaki fark gibidir. Ardışık dosyalar Teyp kaydı
şeklinde birbiri ardı sıra gelen bilgilerden oluşur. Raslantısal Ulaşım
sisteminde ise CD gibi herhangi bir kayıta kayıt numarası kullanılarak doğrudan
ulaşmak mümkündür. Raslantısal Ulaşım dosyası işlemleri RandomAccessFile
sınıfı üzerinden yapılır. Bu sınıfın tanımı :
public class
RandomAccessFile extends Object implements DataOutput, DataInput
{
public
RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode) throws IOException
public
RandomAccessFile(File file,String mode) throws IOException
public final
FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException
public int
read() throws IOException
public int
read(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException
public int
read(byte b[]) throws IOException
public final
void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException
public final
void readFully(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException
public int
skipBytes(int n) throws IOException
public void
write(int b) throws IOException
public void
write(byte b[]) throws IOException
public void
write(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
public long
getFilePointer() throws IOException;
public void
seek(long pos) throws IOException;
public void
seek(long pos) throws IOException;
public long
length() throws IOException;
public void
close() throws IOException;
public final
byte readByte() throws IOException;
public final
int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException;
public final
short readShort() throws IOException;
public final
int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException;
public final
char readChar() throws IOException;
public final
int readInt() throws IOException;
public final
long readLong() throws IOException;
public final
float readFloat() throws IOException;
public final
double readDouble() throws IOException;
public final
String readLine() throws IOException;
public final
String readUTF() throws IOException;
public final
void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeByte(int v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeShort(int v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeChar(int v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeInt(int v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeLong(long v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException;
public final
void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException;
public final
void writeChars(String s) throws IOException;
public final
void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException;
}
Burada tanımlanan
metodların görevlerine kısaca bir bakacak olursak :
getFD()
: dosya (File) tanımını verir
getFilePointer() : Dosyanın (File) o anda hangi dosya referansını
gösterdiğini belirtir.
length() : Dosyadaki toplam referans sayısını verir.
read() : Byte (char değişkeni karşılığı) olarak dosyadan bilgiyi
okur (bir byte).
read(byte[]) : Byte (char değişkeni karşılığı) olarak dosyadan
bilgiyi okur (byte[] değişkeninin boyu kadar) ve byte degişkenine aktarır.
read(byte[], int baslangıç_indisi, int indis_boyutu) : Byte (char
değişkeni karşılığı) olarak dosyadan bilgiyi okur (byte[] değişkeninin boyu
kadar, başlangıç indisinden başlayarak, indis_boyutu uzunluğunda) ve byte
degişkenine aktarır.
readBoolean() : boolean değişken okur
readByte() : dosyadan integer tipi byte değişken (işaretli 8-bit
) okur.
readChar() : Dosyadan Unicode karekter (character) okur.
readDouble() : Dosyadan double değişkeni okur.
readFloat() : Dosyadan float değişkeni okur.
readFully(byte[] b) : dosyadan byte olarak okur
readFully(byte[] b, int baslangıç_indisi, int toplam_boy) : dosyadan
bte olarak sadece byte boyutlu değişkeninin başlangıc_indisinden başlamak
üzere taplam_boy kadar kısmını okur.
readInt() : Dosyadan int değişkeni okur.
readLine() : Dosyadan \n = yeni satır işaretini veya \r satırbaşı
işaretini veya herikisini birden arka arkaya görene kadar yazılan her şeyi
bütün bir satır olarak okur.
readLong(): Dosyadan Long (Long integer) değişkeni okur.
readShort(): Dosyadan Short (Short integer) değişkeni okur.
readUnsignedByte(): İşaretsiz Byte değeri okur.
readUnsignedShort(): İşaretsiz 16 bitlik Short integer değeri okur.
readUTF()
: UTF stringi okur
seek(long) : indisi herhangi bir bilgi gurubu indisine ayarlar.
skipBytes(int n) : n bit input değerini okumadan atlar
Aşağıdaki tanımlar
read tanımlarına parelel olan write terimleridir.
write(byte[])
: byte boyutlu değişkenini
yazar.
write(byte[],int baslangıç_indisi, int toplam_boy) : dosyaya byte
olarak sadece byte boyutlu değişkeninin başlangıc_indisinden başlamak üzere
taplam_boy kadar kısmını yazar.
write(int) : dosyaya byte boyutlu değişkenini yazar
writeBoolean(boolean) : dosyaya boolean boyutlu değişkenini yazar
writeByte(int) : dosyaya int girdisini byte olarak yazar
writeBytes(String) : dosyaya String girdisini byte boyutlu değişkeni
olarak yazar
writeChar(int) : dosyaya int girdisini Char olarak yazar
writeChars(String) : dosyaya string girdisini char boyutlu değişkeni
olarak yazar
writeDouble(double) : dosyaya double girdisini double olarak yazar.
writeFloat(float) : dosyaya float girdisini float olarak yazar
writeInt(int) : dosyaya int girdisini int olarak yazar.
writeLong(long)
: dosyaya long(integer) girdisini long(integer) olarak yazar
writeShort(int) : dosyaya integer gidisini short(integer) olarak
yazar.
writeUTF(String) : dosyaya String girdisini UTF string olarak yazar.
RandomAccessFile
sınıfının tanımından da görüldüğü gibi b sınıf DataOutput ve DataInput
sınıflarını implement eder. DataOutput ve DataInput sınıflarınını tanımı
:
public interface
DataOutput
{
public abstract
void write(int b) throws IOException
public abstract
void write(byte b[]) throws IOException
public abstract
void write(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeByte(int v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeShort(int v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeChar(int v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeInt(int v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeLong(long v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeChars(String s) throws IOException
public abstract
void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException
}
public interface
DataInput
{
public abstract
void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException
public abstract
void readFully(byte b[],int off,int len) throws IOException
public abstract
int skipBytes(int n) throws IOException
public abstract
boolean readBoolean() throws IOException
public abstract
byte readByte() throws IOException
public abstract
int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException
public abstract
short readShort() throws IOException
public abstract
int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException
public abstract
int readInt() throws IOException
public abstract
long readLong() throws IOException
public abstract
float readFloat() throws IOException
public abstract
double readDouble() throws IOException
public abstract
String readLine() throws IOException
public abstract
String readUTF() throws IOException
}
RandomAccessFile
Çok daha çabuk ulaşım olanakları yaratır. Raslantısal Ulaşım dosyası örneği
olarak aşağıdaki paketi veriyoruz. Kayit sınıfı tek bir kayıtın yazılıp
okunabilmesi için gerekli olan bilgileri içeriyor. Kayıtların hesap numarası,
isim, soyisim ve hesaptaki paradan oluştuğunu kabul ediyoruz. Bütün bu kayıtları
bir arada yapmak için oku ve yaz metotları bu sınıfın içindr tanımlanmıştır.
Raslantısal ulaşım kanalının dosyaya açılması için :
try{
girdi=new RandomAccessFile("musteri1.dat","rw");
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya acma hatasi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
yapısı kullanbilir.
Buradaki rw yapısı dosyaya hem yazı yazılıp hem okunabileceğini belirtir.
r sadece okumak için w sadece yazmak için kullanılır.
RandomAccessFile
içinde yer alan
close()
metodu RandomAccessFile (Raslantısal Ulaşım Dosyası) kanalını ve ilgili
tüm sınıfları kapatır. örnek olarak :
private
void closeFile()
{
try{
girdi.close();
System.exit(0);
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error closing filr\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
metotu verilebilir.
Şimdi de örnek
programın listelerini verelim:
Program
10.10 Kayit.java raslantısal ulaşım dosyası kayıt programı
import java.io.*;
public class Kayit
{
private int hesap;
private String soyIsim;
private String Isim;
private double hesaptakiPara;
public void
oku(RandomAccessFile dosya) throws IOException
{
//RandomAccessFile = Raslantisal Ulasim dosyasi
hesap=dosya.readInt();
char first[]=new char[15];
for(int i=0;i<first.length;i++)
{ first[i]=dosya.readChar(); }
Isim=new String(first);
char last[]=new char[15];
for(int i=0;i<first.length;i++)
{ last[i]=dosya.readChar(); }
soyIsim=new String(last);
hesaptakiPara=dosya.readDouble();
}
public void
yaz(RandomAccessFile dosya) throws IOException
{
StringBuffer buf;
dosya.writeInt(hesap);
if(Isim!=null)
buf=new StringBuffer(Isim);
else
buf=new StringBuffer(15);
buf.setLength(15);
dosya.writeChars(buf.toString());
if(soyIsim!=null)
buf=new StringBuffer(soyIsim);
else
buf=new StringBuffer(15);
buf.setLength(15);
dosya.writeChars(buf.toString());
dosya.writeDouble(hesaptakiPara);
}
public void yazhesap(int a) {hesap = a;}
public int okuhesap() {return hesap;}
public void yazIsim(String f){Isim=f;}
public String okuIsim() {return Isim;}
public void yazsoyIsim(String f){soyIsim=f;}
public String okusoyIsim() {return soyIsim;}
public void yazhesaptakiPara(double b) {hesaptakiPara=b;}
public double okuhesaptakiPara() {return hesaptakiPara;}
public static int boyut() {return 72;}
}
Program
10.11 RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYarat
.java programı
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import Kayit;
public class RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYarat
{
private Kayit hesapDosyasi;
private RandomAccessFile girdi;
public RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYarat()
{
hesapDosyasi = new Kayit();
try{
girdi = new RandomAccessFile("musteri1.dat","rw");
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
{ hesapDosyasi.yaz(girdi); }
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya acma hatasi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYarat H=
new RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYarat();
}
}
Program
10.12 RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYaz
.java programı
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import Kayit;
public class
RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYaz extends Frame implements ActionListener
{
private TextField hesapAlani,isimAlani,soyisimAlani,hesaptakiParaAlani;
private Button birsonraki,kapat;
private RandomAccessFile girdi;
private Kayit hesapDosyasi;
public RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYaz()
{
super("Tesadufi ulasim dosyasina yaz");
hesapDosyasi=new Kayit();
try{
girdi=new RandomAccessFile("musteri1.dat","rw");
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Dosya acma hatasi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
setSize(300,150);
setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
add(new Label("Hesap numarasi:"));
hesapAlani=new TextField();
add(hesapAlani);
add(new Label("isim : "));
isimAlani=new TextField(20);
add(isimAlani);
add(new Label("Soyisim : "));
soyisimAlani=new
TextField(20);
add(soyisimAlani);
add(new Label("Hesaptaki para : "));
hesaptakiParaAlani=new TextField(20);
add(hesaptakiParaAlani);
birsonraki=new Button("Gir");
birsonraki.addActionListener(this);
add(birsonraki);
kapat=new Button("cikis");
kapat.addActionListener(this);
add(kapat);
setVisible(true);
}
public void
addKayit()
{
int accountNumber=0;
Double d;
if(!hesapAlani.getText().equals(""))
{
try{
accountNumber=Integer.parseInt(hesapAlani.getText());
if(accountNumber0 && accountNumber <=100)
{
hesapDosyasi.yazhesap(accountNumber);
hesapDosyasi.yazIsim(isimAlani.getText());
hesapDosyasi.yazsoyIsim(soyisimAlani.getText());
d=new Double(hesaptakiParaAlani.getText());
hesapDosyasi.yazhesaptakiPara(d.doubleValue());
girdi.seek((long)(accountNumber-1)*Kayit.boyut());
hesapDosyasi.yaz(girdi);
}
hesapAlani.setText("");
isimAlani.setText("");
soyisimAlani.setText("");
hesaptakiParaAlani.setText("");
}
catch(NumberFormatException
nfe)
{
System.err.println("Hesap numarasi tamsayi degisken olamalidir");
}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosyaya yazarken hata olustu\n"+io.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
addKayit();
if(e.getSource()==kapat)
{
try{ girdi.close();}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosya kapatilamadi\n"+io.toString());
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static
void main(String args[])
{
new RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiYaz();
}
}
Program
10.13 RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiOku
.java programı
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import Kayit;
public class
RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiOku extends Frame implements ActionListener
{
private TextField hesapAlani,isimAlani,soyisimAlani,hesaptakiParaAlani;
private Button birsonraki,kapat;
private RandomAccessFile girdi;
private Kayit hesapDosyasi;
public RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiOku()
{
super("Musteri dosyasini oku");
try{
girdi=new RandomAccessFile("musteri1.dat","r");
} catch(IOException e)
{ System.err.println("Dosya acilamadi\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
hesapDosyasi=new Kayit();
setSize(300,150);
setLayout(new GridLayout(5,2));
add(new Label("Hesap numarasi :"));
hesapAlani=new
TextField();
add(hesapAlani);
add(new Label("isim : "));
isimAlani=new TextField(20);
add(isimAlani);
add(new Label("soyisim : "));
soyisimAlani=new TextField(20);
add(soyisimAlani);
add(new Label("Hesaptaki para : "));
hesaptakiParaAlani=new TextField(20);
add(hesaptakiParaAlani);
birsonraki=new Button("bir sonraki hesap");
birsonraki.addActionListener(this);
add(birsonraki);
kapat=new Button("cikis");
kapat.addActionListener(this);
add(kapat);
setVisible(true);
}
public void
okuKayit()
{
int hesap;
String ilk,son;
double balance;
{
try{
do{
hesapDosyasi.oku(girdi);
} while(hesapDosyasi.okuhesap()==0);
hesapAlani.setText(String.valueOf(hesapDosyasi.okuhesap()));
isimAlani.setText(String.valueOf(hesapDosyasi.okuIsim()));
soyisimAlani.setText(String.valueOf(hesapDosyasi.okusoyIsim()));
hesaptakiParaAlani.setText(String.valueOf(hesapDosyasi.okuhesaptakiPara()));
}
catch(EOFException eof)
{
closeFile();
}
catch(IOException io)
{
System.err.println("Dosyayı okurken hata olustu\n"+io.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if(e.getSource()==birsonraki)
okuKayit();
else
closeFile();
}
private void closeFile()
{
try{
girdi.close();
System.exit(0);
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error closing filr\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
new RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiOku();
}
}
10003.JPG

Şekil 10.3
RaslantisalUlasimDosyasiOku.java Frame çıktısı
Yukardaki programın ilginç bir yönü de Frame sınıfını kullanmış
olmasıdır. Frame ve swing eşiti JFrame konsol ortamında kullanılabilen
grafik ortamı programlamasıdır. Temel olarak applet yapılarında kullanılan
heryerde Frame de kullanılabilir. Frame main programdan başlatılır.
Html dosyasından başlatılmaz.
java.util.zip
paketi veri sıkıştırmaya yarayan dosyalarıiçerir. Günümüz bilgisayar kullanımında
GZIP ve ZIP adı verilen bu yapılar ZLIB sıkıştırma algoritmasında tanımlanmıştır.
Bu algoritm RFC 1950,RFC 1951 ve RFC 1952 dökümanlarında tanımlanmıştır.
Bu dökümanlara
http://www.faqs.org/rfcs
adresinden ulaşılabilir. Kullanma
açısından bu dökümanlara ihtiyacınız yoktur. Gerekli programlar java zip
paketinde bulunmaktadır.
GZIP tek bir
dosyayı sıkıştırarak isim.gz ismiyle sıkıştırılmış dosya oluşturur. Bunun
için GZIPOutputStream dosyasına bir FileOutptStream açmamız kafidir. Program
10.4 den de görüleceği gibi
GZIPOutputStream zipout;
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(zipname);
zipout = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya oluşturma hatası : " + zipname
+ ".");
return;
}
deyimi dosyanın gzip olarak yazılması için gerekli kanalı oluşturur.
Program
10.14 Gzip.java
dosya sıkıştırma programı
//dosya: GZip.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.*;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class GZip {
public static int sChunk = 8192;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 1) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"KULLANIM: java GZip girisdosyasi");
return;
}
// çıktı doyası oluştur.
String zipname = args[0] + ".gz";
GZIPOutputStream zipout;
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(zipname);
zipout = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya oluşturma hatası : " + zipname
+ ".");
return;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[sChunk];
// dosyayı sıkıştır
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
int length;
while ((length = in.read(buffer, 0, sChunk)) != -1)
zipout.write(buffer, 0, length);
in.close( );
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya sıkıştırma hatası : " + args[0]
+ ".");
}
try { zipout.close( ); }
catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
GZIP işleminin tersini yapmak içinse parelel olarak :
GZIPInputStream zipin;
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(zipname);
zipin = new GZIPInputStream(in);
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya açma hatası : " + zipname
+ ".");
return;
}
yapısı kullanılır.
Programların çalışması için java isim deyiminden sonra dostya ismini
vermek kafidir.
C:\co\java\prog>java Gzip a.dat
veya
C:\co\java\prog >java Gunzip a.dat.gz
gibi.
Program
10.15 GUnzip.java
dosya sıkıştırılmış dosyayı açma programı
//dosya : GUnzip.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.*;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class GUnzip {
public static int sChunk = 8192;
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 1) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"KULLANIM: java GUnzip girisdosyasi");
return;
}
// girdi dosyasını incele
String zipname, source;
if (args[0].endsWith(".gz")) {
zipname = args[0];
source = args[0].substring(0, args[0].length( ) - 3);
}
else {
zipname = args[0] + ".gz";
source = args[0];
}
GZIPInputStream zipin;
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(zipname);
zipin = new GZIPInputStream(in);
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya açma hatası : " + zipname
+ ".");
return;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[sChunk];
// dosyayı aç (decompress)
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(source);
int length;
while ((length = zipin.read(buffer, 0, sChunk)) != -1)
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
out.close( );
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Dosya sıkıştırılması açılma hatası
: " + args[0] + ".");
}
try { zipin.close( ); }
catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
ZIP ve UNZIP
biraz daha kompleks bir yapıya sahiptir. Çünki bu proseste direktory içindeki
dosyaların açılma işlemi söz konusudur.
Prosesi izah
etmek için önce ZIP işlemi yapan bir programa göz atalım :
Program
10.16 zip.java dosya
sıkıştırma programı
// dosya : zip.java
// Turhan Çoban 24.2.2001
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.zip.*;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class zip {
public static int sChunk = 8192;
public static String[] dosyalistesi(String p)
{
File path=new File(p);
if(path.isDirectory())
{
Vector x=new Vector();
File files[];
files=path.listFiles();
int n=files.length;
int n1=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(!files[i].isDirectory())
{
x.addElement(files[i].toString());
n1++;
}
}
String s1[];
s1=new String[n1];
Enumeration nn=x.elements();
int k=0;
while(nn.hasMoreElements())
{
s1[k++]=(String)nn.nextElement();
}
return s1;
}
else
{
String[] s1 = new String[1];
s1[0]=p;
return s1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="";
FileOutputStream out;
ZipOutputStream zout;
String zipname, source;
String s="KULLANIM: \n"+
"java zip zipdosyası dosya(veyadirectory)ismi1 dosya(veyadirectory)ismi1...\n"+
" zip dosyası yarat ve dosya(veya directorylerdeki dosyaları) sıkıştır
"+
" alt direktoryler atlanmaktadır tekrar tanımla";
// anahtarı kontrol et
if(args.length<1 )
{
String s1="zipdosyası isim.zip tanımlanmadı lütfen argümanları giriniz\n"+s;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,s1);
System.exit(0);
return;
} // girdi dosyasını incele
else if(args.length<2)
{
String s1="sıkıştırılacak dosya(veya direktory) isimleri tanımlanmadı\n"+
" lütfen argümanları giriniz\n"+s;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,s1);
System.exit(0);
return;
}
if (args[0].endsWith(".zip")) {
zipname = args[0];
source = args[0].substring(0, args[0].length( ) - 3);
}
else {
zipname = args[0] + ".zip";
source = args[0];
}
//zip kanalını tanımla
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(zipname);
zout=new ZipOutputStream(out);
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"Dosya oluşturma hatası : " +
zipname + ".");
return;
}
int k=1;
while(k<args.length)
{
try
{
String ss[];
ss=dosyalistesi(args[k]);
int j=0;
byte[] buffer=new byte[sChunk];
while(j<ss.length)
{
ZipEntry giris=new ZipEntry(ss[j]);
zout.putNextEntry(giris);
try {
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(ss[j]);
int length;
while((length=in.read(buffer,0,sChunk))!=-1)
zout.write(buffer,0,length);
in.close();
} //try sonu
catch (IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"Dosya sıkıştırma hatası
: " +ss[j] );
} //catch sonu }
str+="ss["+j+"] = "+ss[j]+" "+giris+" iceri girdi\n";
j++;
}//while sonu
} //try sonu
catch(IOException io) {}
k++;
} //while(k< sonu
try{
zout.close();
out.close();
}
catch(IOException e){}
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,str);
System.exit(0);
}
}
örnek program
girdisi :
java zip
zip1.zip c:\co\java\prog\a d.dat c:\co\java\prog\a\b
10004.JPG
Şekil 10.3 zip.java programını çıktısı
şimdi de ZIP
yapılmış bir dosyayı açan Unzip.java programına bir göz atalım :
Program
10.16 Unzip.java
dosya sıkıştırılmış dosyayı açma programı
//dosya : Unzip.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.zip.*;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Unzip {
public static int sChunk = 8192;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String zipname, source;
String s="";
if (args.length != 1) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"KULLANIM: java Unzip girisdosyasi");
System.exit(0);
return;
}
// girdi dosyasını incele
if (args[0].endsWith(".zip")) {
zipname = args[0];
source = args[0].substring(0, args[0].length( ) - 3);
}
else {
zipname = args[0] + ".zip";
source = args[0];
}
s+="zip dosyası : "+zipname+" içideki sıkıştırılmış \n";
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(zipname);
ZipInputStream zin=new ZipInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[sChunk];
// dosyayı aç (decompress
try{
ZipEntry z;
do
{
z=zin.getNextEntry();
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(z.getName());
int length;
while ((length = zin.read(buffer, 0, sChunk)) != -1)
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
out.close( );
}
catch (IOException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,
"Dosya sıkıştırma hatası : " + args[0] + ".");
System.exit(0);
}
s+=" "+z.getName()+" \n";
}while(z!=null);
} catch(NullPointerException npe)
{ s+="dosyaları açıldı";JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,s);
System.exit(0);
}
try { zin.close(); } catch (IOException e) {}
}
catch(IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"Dosya açılma hatası :
" + zipname);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
programı
java unzip zip1.zip
komutu kullanarak çalıştırırsak :
10005.JPG
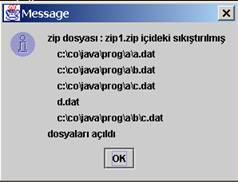
Şekil 10.4 unzip.java programını çıktısı
Çıktısını elde ederiz.
Burada zip dosyasına ulaşmak için :
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(zipname);
ZipInputStream zin=new ZipInputStream(in);
Deyimini kullandık. Zipli dosyayı okumak için ise :
ZipEntry z;
do
{
z=zin.getNextEntry();
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(z.getName());
int length;
while ((length = zin.read(buffer, 0, sChunk)) != -1)
out.write(buffer, 0, length);
out.close( );
}
gurubunu kullandık. Burada temel olarak iki yeni sınıf kullanıldı. Bunlardan
birincisi ZipInputStream, diğeri ise ZipEntry sınıfları idi. Şimdi bu iki
sınıfın tanımlarına göz atalım :
public class
ZipInputStream
extends InflaterInputStream implements ZipConstants {
private
ZipEntry entry;
private
CRC32 crc;
private
long remaining;
private
byte[] tmpbuf ;
private
static final int STORED;
private
static final int DEFLATED;
private
boolean closed ;
private
boolean entryEOF;
private
void ensureOpen() throws IOException;
public
ZipInputStream(InputStream in) ;
public
ZipEntry getNextEntry() throws IOException;
public
void closeEntry() throws IOException;
public
int available() throws IOException ;
public
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
public
long skip(long n) throws IOException ;
public
void close() throws IOException;
private
ZipEntry readLOC() throws IOException;
private
static String getUTF8String(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
protected
ZipEntry createZipEntry(String name) throws IOException;
private
void readEnd(ZipEntry e) throws IOException;
private
void readFully(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException;
private
static final int get16(byte b[], int off);
private
static final long get32(byte b[], int off);
}
ZipOutputStreamin
tanımı ise :
public class
ZipOutputStream
extends DeflaterOutputStream implements ZipConstants {
private
ZipEntry entry;
private
Vector entries;
private
Hashtable names ;
private
CRC32 crc;
private
long written;
private
long locoff ;
private
String comment;
private
int method ;
private
boolean finished;
private
boolean closed = false;
private
void ensureOpen() throws IOException
public
static final int STORED ;
public
static final int DEFLATED;
public
ZipOutputStream(OutputStream out)
public
void setComment(String comment)
public
void setMethod(int method
public
void setLevel(int level)
public
void putNextEntry(ZipEntry e) throws IOException
public
void closeEntry() throws IOException
public
void close() throws
private
void writeLOC(ZipEntry e) throws IOException
private
void writeEXT(ZipEntry e) throws IOException
private
void writeCEN(ZipEntry e) throws IOException
private
void writeEND(long off, long len) throws IOException
private
void writeShort(int v) throws IOException
private
void writeInt(long v) throws IOException
private
void writeBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException
private
static byte[] getUTF8Bytes(String s)
}
şeklindedir.
Ayrıca zip dosyasının içindeki elemanlar ZipEntry sınıfında tanımlanmaktadır.
ZipEntry sınıfı :
public class
ZipEntry implements ZipConstants, Cloneable
{
String
name;
long
time;
long
crc ;
long
size;
long
csize;
int method;
byte[]
extra;
String
comment;
int flag;
int version;
long offset;
public
static final int STORED ;
public
static final int DEFLATED;
private
static native void initIDs();
public
ZipEntry(String name)
public
ZipEntry(ZipEntry e
ZipEntry(String
name, long jzentry
ZipEntry(long
jzentry)
public
String getName()
public
void setTime(long time)
public
long getTime()
public
void setSize(long size)
public
long getSize()
public
long getCompressedSize()
public
void setCompressedSize(long csize)
public
void setCrc(long crc)
public
long getCrc()
public
void setMethod(int method)
public
int getMethod()
public
void setExtra(byte[] extra)
public
byte[] getExtra()
public
void setComment(String comment)
public
String getComment()
public
boolean isDirectory()
public
String toString()
private
static long dosToJavaTime(long dtime)
private
static long javaToDosTime(long time)
public
int hashCode()
public
Object clone()
}
şeklinde
tanımlanmıştır. Burada şu ana kadar verdiğimiz sınıf tanımları ile ilgili
şunu söyliyelim. Tanımlamalar sadece sınıf ve değişken adlarını vermektedir,
gerçek programı açtığınızda göreceğiniz koda benzemezler sadece metod isimlerini
taşırlar.
1. H9O1.java
programını inceleyiniz.
Bu programda sayılar dosyadan okunup ortalamaları hesaplanmaktadır.
Program
10.14 H9O1.java
programı
import java.io.*;
import Text;
// (c) Ali SAYGIVAR
public class H9O1
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
DataInputStream input;
int[] i= new int[100];
String s1;
Text cin= new Text();
System.out.print("Lutfen dosya ismini giriniz: ");
s1 = cin.readString();
File myfile = new File(s1);
BufferedReader b= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(myfile));
int toplam=0;
boolean EOF=false;
int j=0;
while (!EOF)
{
try
{
i[j]= Text.readInt(b);
toplam+=i[j];
++j;
}
catch (EOFException e)
{
b.close();
EOF=true;
}
} //while
System.out.println("Dosyanin icindeki sayilarin adedi: "+j);
System.out.println("Ortalama: "+(double)toplam/20);
} //main
} //class
2. Karsilastir.java
verilen iki sosyayı
karşılaştırmaktadır. Dosya isimleri program kullanımı sırasında verilecektir.
Örnek :
java Karsilastir
a.dat a1.dat
Program
10.15 Karsilastir.
java programı
import java.io.*;
public class Karsilastir {
//
// RandomAccessFile örneği
// program main()
//
// dışarıdan iki tane dosya ismi giriniz
// dosyaları açar ve içindekileri yükler
// dosyaları değerlendirir (karşılaştırır)
// dosyaları kapatır
//
public static void main (String args[]) {
RandomAccessFile fh1 = null;
RandomAccessFile fh2 = null;
int bufsize; // en küçük dosyanın byutu
long filesize1 = -1;
long filesize2 = -1;
byte buffer1[];
byte buffer2[];
// dışarıdan okunan veriyi kontrol et
if (args.length == 0 || args[0].equals("?") ) {
System.err.println ("Random Acsess dosya Karşilaştirma : ");
System.err.println ("-----");
System.err.println ("KULLANIM : java Karsilastir <dosya1>
<dosya2> | ?");
System.err.println ();
System.exit(0);
}
// birinci dosyayı okumak için aç
try {
fh1 = new RandomAccessFile(args[0], "r");
filesize1 = fh1.length();
} catch (IOException ioErr) {
System.err.println ("Dosya bulunamadi : " + args[0]);
System.err.println (ioErr);
System.exit(100);
}
// ikinci dosyayı okumak için aç
try {
fh2 = new RandomAccessFile (args[1], "r");
filesize2 = fh2.length();
} catch (IOException ioErr) {
System.err.println ("Dosya bulunamadi :" + args[1]);
System.err.println (ioErr);
System.exit(100);
}
if (filesize1 != filesize2) {
System.out.println ("Dosya boyutlari ayni degil! ");
System.out.println ("Dosya 1 : " + args[0] + "boyutu " + filesize1
+ " bytes");
System.out.println ("Dosya 2 : " + args[1] + "boyutu " + filesize2
+ " bytes");
}
// iki dosyanında içeriğini alabilecek bir yer ayır
bufsize = (int) Math.min(filesize1, filesize2);
buffer1 = new byte [bufsize];
buffer2 = new byte [bufsize];
// dosyaları toptan oku
try {
fh1.readFully (buffer1, 0, bufsize);
fh2.readFully (buffer2, 0, bufsize);
// şimdi gelelim asıl işimize...
for (int i = 0; i < bufsize; i++) {
if (buffer1[i] != buffer2[i]) {
System.out.println ("dosyalar index " + i+"de degisiyor");
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException ioErr) {
System.err.println ("HATA: dosyaları icelerken bir hata oluştu");
System.err.println (ioErr.toString());
} finally {
try {
fh1.close();
fh2.close();
} catch (IOException ignored) {}
}
}
}
3. File
sınıfı uygulaması :
dir.java programı istenilen directory ve alt dirctory dosyalarını sırayla
listeler.
Program
10.16 dir.java
programı
//------------------------------------
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class dir {
static int indentLevel = -1;
dir (String path) {
listPath (new File (path));
}
void listPath (File path) {
File files[]; // directory'dekidosyaların listesi
indentLevel++; // sayılıyor...
// bu directory'deki dosyaların listesini hazırla
files = path.listFiles();
// Dosya isimlerini sıraya sok
Arrays.sort (files);
for (int i=0, n=files.length; i < n; i++) {
for (int indent=0; indent < indentLevel; indent++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println(files[i].toString());
if (files[i].isDirectory()) {
listPath(files[i]);
}
}
indentLevel--;
}
public static void main (String args[]) {
new dir(args[0]);
}
}
java dir
c:\Driver\hpscanner\disk1
komutu sonucu :
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\!hwp2002.cfg
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\!hwp2080.cfg
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\@621f.adf
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\@631f.adf
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\_inst32i.ex_
C:\Drive\hpscanner\disk1\_isdel.exe
4. zip.java sınıfı içerisindeki
public static String[] dosyalistesi(String p) metodu alt direktoryleri
okumadan atlamaktadır. Alt direktoryleri de okuyup zipleyecek yeni bir zip1.java
programı yazınız.
5.
Bu problemde gerçek bir bilgisayar programlama örneğine göz atacağız.
Program 10.8 de Atom.java programına bakmıştık, bu problemde Atom.java
programı kullanılarak yazılmış olan Gas.java programına yer vereceğiz. Bu
program ideal gazların termodinamik özelliklerin hesaplamak amacıyla yazılmıştır.
Program ideal gazların verilerini Gas.txt dosyasından akumaktadır. Gaz isimleri
kurucu metod tarafından aranan gaz isimlerine uyum sağladığında program
geriye kalan veriyi okumaktadır. Gazlar atomlardan yapıldığından veride
okunan Atom isimlerine göre Atom özellikleri de bu sınıfın kurucu metodunda
Atom.txt dosyasından okunmakta ve değerlendirilmektedir. Program çıktısı
almak için GasPropertySWF.java programı da ayrıca verilmiştir. Burada verilen
kod özellikle bu kitap için yazılmamıştır. Uluslararası projelerde kullanıldığından
açıklamaları ingilizcedir.
Program 10.16 Gas
.java programı
//======================================================
// Thermodynamic Package in java
// Class Gas Properties of perfect gases
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : turhan@mam.gov.tr
// File Name : Gas.java
// This file contains the Gas class
// this class sets basic properties of perfect gases
// required data is read from Gas.txt
// =====================================================
// Description : This file contains the gas class
// class gas calculates thermophysical properties of
// perfect gasses
// following properties can be calculated
// T() : Temperature degree K
// h(T) : enthalpy KJ/kmol
// hf : formation enthalpy KJ/kg
// ht(T) : total enthalpy KJ/kg (h+hf)
// M : molar mass kg/kmol
// HT(T) : total enthalpy KJ : M*ht(T)
// P() : presuure bar
// s(T,P) : entropy KJ/kmol K
// Cp(T) : specific heat at constant pressure KJ/kmol
K
// Cv(T) : specific heat at constant volume KJ/kg K
// gamma(T): adiabatic constant Cp/Cv
// u(T) : Internal energy KJ/kmol
// c(T) : speed of sound m/s
// vis(T) : viscosity Ns/m^2
// k(T) : thermal conductivity KJ/kg K
// DATA FILE DEFINATION
// gas datas are written in the data file "Gas.txt"
// if gas data is not given in the data file, it can be curve fitted
// and added to the data file. Additional curve fitting programs supplied
// in Numerical Analysis package. Each data has the following form :
//------------------
// gasName
// n_equation M h0 hf sf
// xa[0] xb[0] xc[0] xd[0] tl[0] th[0]
// .........
// xa[n_equation-1] xb[n_equation-1]......th[n_equation-1]
// n_vis
// xvis[0]
// .........
// xvis[n_vis-1]
// n_k
// xk[0]
// .........
// xk[n_k-1]
//-------------------
// unit of the xa : kcal/kmol
// note : if any curvefitting applied for a new gas temperature values
// in K nad enthalpy values in the unit of Kcal.kmol should be supply
// for the Cp curve fitting
//============================================================
// VARIABLE IDENTIFICATION
// all the variables that type is not defined is a double variable
// PROTECTED VARIABLES :
// xa,xb,xc,xd ,tl,th : double pointers. This values used to calculate
// specific heat at constant pressure from the following equation :
// Cp(T) = xa[i]+xb[i]*1e-3*T+xc[i]*1.0e5/T^2+xd[i]*1e-6*T^3
// where tl[i] <= T <= th[i]
// n_equation : number of equations (xa,xb,xc,xd,tl,th) for a gas
// xvis : real pointers to define viscosity according to formula :
// vis(T)=sum(xvis(i)*T^i) , for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
// n_vis : number of coefficients in polynomial viscosity curve fitting
// xk :real pointers to define thermal conductivity according to formula
// k(t)=sum(xk(i)*T^i) , for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
// PUBLIC VARIABLES :
// gasName : name of the gas example : H2O :variable class str
// (class str is defined at file cstr.h and str.cpp, written by Timotyhy
A. Budd)
// M : mol number of the gas example mol number of H2O is 18.016 kg/kmol
// h0 : value of enthalpy at 298 K in the unit of Kcal/kmol
// hf : formation enthalpy at 298 K in the unit of Kcal/kmol
// sf : value of enthalpy at 298 K and 1 bar pressure
// N : molar weight of the gas, kmol
// ierror : integer variable, error flag
//============================================================
import java.io.*;
import Text;
import Atom;
class Gas
{
double xa[],xb[],xc[],xd[],tl[],th[];
int n_equation;
int n_vis;
int n_k;
double xvis[];
double xk[];
int natom;
String gasName;
Atom atomList[];
double M; // molar mass of atom kg/kmol
double h0; // enthalpy at T=298 K
double hf; // enthalpy of formation
double sf; // entropy of formation kJ/kmol K
double N; // moles of gas kmol
int ierror;
BufferedReader fin;
File gasDir;
// definations of class functions
// constructors
//===================================================================
public Gas()
{
//empty constructor
int i;
gasName="******************************";
natom=1;
atomList=new Atom[natom];
M=0;
N=1.0;
h0=0;
hf=0;
sf=0;
n_equation=6;
n_vis=10;
n_k=10;
xa=new double[6];
xb=new double[6];
xc=new double[6];
xd=new double[6];
tl=new double[6];
th=new double[6];
xvis=new double[10];
xk=new double[10];
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{xa[i]=0.0;xb[i]=0.0;xc[i]=0.0;xd[i]=0.0;tl[i]=293.0;th[i]=293.0;}
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{xvis[i]=0.0;}
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{xk[i]=0.0;}
}
//===================================================================
public Gas(String gName,double Nnew) throws IOException
{
int i;
String aName;
double aN;
ierror=1;
N=Nnew;
String tempGasName="";
try{
fin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Gas.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File Gas.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try{
while(fin!=null)
{
tempGasName=Text.readString(fin);
if (tempGasName.equals(gName)) {ierror=0;break;}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required gas "+tempGasName+" is not found");
fin.close();return;
}
gasName=gName;
natom=Text.readInt(fin);
atomList=new Atom[natom];
M=0;
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
aName=Text.readString(fin);
aN=Text.readDouble(fin);
atomList[i]=new Atom(aName,aN);
M+=atomList[i].mass;
}
n_equation=Text.readInt(fin);
h0=Text.readDouble(fin);
hf=Text.readDouble(fin);
sf=Text.readDouble(fin);
hf*=4.1868;
xa=new double[n_equation];
xb=new double[n_equation];
xc=new double[n_equation];
xd=new double[n_equation];
tl=new double[n_equation];
th=new double[n_equation];
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
xa[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xb[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xc[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xd[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
tl[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
th[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_vis=Text.readInt(fin);
xvis=new double[n_vis];
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{
xvis[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_k=Text.readInt(fin);
xk=new double[n_k];
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{
xk[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
}
public Gas(String gName) throws IOException
{
double Nnew=1;
int i;
String aName;
double aN;
ierror=1;
N=Nnew;
String tempGasName="";
try{
fin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Gas.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File Gas.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try{
while(fin!=null)
{
tempGasName=Text.readString(fin);
if (tempGasName.equals(gName)) {ierror=0;break;}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required gas "+tempGasName+" is not found");
fin.close();return;
}
gasName=gName;
//fin>>natom;
natom=Text.readInt(fin);
atomList=new Atom[natom];
M=0;
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
//fin>>aName>>aN;
aName=Text.readString(fin);
aN=Text.readDouble(fin);
atomList[i]=new Atom(aName,aN);
M+=atomList[i].mass;
}
//fin>>n_equation>>h0>>hf>>sf;
n_equation=Text.readInt(fin);
h0=Text.readDouble(fin);
hf=Text.readDouble(fin);
sf=Text.readDouble(fin);
hf*=4.1868;
xa=new double[n_equation];
xb=new double[n_equation];
xc=new double[n_equation];
xd=new double[n_equation];
tl=new double[n_equation];
th=new double[n_equation];
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
xa[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xb[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xc[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
xd[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
tl[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
th[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_vis=Text.readInt(fin);
xvis=new double[n_vis];
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{
xvis[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_k=Text.readInt(fin);
xk=new double[n_k];
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{
xk[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
}
public String readGasNames() throws IOException
{
String temp1="";
int natom;
String temp=new String("");
String pgasName;
String aName;
double aN;
double ppercent;
int n_equation;
double h0,hf,sf;
double xai,xbi,xci,xdi,tli,thi;
int n_vis,n_k;
double xvisi,xki;
int i;
try{
fin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Gas.txt"));
try {
while(fin!=null)
{
temp1=temp1+Text.readString(fin)+ " ";
natom=Text.readInt(fin);
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
aName=Text.readString(fin);
aN=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_equation=Text.readInt(fin);
h0=Text.readDouble(fin);
hf=Text.readDouble(fin);
sf=Text.readDouble(fin);
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
xai=Text.readDouble(fin);
xbi=Text.readDouble(fin);
xci=Text.readDouble(fin);
xdi=Text.readDouble(fin);
tli=Text.readDouble(fin);
thi=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_vis=Text.readInt(fin);
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{
xvisi=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
n_k=Text.readInt(fin);
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{
xki=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
} //end of while
} catch(EOFException e_eof) {fin.close();}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fnfe) {System.out.println("File Gmix.dat
not found");}
return temp1;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gas(Gas g) throws IOException
{
int i;
gasName=g.gasName;
natom=g.natom;
atomList=new Atom[natom];
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
atomList[i]=g.atomList[i];
}
M=g.M;
N=g.N;
h0=g.h0;
hf=g.hf;
sf=g.sf;
n_equation=g.n_equation;
n_vis=g.n_vis;
n_k=g.n_k;
xa=new double[n_equation];
xb=new double[n_equation];
xc=new double[n_equation];
xd=new double[n_equation];
tl=new double[n_equation];
th=new double[n_equation];
xvis=new double[n_vis];
xk=new double[n_k];
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{xa[i]=g.xa[i];xb[i]=g.xb[i];xc[i]=g.xc[i];xd[i]=g.xd[i];tl[i]=g.tl[i];th[i]=g.th[i];}
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{xvis[i]=g.xvis[i];}
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{xk[i]=g.xk[i];}
}
//===================================================================
//change/assign new molar mass
// see also * operator for the similar function
public void changeN(double Nnew)
{
N=Nnew;
}
//===================================================================
public String toString()
{
//return the chemical symbol of the gas
String s="";
for(int i=0;i<natom;i++)
s=s+atomList[i].toString();
return s;
}
//===================================================================
public double vis(double T)
{
// dynamic viscosity of the gas
double visg=0;
if(n_vis!=0.0)
{
visg=xvis[n_vis-1];
for(int i=n_vis-2;i>=0;i--)
{ visg=visg*T+xvis[i]; }
visg*=1.0e-7;
}
else
visg=0;
return visg;
}
//===================================================================
public double k(double T)
{
// thermal conductivity of the gas
double kg;
if(n_k!=0.0)
{
int nk=n_k-1;
kg=xk[nk];
for(int i=n_k-2;i>=0;i--)
{ kg+=kg*T+xk[i]; }
kg*=1.0e-3;
}
else
kg=0;
return kg;
}
//===================================================================
public double h(double T)
{
// enthalpy KJ/kmol
//integration of function dh=Cp(T)*dT
double hh = - h0;
for(int i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
if(((T>th[i]) && (i== (n_equation-1)
) )
|| ((T<tl[i]) && (i== 0 )
) )
{
hh+= xa[i]*(T- tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0e-3/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5*(1/T-1/tl[i])
+ xd[i]*1e-6*(T*T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]*tl[i])/3.0;
}
else if((T<= th[i]) && (T> tl[i]))
{
hh+= xa[i]*(T- tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0e-3/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5*(1/T-1/tl[i])
+ xd[i]*1e-6*(T*T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]*tl[i])/3.0;
}
else if(T>th[i])
{
hh+= xa[i]*(th[i]- tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0e-3/2.0*(th[i]*th[i] - tl[i]*tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5*(1/th[i]-1/tl[i])
+ xd[i]*1e-6*(th[i]*th[i]*th[i]-tl[i]*tl[i]*tl[i])/3.0;
}
}
return (hh*4.1868);
}
//===================================================================
public double ht( double t)
{
return h(t)+hf;
}
//===================================================================
public double H(double t)
{
return h(t)*N;
}
//===================================================================
public double HT(double t)
{
return ht(t)*N;
}
//===================================================================
public double u(double T)
{
// internal energy KJ/kmol
// Integration of function du = Cv(T)*dT
return (h(T) - 8.3145*T);
}
//===================================================================
public double v(double T,double P)
{
// specific volume of the gas m^3/kmol
return 8314.5*T/(P*1e5);
}
public double v(double T)
{
double P=1.0;
// specific volume of the gas m^3/kmol
return 8314.5*T/(P*1e5);
}
//===================================================================
public double c(double t)
{
// speed of sound m/s
return Math.sqrt(8314.5/M*t*gamma(t));
}
//===================================================================
public double s(double T, double P)
{
//entropy KJ/kmol K
//integration of function
// ds = Cp(T) * dt/T - R dP/P
double ss=sf;
for(int i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
if( ( T > th[i] && i==n_equation - 1 )
||( T < tl[i] && i==0
))
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(T/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(T-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(T*T) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
else if((T <= th[i]) && (T > tl[i]))
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(T/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(T-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(T*T) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
else if( T > th[i] )
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(th[i]/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(th[i]-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(th[i]*th[i]) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(th[i]*th[i] - tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
}
ss*=4.1868;
return (ss-8.3145*Math.log(P));
}
public double S(double T, double P)
{
return s(T,P)*N;
}
public double s(double T)
{
//entropy KJ/kmol K
//integration of function
// ds = Cp(T) * dt/T - R dP/P
double ss=sf;
for(int i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
if( ( T > th[i] && i==n_equation - 1 )
||( T < tl[i] && i==0
))
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(T/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(T-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(T*T) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
else if((T <= th[i]) && (T > tl[i]))
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(T/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(T-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(T*T) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(T*T-tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
else if( T > th[i] )
{
ss+=xa[i]*Math.log(th[i]/tl[i])
+ xb[i]*1.0E-3*(th[i]-tl[i])
- xc[i]*1e5/2.0*(1.0/(th[i]*th[i]) - 1.0/(tl[i]*tl[i]))
+ xd[i]*1e-6/2.0*(th[i]*th[i] - tl[i]*tl[i]);
}
}
ss*=4.1868;
return ss;
}
//===================================================================
public double s0(double T)
{
return s(T);
}
//===================================================================
public double g(double T,double P)
{
return h(T)-T*s(T,P);
}
public double gt(double T,double P)
{
return h(T)+hf-T*s(T,P);
}
public double gt(double T)
{
return h(T)+hf-T*s(T,1);
}
public double g(double T)
{
double P=1.0;
return h(T)-T*s(T,P);
}
public double G(double T,double P)
{
return g(T,P)*N;
}
public double G(double T)
{
return g(T)*N;
}
public double GT(double T)
{
return gt(T)*N;
}
public double GT(double T,double P)
{
return gt(T,P)*N;
}
//===================================================================
public double g0(double T)
{
return h(T)-T*s0(T);
}
//===================================================================
public double Cp(double T)
{
//specific heat at constant pressure KJ/kmol K
double cp=0.0;
for (int i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{
if( ( T > th[i] && i==n_equation - 1 )
||( T < tl[i] && i==0
))
{
cp=xa[i]+xb[i]*1.0e-3*T+xc[i]*1.0e5/T/T+xd[i]*1.0e-6*T*T;
break;
}
else if((T <= th[i]) && (T > tl[i]) )
{
cp=xa[i]+xb[i]*1.0e-3*T+xc[i]*1.0e5/T/T+xd[i]*1.0e-6*T*T;
break;
}
}
return (cp*4.1868);
}
//===================================================================
public double Cv(double T)
{
//specific heat at constant volume KJ/kmol K
double cv;
cv=Cp(T) - 8.3145;
return cv;
}
//===================================================================
public double gamma(double T)
{
//adiabatic constant
return Cp(T)/Cv(T);
}
//===================================================================
public double T( char name,double y0,double p)
{
// name can have values h : for enthalpy
// u : for internal energy
// s : for entropy
// v : specific volume
// yo : the value of the variable given by variable name
double t=300;
if(name=='v') {t= p*1e5*y0/8.3145e3;}
else
{
double dt=0;
int nmax=400;
double tolerance=1.0e-8;
for(int i=0;i<nmax;i++)
{
// apply newtons method for finding roots of equation
if (name=='h') dt=-( h(t) - y0 ) /Cp(t);
else if(name=='u') dt=-( u(t) - y0 ) /Cv(t);
else if(name=='s') dt=-( s(t,p) - y0 ) /(Cp(t)/t);
else { System.out.println("wrong name defined please try h,u,s ot
v");}
t+=dt;
// if error range is less than tolerance, exit
if(Math.abs(dt)<tolerance) break;
}
}
return t;
}
public double T( char name,double y0)
{
// name can have values h : for enthalpy
// u : for internal energy
// s : for entropy
// v : specific volume
// yo : the value of the variable given by variable name
double t=300;
double p=1.0;
if(name=='v') {t= p*1e5*y0/8.3145e3;}
else
{
double dt=0;
int nmax=400;
double tolerance=1.0e-8;
for(int i=0;i<nmax;i++)
{
// apply newtons method for finding roots of equation
if (name=='h') dt=-( h(t) - y0 ) /Cp(t);
else if(name=='u') dt=-( u(t) - y0 ) /Cv(t);
else if(name=='s') dt=-( s(t,p) - y0 ) /(Cp(t)/t);
else { System.out.println("wrong name defined please try h,u,s ot
v");}
t+=dt;
// if error range is less than tolerance, exit
if(Math.abs(dt)<tolerance) break;
}
}
return t;
}
//===================================================================
public double P( char name,double y0,double t1)
{
// name can have values v : for specific volume
// s : for entropy
// note : for a perfect gas enthalpy and internal energy
// is not function of pressure
// yo : the value of the variable given by variable name
if(name=='v') return 8.3145e3*t1/y0*1e-5;
else if (name=='s') return Math.exp((s(t1,1.0)-y0)/8.3145);
else { System.out.println("wrong name defined please try s or v"); return
1.0;}
}
//===================================================================
public double Pr(double t)
{
// Prandtl number
return Cp(t)*vis(t)/k(t)/M*1e3;
}
//===================================================================
public void assign(Gas g1) throws IOException
{
// assign operator (assigning a new gas to the gas variable)
int i;
ierror=1;
gasName=g1.gasName;
N=g1.N;
n_equation=g1.n_equation;
n_k=g1.n_k;
n_vis=g1.n_vis;
M=g1.M;
h0=g1.h0;
hf=g1.hf;
sf=g1.sf;
natom=g1.natom;
atomList=new Atom[natom];
M=0;
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
atomList[i]=new Atom(g1.atomList[i].name,g1.atomList[i].N);
}
xa=new double[n_equation];
xb=new double[n_equation];
xc=new double[n_equation];
xd=new double[n_equation];
tl=new double[n_equation];
th=new double[n_equation];
xvis=new double[n_vis];
xk=new double[n_k];
for(i=0;i<n_equation;i++)
{ xa[i]=g1.xa[i];
xb[i]=g1.xb[i];
xc[i]=g1.xc[i];
xd[i]=g1.xd[i];
tl[i]=g1.tl[i];
th[i]=g1.th[i];
}
for(i=0;i<n_vis;i++)
{ xvis[i]=g1.xvis[i];}
for(i=0;i<n_k;i++)
{xk[i]=g1.xk[i];}
}
//===================================================================
public Gas multiply(double Nnew, Gas g1) throws IOException
{
Gas g2=new Gas(g1);
g2.N*=Nnew;
return g2;
}
public boolean equals(Gas g)
{
if(gasName.equals(g.gasName))
return true;
else
return false;
}
//=================================================================
}
//=================================================================
Gaz özelliklerinin yer aldığı bilgi dosyası Gas.txt (sadece iki örnek
gaz ch4 ve c2h6 için veri listelenmiştir.) :
ch4
2
C 1
H 4
6 0 -17883.1088181 44.4764979459
.569592791684135E+01 .230885866354099E+02 .257021911461535E-03 -.514500509673528E+02
298. 300.0
.549418872803147 23.348756180407 1.4381268667348 -6.89019972775113 300.0
1000.00
11.8834319588735 9.20574503493484 -21.4292411101953 -1.8024921550441
1000.0 2000.0
23.037791919106 1.1029857730146 -87.1157168947875 -.127020658512245 2000.0
3000.0
22.0766220965729 1.36002847842152 -59.4550709113699 -0.1402094192352699
3000.0 4000.0
25.8471557797976 -0.0210627042222442 -144.63391429225 0.00254109611861818
4000.0 6000.0
4
-.317434898401931E+01
.455271007474814E+00
-.273399388607163E-03
.895312831114117E-07
4
.399296677905716E+01
.551053536678452E-01
.172999763063988E-03
-.657213363465470E-07
c2h6
2
C 2
H 6
3 0 -20226.42591 54.8394955574
5.255293329509001 29.744079588767550 -1.128964437911497 -4.086756508274219
298.15 600.0
3.855945449740792 35.946345289228690 -1.504708264372915 -10.330104368611350
600.0 1000.0
21.017162073226170 15.065627352784930 -34.594573805677190 -3.233353234903328
1000.0 1473.15
3
-0.492854013060778E+01
0.379062761757185E+00
-0.148297458234132E-03
3
-0.173496859087276E+02
0.117899036192513E+00
0.399524288778580E-04
Program 10.17 GasModel.java : bu program veri çıktısının bir parçasıdır,
çıktıyı tablo formunda elde etmemiz amacıyla kullanılmıştır.
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
class GasModel extends AbstractTableModel
{
Object[][] veri={
{"Gas Formula : ","0"," "},
{"M : ","0","kg/kmol"},
{"h, enthalpy : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"u, Internal energy : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"s, Entropy : ","0","KJ/kmol K"},
{"v, Specific volume : ","0","m^3/kmol"},
{"k, Thermal conductivity : ","0","W/m K"},
{"h+hf, enthalpy+formation enth. : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"Density : ","0","kg/m^3"},
{"Cp : ","0"," KJ/kmol K"},
{"Cv : ","0","KJ/kmol K"},
{"Cp/Cv adiabatic constant : ","0"," "},
{"c speed of sound : ","0","m/s"},
{"Viscosity : ","0","N s/m^2"},
{"Pr,Prandtl Number : ","0"," "}};
String[] baslik={"Property ","Value ","Units"};
public GasModel(Gas g1,double TK,double P)
{
setValues(g1,TK,P);
}
public int getRowCount() {return veri.length;}
public int getColumnCount() {return baslik.length;}
public Object getValueAt(int satir,int sutun) {return veri[satir][sutun];}
public String getColumnName(int c) {return baslik[c];}
public void setValueAt(Object val, int row, int col)
{
veri[row][col] = val;
}
public void setValues(Gas g1,double T,double P)
{
double TK=T+273.0;
setValueAt(g1.toString(),0,1);
setValueAt((""+g1.M),1,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.h(TK)),2,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.u(TK)),3,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.v(TK,P)),4,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.s(TK,P)),5,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.k(TK)),6,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.ht(TK)),7,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.M/g1.v(TK)),8,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Cp(TK)),9,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Cv(TK)),10,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.gamma(TK)),11,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.c(TK)),12,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.vis(TK)),13,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Pr(TK)),14,1);
}
public boolean isCellEditable(int row, int col) {return true;}
}
Program 10.18 GasPropertySWF.java
// ======================================================
// Thermodynamics package in java
// GasPropertySWF class to calculate properties of gases
// user interface (JFrame)
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBITAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : Turhan.Coban@posta.mam.gov.tr
// =====================================================
import java.io.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import GasModel;
public class GasPropertySWF extends JFrame implements ActionListener,ItemListener
{
JPanel inputPanel;
JPanel outputPanel;
JPanel totalPanel;
JTextField promptGasName; // Label prompt GasName
JTextField promptTemperature; // Label prompt Temperature
JTextField promptPressure; // Label prompt Pressure
JComboBox inputGasName; // input GasName
JTextField inputTemperature; // input (from list )Temperature
JTextField inputPressure; // input Pressure
JTextArea outputTextArea;
GasModel gm;
JTable jt;
double T;
double P;
String gasName;
Gas g1;
protected File gmixFile;
protected StringTokenizer token;
String st[];
final static Color bg=Color.lightGray;
final static Color fg=Color.black;
final static Color kirmizi=Color.red;
final static Color beyaz=Color.white;
public GasPropertySWF()
{
super("Properties of perfect gases ");
Container c=getContentPane();
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
//adding max-min prompts and input fields
gasName=new String("air");
T=27.0;
P=1.0;
inputPanel=new JPanel();
inputPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2));
outputPanel=new JPanel();
outputPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
totalPanel=new JPanel();
totalPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
try{
g1=new Gas(gasName);
token=new StringTokenizer(g1.readGasNames());
st=new String[token.countTokens()];
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
int i=0;
while(token.hasMoreTokens())
{
st[i++]=new String((String)token.nextToken());
}
inputGasName=new JComboBox(st);
gasName=(String)inputGasName.getSelectedItem();
try{
g1=new Gas(gasName);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
promptGasName= new JTextField(20);
promptGasName.setText("Name of gas mixture : ");
promptGasName.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
promptTemperature=new JTextField(20);
promptTemperature.setText("Temperature (°C) : ");
promptTemperature.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputTemperature=new JTextField(20);
inputTemperature.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
promptPressure= new JTextField(20);
promptPressure.setText("Pressure (Bars) : ");
promptPressure.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
outputTextArea = new JTextArea();
outputTextArea.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputPressure=new JTextField(20);
inputPressure.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputPanel.add(promptGasName);
inputPanel.add(inputGasName);
inputPanel.add(promptTemperature);
inputPanel.add(inputTemperature);
inputPanel.add(promptPressure);
inputPanel.add(inputPressure);
inputGasName.addItemListener(this);
inputTemperature.addActionListener(this);
inputPressure.addActionListener(this);
gm=new GasModel(g1,T,P);
jt=new JTable(gm);
jt.setBackground(c.getBackground());
setArea();
outputPanel.add(outputTextArea,BorderLayout.NORTH);
outputPanel.add(jt,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
totalPanel.add(inputPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH);
totalPanel.add(outputPanel,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
c.add(totalPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH);
}
public void setArea()
{
double TK=T+273.0;
inputTemperature.setText(Double.toString(T));
inputPressure.setText(Double.toString(P));
String s="additional data can be added to Gas.txt file \n";
s+="Dr. Turhan Çoban, TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center\n";
s+="Energy Systems & Environmental Research Institute\n";
s+="PO Box 21, Gebze - Kocaeli, Turkey\n";
s+="email: Turhan.Coban@posta.mam.gov.tr\n";
//note if you would like to list additional information on the screen
//add to string s
// s+="Gas Formula : "+g1.toString("formula")+"\n";
// s+= "Gas Composition : "+g1.toString("composition")+"\n";
gm.setValues(g1,T,P);
outputTextArea.setText(s);
}
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent ev)
{
gasName=(String)inputGasName.getSelectedItem();
try{
g1=new Gas(gasName);
} catch(IOException ioe1) {System.out.println("IOException");}
setArea();
repaint();
}
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent e)
{
Double valTemp=new Double(inputTemperature.getText());
T=valTemp.doubleValue();
Double valPressure=new Double(inputPressure.getText());
P=valPressure.doubleValue();
getContentPane().setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
setArea();
repaint();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GasPropertySWF pencere= new GasPropertySWF();
pencere.addWindowListener(
new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {System.exit(0);}
} );
pencere.pack();
pencere.setVisible(true);
}
}
Program çıktısı :
6. Bu problemde bir önceki problemde verilen uygulamanın bir kademe daha
ilerine gideceğiz. Burada Gazları karıştırıp bir gaz karışımı elde edecek
ve bu gaz karışımının termodinamik özelliklerine bakacağız. Programımızın
ismi Gmix.java, gazları karıştırdığımız veri dosyası Gmix.txt ve çıktı dosyalarımız
GmixModel.java ve GmixPropertySWF.java
Program 10.19 Gmix.java
// ==============================================================
// File Name : Gmix.java
// Author : Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : Turhan.Coban@posta.mam.gov.tr
// Description : This file contains class gmix which calculates
// thermophysical properties of mixture of perfect gases.
// following properties can be calculated
// T() : Temperature degree K
// h(T) : enthalpy KJ/kmol
// hf : formation enthalpy KJ/kg
// ht(T) : total enthalpy KJ/kg (h+hf)
// M : molar mass kg/kmol
// HT(T) : total enthalpy KJ : M*ht(T)
// P() : presure bar
// s(T,P) : entropy KJ/kmol K
// Cp(T) : specific heat at constant pressure KJ/kmol
K
// Cv(T) : specific heat at constant volume KJ/kg K
// gamma(T): adiabatic constant Cp/Cv
// c(T) : speed of sound m/s
// u(T) : Internal energy KJ/kmol
// vis(T) : viscosity
// k(T) : thermal conductivity KW/kg K
// DATA FILE DEFINATION
// gas mixture definations are given the data file "Gmix.txt"
// if gas mixture data is not given in the Gmix.txt user can be add
// his own data to the file which has the following format
//------------------
// gmixName
// ngas
// gname_0 N_0
// .........
// gname_ngas-1 N_ngas-1
//-------------------
// and defination : gmix a(gmixName); will defined this gas mixture
// the same mixture can be defined directly in the main program as :
// -------------------
// Gas a_0=new Gas("a_0");
//.......
// Gas a_ngas=new Gas("a_ngas);
// Gmix a=new Gmix;
// a=N_0*a_0+...+N_ngas*a_ngas;
// -------------------
//============================================================
// VARIABLE IDENTIFICATION
// all the variables that type is not defined is a double variable
// PUBLIC VARIABLES :
// gasName : String class variable of gas mixture name
// ngas : int variable, number of simple gasses
// N : total molar mass of the gas mixture
// gasList :gas class vector variables
// All the other variables defined for class gas is also valid for gmix
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import Text;
import Atom;
import Gas;
// ==============================================================
class Gmix{
// this class calculates perfect gas thermodynamic
// properties when the perfect gas constitutes of
// several single gases
public int ngas; // number of simple gasses inside of the gas
mixture
String gasName;
public double M; // molar mass of atom kg/kmol
public double h0; // enthalpy at T=298 K
public double hf; // enthalpy of formation
public double sf; // entropy of formation kJ/kmol K
public double N; // moles of gas kmol
int ierror;
int natom; //number of unique atoms in the atom list
Gas gasList[]; //list of the component gasses
Atom atomList[]; //list of component atoms
File gmixFile; // File name and directory
BufferedReader cfin;
// construction methods :
//========definations of class gmix =============================
//constructor functions
public Gmix(String name) throws IOException
{
// class complex gas construction function
// this function reads the initial gases in
// the mixture and their molar weight from
// the file Gmix.txt and construct mixed gas
try{
cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Gmix.txt"));
int ierror=1;
int i,j;
N=0;
M=0;
hf=0;
natom=0;
try{
while(cfin!=null)
{
gasName=Text.readString(cfin);
if(gasName.equals(name)) { ierror=0; break;}
} //end of while
} catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required gas mixture "+name+" is not
found");
cfin.close();return;
}
//cfin>>ngas;
ngas=Text.readInt(cfin);
gasList=new Gas[ngas];
//ierror=0;
String pgasName;
double ppercent;
Gas tempgas;
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
pgasName=Text.readString(cfin);
ppercent=Text.readDouble(cfin);
//cfin>>pgasName>>ppercent;
tempgas=new Gas(pgasName,ppercent);
ierror=tempgas.ierror;
{
if(ierror!=1)
{
try{
gasList[i]=new Gas(tempgas);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
N+=tempgas.N;
M+=tempgas.N*tempgas.M;
hf+=tempgas.N*tempgas.hf;
}
else
{
System.out.println("gas is not found in the list");
System.out.println("this gas is not added to the list");
i--;
ngas--;
}
}
}
M=M/N;
hf=hf/N;
arrange_atoms();
} catch(FileNotFoundException fnfe) {System.out.println("File not
found");}
}
// ==============================================================
public String readGmixNames() throws IOException
{
String temp=new String("");
String pgasName;
double ppercent;
try{
cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Gmix.txt"));
try {
while(cfin!=null)
{
temp=temp+Text.readString(cfin)+ " ";
ngas=Text.readInt(cfin);
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
pgasName=Text.readString(cfin);
ppercent=Text.readDouble(cfin);
} //end of while
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof) {cfin.close();}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fnfe) {System.out.println("File Gmix.txt
not found");}
return temp;
}
// ==============================================================
public void arrange_atoms() throws IOException
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<gasList[i].natom;j++)
{
add_atom(i,j);
}
}
}
public int add_atom(int i,int j) throws IOException
{
int k;
//Atom tempAtom=new Atom(gasList[i].atomList[j].symbol,gasList[i].atomList[j].N*gasList[i].N/N);
for(k=0;k<natom;k++)
{
if(gasList[i].atomList[j].symbol.equals(atomList[k].symbol))
{
atomList[k]=new Atom(atomList[k].symbol,atomList[k].N+gasList[i].atomList[j].N*gasList[i].N/N);
return 1;
}
}
Atom atomL[];
atomL=new Atom[natom+1];
for(k=0;k<natom;k++)
atomL[k]=new Atom(atomList[k]);
atomL[natom]=new Atom(gasList[i].atomList[j].symbol,gasList[i].atomList[j].N*gasList[i].N/N);
atomList=atomL;
natom+=1;
return 2;
}
//===============================================================
public Gmix() throws IOException
{
//empty construction function
N=0;
M=0;
String pgasname="\0";
ngas=0;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix(Gmix g1) throws IOException
{
gasName=g1.gasName;
gasName=gasName;
N=g1.N;
M=g1.M;
hf=g1.hf;
ngas=g1.ngas;
natom=g1.natom;
gasList=new Gas[ngas];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++) gasList[i]=new Gas(g1.gasList[i]);
for(int i=0;i<natom;i++) atomList[i]=new Atom(g1.atomList[i]);
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix(Gas g1) throws IOException
{
gasName=g1.gasName;
gasName=gasName;
N=g1.N;
M=g1.M;
hf=g1.hf;
ngas=1;
natom=g1.natom;
gasList=new Gas[ngas];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++) gasList[i]=new Gas(g1);
for(int i=0;i<natom;i++) atomList[i]=new Atom(g1.atomList[i]);
}
// ==============================================================
public void changeN(double newN) throws IOException
{
normalise();
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ gasList[i].N*=newN; }
N=newN;
}
// ==============================================================
public void add(Gas g1) throws IOException
{
// this function adds a single gas to the mixture
int gasflag=1;
// if the gas exist in the list simply change N and M values
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(gasList[i].gasName.equals(g1.gasName))
{
gasflag=0;
M=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
gasList[i].N+=g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=M/N;
}
}
if(gasflag!=0)
{
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas+1];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
newGas[i]=new Gas(gasList[i]);
}
ngas++;
double MT=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=MT/N;
newGas[ngas-1]=new Gas(g1);
gasList=newGas;
}
arrange_atoms();
}
// ==============================================================
public void remove(String name) throws IOException
{
// this function removes a single gas
// from the list
int i,k;
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(gasList[i].gasName.equals(name))
{
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas];
M=0;
N=0;
for(k=0;k<i;k++)
{ newGas[k]=new Gas(gasList[k]);
M+=newGas[k].M*newGas[k].N;
N+=newGas[k].N;
}
for( k=i;k<(ngas-1);k++)
{
newGas[k]=new Gas(gasList[k+1]);
M+=newGas[k].M*newGas[k].N;
N+=newGas[k].N;
}
M=M/N;
ngas--;
gasList=newGas;
break;
}
}
arrange_atoms();
// correct dynamic memory size
}
// ==============================================================
public void add(String name,double Nnew) throws IOException
{
// this function adds a single gas to the mixture
Gas g1=new Gas(name,Nnew);
int gasflag=1;
// if the gas exist in the list simply change N and M values
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(gasList[i].gasName.equals(g1.gasName))
{
gasflag=0;
M=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
gasList[i].N+=g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=M/N;
}
}
if(gasflag!=0)
{
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas+1];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
newGas[i]=new Gas(gasList[i]);
}
ngas++;
double MT=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=MT/N;
newGas[ngas-1]=new Gas(g1);
gasList=newGas;
}
arrange_atoms();
}
// ==============================================================
public void simplify() throws IOException
{
// this function combines any single gas
// that repeated in the list
double ngasold=ngas;
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<ngas;j++)
{
if(gasList[i].gasName.equals(gasList[j].gasName))
{
gasList[i].N+=gasList[j].N;
for(k=j;k<(ngas-1);k++)
{ gasList[k]=new Gas(gasList[k+1]); }
ngas--;
}
}
}
// correct dynamic memory size
if(ngasold!=ngas)
{
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas];
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
newGas[i]=new Gas(gasList[i]);
}
gasList=newGas;
}
}
// ==============================================================
public void normalise() throws IOException
{
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
gasList[i].N=gasList[i].N/N;
}
N=1.0;
arrange_atoms();
}
// ==============================================================
public void changeMix(double Nmix[]) throws IOException
{
// this function changes
// all the molar weights in the mixture
N=0;
M=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
gasList[i].N=Nmix[i];
N+=Nmix[i];
M+=Nmix[i]*gasList[i].M;
}
M=M/N;
arrange_atoms();
}
// ==============================================================
public double vis(double T)
{
// dynamic viscosity of the mixture
// note that viscosity of the mixture IS NOT the simple addition
// of viscosity of component gasses
double vmix=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
T=T;
double fij;
double xj=0;
double p1;
double c1,c2,c3;
for(int j=0;j<ngas;j++)
{
double vratio;
double xi=gasList[i].M/gasList[j].M;
if(gasList[j].vis(T)!=0)
{
c1=gasList[i].vis(T)/gasList[j].vis(T);
vratio=Math.sqrt(c1);
}
else
vratio=0;
c2=Math.pow(xi,0.25);
p1=(1+vratio/c2);
c3=8.0+8.0*xi;
fij=p1*p1 / Math.sqrt(c3);
xj+=fij*gasList[j].N/N;
}
vmix+=gasList[i].N/N*gasList[i].vis(T)/xj;
}
return vmix;
}
// ==============================================================
public double k(double T)
{
// thermal conductivity of the mixture
// note that thermal conductivity of the mixture IS NOT the
// simple addition of the thermal conductivity of component gasses
double vmix=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
T=T;
double fij;
double xj=0;
double p1;
double c1,c2,c3;
for(int j=0;j<ngas;j++)
{
double vratio;
double xi=gasList[i].M/gasList[j].M;
if(gasList[j].k(T)!=0)
{
c1=gasList[i].k(T)/gasList[j].k(T);
// if(c1<0) System.out.println("negative c1 value ");
vratio=Math.sqrt(c1);
}
else
vratio=0;
c2=Math.pow(xi,0.25);
p1=(1+vratio/c2);
c3= 8.0+8.0*xi;
// if(c2<0) System.out.println(" negative c2 value ");
fij=p1*p1/Math.sqrt(c3);
xj+=fij*gasList[j].N/N;
}
vmix+=gasList[i].N/N*gasList[i].k(T)/xj;
}
return vmix;
}
// ==============================================================
public double Pr(double t)
{
// Prandtl number
return Cp(t)*vis(t)/k(t)/M*1e3;
}
// ==============================================================
public double h(double T)
{
//specific enthalpy of the mixture KJ/kmol
double HH=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ HH+=gasList[i].h(T)*gasList[i].N; }
return HH/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double ht(double T)
{
//specific enthalpy of the mixture ht=h+hf
// hf : formation enthalpy
double HH=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ HH+=gasList[i].ht(T)*gasList[i].N; }
return HH/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double H(double t)
{
//total enthalpy of the mixture KJ
return h(t)*N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double HT(double t)
//total enthalpy of the mixture HT=N*(h+hf) KJ
{
return ht(t)*N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double u(double T)
{
// specific internal energy of the mixture KJ/kmol
double UU=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ UU+=gasList[i].u(T)*gasList[i].N; }
return UU/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double Cp(double T)
{
// Specific energy at constant pressure KJ/kmol K
double C=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ C+=gasList[i].Cp(T)*gasList[i].N; }
return C/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double Cv(double T)
//Specific energy at constant volume KJ/kmol K
{
double C=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ C+=gasList[i].Cv(T)*gasList[i].N; }
return C/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double gamma(double T)
{
//adiabatic constant
return Cp(T)/Cv(T);
}
// ==============================================================
public double c(double T)
//speed of sound m/s
{
return Math.sqrt(8314.5/M*T*gamma(T));
}
// ==============================================================
public double s(double T, double P)
{
//specific entropy KJ/kmol K
double SS=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
SS+=gasList[i].s(T,P)*gasList[i].N;
}
return SS/N;
}
public double s(double T)
{
//specific entropy KJ/kmol K
double P=1.0;
double SS=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
SS+=gasList[i].s(T,P)*gasList[i].N;
}
return SS/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double v(double T, double P)
{
double VV=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ VV+=gasList[i].v(T,P)*gasList[i].N; }
return VV/N;
}
// ==============================================================
public double T( char name,double y0,double p)
{
double t=300;
if(name=='v') {t= p*1e5*y0/8.314e3;}
else
{
double dt;
int nmax=400;
double tolerance=1.0e-8;
for(int i=0;i<nmax;i++)
{
if (name=='h') dt=-( h(t) - y0 ) /Cp(t);
else if(name=='u') dt=-( u(t) - y0 ) /Cv(t);
else if(name=='s') dt=-( s(t,p) - y0 ) /(Cp(t)/t);
else { System.out.println("wrong name defined please
try h,u,s ot v"); break;}
t+=dt;
if(Math.abs(dt)<tolerance) break;
}
}
return t;
}
// ==============================================================
public double P( char name,double y0,double t1)
{
if(name=='v') return 8.314e3*t1/y0*1e-5;
else if (name=='s') return Math.exp((s(t1,1.0)-y0)/8.314);
else { System.out.println("wrong name defined please try s or v"); return
1.0;}
}
// ==============================================================
public void multiplyassign(double Nx)
{
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ gasList[i].N*=Nx; }
N*=Nx;
}
// ==============================================================
public void addassign(Gas g1) throws IOException
{
// this function adds a single gas to the mixture
int gasflag=1;
// if the gas exist in the list simply change N and M values
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(gasList[i].gasName==g1.gasName)
{
gasflag=0;
M=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
gasList[i].N+=g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=M/N;
}
}
if(gasflag!=0)
{
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas+1];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
newGas[i]=new Gas(gasList[i]);
}
ngas++;
double MT=M*N+g1.M*g1.N;
N+=g1.N;
M=MT/N;
newGas[ngas-1]=new Gas(g1);
gasList=newGas;
}
}
// ==============================================================
public void addassign(Gmix right) throws IOException
{
// this function adds a gas mixture to the mixture
for(int i=0;i<right.ngas;i++)
{
add(right.gasList[i]);
}
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix multiply( double Nx,Gmix right) throws IOException
{
Gmix g1=new Gmix(right);
g1.N*=Nx;
for(int i=0;i<g1.ngas;i++)
{
g1.gasList[i].N*=Nx;
}
return g1;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix add(Gas l,Gas r) throws IOException
{
Gmix g1=new Gmix(r);
Gas g2=new Gas(l);
g1.add(g2);
return g1;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix add(Gmix l,Gas r) throws IOException
{
Gmix g1=new Gmix(l);
Gas g2=new Gas(r);
g1.add(g2);
return g1;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix add(Gas l,Gmix r) throws IOException
{
Gmix g1=new Gmix(r);
Gas g2=new Gas(l);
g1.add(g2);
return g1;
}
// ==============================================================
public Gmix add(Gmix l,Gmix r) throws IOException
{
Gmix g1=new Gmix(l);
for(int i=0;i<r.ngas;i++)
{
g1.add(r.gasList[i]);
}
return g1;
}
// ==============================================================
public void assign(Gmix g1) throws IOException
{
gasName=g1.gasName;
N=g1.N;
M=g1.M;
ngas=g1.ngas;
Gas newGas[];
newGas=new Gas[ngas];
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++) newGas[i]=g1.gasList[i];
gasList = newGas;
}
// ==============================================================
public void assign(Gas g1) throws IOException
{
// a single gas is assigned to the mixture
gasName=g1.gasName;
N=g1.N;
M=g1.M;
ngas=1;
gasList=new Gas[ngas];
gasList[0]=new Gas(g1);
}
public String toString(String ch)
{
//return the c
String s="";
int i,j;
if(ch.equals("name"))
s=s+gasName+"\n";
else if(ch.equals("formula"))
{
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{ s=s+" "+gasList[i].toString()+" "+gasList[i].N+"\n"; }
}
else if(ch.equals("composition"))
{
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
s=s+atomList[i].toString()+"\n";
}
return s;
}
}//end of class
Gmix veri dosyası Gmix.txt (kısmi liste )
diesel1
25
c9h20 0.0122
c10h22 0.0243
c11h24 0.0517
c12h26 0.0912
c13h28 0.2007
c14h30 0.1959
c15h32 0.098
c16h34 0.049
c17h36 0.0245
c18h38 0.0122
c19h40 0.0061
c20h42 0.0031
c11h16 0.0027
c12h18 0.0041
c13h20 0.0055
c14h22 0.0058
c15h24 0.0059
c16h26 0.0065
c17h28 0.0030
c18h30 0.0020
c10h8 0.0302
c11h10 0.0654
c12h12 0.0453
c13h14 0.0322
c14h16 0.0215
metanolreformeryanmaodasi
4
co2 1
h2o 2.1
n2 7.5238
o2 0.5
biogaz
5
h2 0.116
co 0.174
ch4 0.082
co2 0.131
n2 0.382
yanmahavasi
2
o2 2.463
n2 9.26557
Program 10.20 GmixMethod.java
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
class GmixModel extends AbstractTableModel
{
Object[][] veri={
{"M : ","0","kg/kmol"},
{"h, enthalpy : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"u, Internal energy : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"s, Entropy : ","0","KJ/kmol K"},
{"v, Specific volume : ","0","m^3/kmol"},
{"k, Thermal conductivity : ","0","W/m K"},
{"h+hf, enthalpy+form. enth. : ","0","KJ/kmol"},
{"Density : ","0","kg/m^3"},
{"Cp : ","0"," KJ/kmol K"},
{"Cv : ","0","KJ/kmol K"},
{"Cp/Cv adiabatic constant : ","0"," "},
{"c speed of sound : ","0","m/s"},
{"Viscosity : ","0","N s/m^2"},
{"Pr,Prandtl Number : ","0"," "}};
String[] baslik={"Property ","Value ","Units"};
public GmixModel(Gmix g1,double TK,double P)
{
setValues(g1,TK,P);
}
public int getRowCount() {return veri.length;}
public int getColumnCount() {return baslik.length;}
public Object getValueAt(int satir,int sutun) {return veri[satir][sutun];}
public String getColumnName(int c) {return baslik[c];}
public void setValueAt(Object val, int row, int col)
{
veri[row][col] = val;
}
public void setValues(Gmix g1,double T,double P)
{
double TK=T+273.0;
setValueAt((""+g1.M),0,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.h(TK)),1,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.u(TK)),2,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.v(TK,P)),3,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.s(TK,P)),4,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.k(TK)),5,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.ht(TK)),6,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.M/g1.v(TK,P)),7,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Cp(TK)),8,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Cv(TK)),9,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.gamma(TK)),10,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.c(TK)),11,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.vis(TK)),12,1);
setValueAt(Double.toString(g1.Pr(TK)),13,1);
}
public boolean isCellEditable(int row, int col) {return false;}
}
Program 10.21 GmixPropertySWF.java
// ======================================================
// Thermodynamics package in java
// GmixPropertySWF class to calculate properties of perfect
// gas mixtures user interface (JFrame)
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBITAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : Turhan.Coban@posta.mam.gov.tr
// =====================================================
import java.io.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
import GmixModel;
public class GmixPropertySWF extends JFrame implements ActionListener,ItemListener
{
final static String MAIN = "Main Page";
final static String GASFORMULA = "Gas Formula";
JTabbedPane tabbedPane;
JPanel inputPanel;
JPanel outputPanel;
JPanel totalPanel;
JTextField promptGmixName; // Label prompt GmixName
JTextField promptTemperature; // Label prompt Temperature
JTextField promptPressure; // Label prompt Pressure
JComboBox inputGmixName; // input GmixName
JTextField inputTemperature; // input (from list )Temperature
JTextField inputPressure; // input Pressure
JTextArea outputTextArea;
JTextArea outputTextArea1;
GmixModel gm;
JTable jt;
double T;
double P;
String GmixName;
Gmix g1;
protected File gmixFile;
protected StringTokenizer token;
String st[];
final static Color bg=Color.lightGray;
final static Color fg=Color.black;
final static Color kirmizi=Color.red;
final static Color beyaz=Color.white;
public GmixPropertySWF()
{
super("Properties of perfect gas mixtures ");
Container c=getContentPane();
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane();
//adding max-min prompts and input fields
GmixName=new String("air");
T=27.0;
P=1.0;
inputPanel=new JPanel();
inputPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2));
outputPanel=new JPanel();
outputPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
totalPanel=new JPanel();
totalPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
try{
g1=new Gmix(GmixName);
token=new StringTokenizer(g1.readGmixNames());
st=new String[token.countTokens()];
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
int i=0;
while(token.hasMoreTokens())
{
st[i++]=new String((String)token.nextToken());
}
inputGmixName=new JComboBox(st);
GmixName=(String)inputGmixName.getSelectedItem();
try{
g1=new Gmix(GmixName);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
promptGmixName= new JTextField(20);
promptGmixName.setText("Simple Gmix Name : ");
promptGmixName.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
promptTemperature=new JTextField(20);
promptTemperature.setText("Temperature (°C) : ");
promptTemperature.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputTemperature=new JTextField(20);
inputTemperature.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
promptPressure= new JTextField(20);
promptPressure.setText("Pressure (Bars) : ");
promptPressure.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
outputTextArea = new JTextArea();
outputTextArea.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
outputTextArea1 = new JTextArea();
outputTextArea1.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputPressure=new JTextField(20);
inputPressure.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
inputPanel.add(promptGmixName);
inputPanel.add(inputGmixName);
inputPanel.add(promptTemperature);
inputPanel.add(inputTemperature);
inputPanel.add(promptPressure);
inputPanel.add(inputPressure);
inputGmixName.addItemListener(this);
inputTemperature.addActionListener(this);
inputPressure.addActionListener(this);
gm=new GmixModel(g1,T,P);
jt=new JTable(gm);
jt.setBackground(c.getBackground());
setArea();
outputPanel.add(outputTextArea,BorderLayout.CENTER);
outputPanel.add(jt,BorderLayout.NORTH);
totalPanel.add(inputPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH);
totalPanel.add(outputPanel,BorderLayout.CENTER);
tabbedPane.addTab(MAIN, totalPanel);
tabbedPane.addTab(GASFORMULA, outputTextArea1);
c.add(tabbedPane);
}
public void setArea()
{
double TK=T+273.0;
inputTemperature.setText(Double.toString(T));
inputPressure.setText(Double.toString(P));
String s="additional data can be added to Gmix.txt file \n";
s+="Dr. Turhan Çoban, TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center\n";
s+="Energy Systems & Environmental Research Institute\n";
s+="PO Box 21, Gebze - Kocaeli, Turkey\n";
s+="email: Turhan.Coban@posta.mam.gov.tr";
//note if you would like to list additional information on the screen
//add to string s
String s1="";
s1+="Gas mixture formula :\n";
s1+="=========================\n"+g1.toString("formula")+"\n";
s1+="Gas mixture composition :\n";
s1+="=========================\n"+g1.toString("composition")+"\n";
gm.setValues(g1,T,P);
outputTextArea.setText(s);
outputTextArea1.setText(s1);
}
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent ev)
{
GmixName=(String)inputGmixName.getSelectedItem();
try{
g1=new Gmix(GmixName);
} catch(IOException ioe1) {System.out.println("IOException");}
setArea();
repaint();
}
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent e)
{
Double valTemp=new Double(inputTemperature.getText());
T=valTemp.doubleValue();
Double valPressure=new Double(inputPressure.getText());
P=valPressure.doubleValue();
getContentPane().setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
setArea();
repaint();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GmixPropertySWF pencere= new GmixPropertySWF();
pencere.addWindowListener(
new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {System.exit(0);}
} );
pencere.pack();
pencere.setVisible(true);
}
}
Veri çıktısı :
Burada hemen bir noktaya dikkat çekelim. Gerçek programlamalarda asıl
veriyi işleyen sınıflar ve insan grafik arayüzü programları genelde ayrı
tutulur. Bu problem seti aynı zamanda sınıfların birbiri üzerine inşasının
da güzel bir örneğini teşkil etmektedir.
6. Bu problemde bir önceki problemde verilen uygulamanın bir kademe daha
ilerine gideceğiz. Burada Gaz karışımlarını bir borudan akıtacağız. Borunun
basınç düşümü ısı transferi gibi çeşitli özelliklerini bu program yardımıyla
değerlendireceğiz. Boruların özellikleri Pipe.txt dosyasında tanımlanmıştır.
Gaz karışımı için Boru basınç düşümü ve ısı transferini hesaplayan programımızın
ismi Pipe.javadır.
Program 10.22 Pipe.java
//===================================================================
// Thermodynamic package in java
// File Name : pipe.java
// Author : Turhan Coban
// TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : turhan@mam.gov.tr
// Description : This file contains the pipe class
// class pipe calculates pressure drops
// and internal heat transfer of pipes
// DATA FILE DEFINATION
// pipe datas are written in the data file "Pipe.txt"
// if gas data is not given in the data file, it can be curve fitted
// and added to the data file. Each data has the following form :
//------------------
// pipeName
// shape
// gasName
// d1 d2 (or only d1 depends on shape)
// mass_flow_rate
//-------------------
// a constructor is also available to define this data as passing values
//============================================================
// VARIABLE IDENTIFICATION
// all the variables that type is not defined is a double variable
// pipeName : String class variable for name
// shape : String class variable for shape of the cross-section
// options :
// circular
// rectangular
// concentric_annulus
// circular_segment
// circular_sector
// right_triangle
// gasName : String class variable for name of the gas mixtures
// g : gmix class variable
// mass_flow_rate : mass flow rate of gas mixture flowing
// through pipe, kg/s
// eps : pipe equivalent roughness m
// -------------------------------------------
// value of equivalent roughness for some pipes:
// Pipe equivalent rougness m
// ------------- ---------------------
// Riveted steel 0.9e-3 - 9e-3
// Concrete 0.3e-3 - 3e-3
// Wood stave 0.18e-3 - 0.9 e-3
// Cast iron 0.26e-3
// Galvanised iron 0.15e-3
// Commercial steel 0.045e-3
// wrought iron 0.045e-3
// drawn tubing 0.0015e-3
// Plastic,glass 0.0 (smooth)
// -------------------------------------------
// P : Pressure bar
// l : length m
// dh : hydraulic diameter m
// A : pipe area m^2
// KL : local pressure drop coefficient
//
//============================================================
import java.io.*;
import Text;
import Gmix;
class pipe{
protected double d1,d2; // m pipe dimensions
// actual meaning of d1 and d2
// can be change according to shape
public String pipeName;
public String shape; //pipe shape "circular","rectangular"...
public String gasName; //name of a gas mixture
public Gmix g;
public double mass_flow_rate; // kg/s
public double eps ; // m
public double P ; // Pressure bar
public double l ; // length
public double dh; // hydraulic diameter
public double A; // pipe area m^2
public double KL; //additional local pressure drop
// pipe functions
//=============================================
public static double tanh(double x)
{
//I couldnt find hyperbolic tangent in java
return (Math.exp(x)-Math.exp(-x))/(Math.exp(x)+Math.exp(-x));
}
public static double f(double Re,double eod)
{
// friction factor for turbulent flow 5000<Re<10^8
double f1=Math.log(eod/3.7+5.74/ Math.pow(Re,0.9))/Math.log(19);;
f1=1.325/(f1*f1);
return f1;
}
public static double fx(double X,double Re,double eod)
{
// colebrook equation to solve
// friction factor for turbulent flow 2000 < Re
double xx=2.0*Math.log(eod/3.7+2.51/Re*X)/Math.log(10.0)+X;
return xx;
}
public static double dfx(double X,double Re,double eod)
{
//derivative of colebrook equation
double xx;
xx = 1+2.0/(eod/3.7+2.51/Re*X)/Math.log(10.0)*2.51/Re;
return xx;
}
public static double fcol(double Re,double eod)
{
//solution of the colebrook equation
// by using newton method
double fi=f(Re,eod);
double x=1.0/ Math.pow(fi,0.5);
int nmax=50;
double tolerance=1.0e-10;
for(int i=0;i<nmax;i++)
{
double fx1=fx(x,Re,eod);
x-=fx1/dfx(x,Re,eod);
if(Math.abs(fx1)<tolerance) return 1.0/(x*x);
}
return 1.0/(x*x);
}
//==============================================
// implementation of constructors functions
// for class pipe
public pipe(String name,double le)
{
//this function reads pipe configuration
//from file Pipe.txt
l=le;
//beginning of try block
try{
BufferedReader cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Pipe.txt"));
int ierror=1;
//************
try{
while(cfin!=null)
{
pipeName=Text.readString(cfin);
if(pipeName.equals(name)) { ierror=0; break;}
} //end of while
} catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required pipe "+name+" is not found");
cfin.close();return;
}
//************
if(ierror==1)
{System.out.println("error required pipe name cannot be found in the
data file\n");return;}
shape=Text.readString(cfin);
gasName=Text.readString(cfin);
g=new Gmix(gasName);
if(g==null)
{
System.out.println("gmix is not found\n");
}
double pi=4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
if(shape.equals("circular"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=0.0;
A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;
}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1;
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);;
dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
}
eps=0.03e-3;
mass_flow_rate=Text.readDouble(cfin);
P=1.0;;
KL=0.0;
//end of try block
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File \n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
public pipe(String name)
{
//this function reads pipe configuration
//from file Pipe.txt
l=1.0;
//beginning of try block
try{
BufferedReader cfin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Pipe.txt"));
int ierror=1;
while(cfin!=null)
{
pipeName=Text.readString(cfin);
if(pipeName.equals(name)) {ierror=0;break;}
}
if(ierror==1)
{System.out.println("error required pipe name cannot be found in the
data file\n");return;}
shape=Text.readString(cfin);
gasName=Text.readString(cfin);
g=new Gmix(gasName);
if(g==null)
{
System.out.println("gmix is not found\n");
}
double pi=4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
if(shape.equals("circular"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=0.0;
A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;
}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);
dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1;
A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;
}
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
{
d1=Text.readDouble(cfin);
d2=Text.readDouble(cfin);;
dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
}
eps=0.03e-3;
mass_flow_rate=Text.readDouble(cfin);
P=1.0;;
KL=0.0;
//end of try block
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File \n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
}
void change_d1(double dim1)
{
d1=dim1;
double pi=4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
if(shape=="circular")
{ A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;}
else if(shape=="rectangular")
{
A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape=="concentric_annulus")
{dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
{dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape=="circular_sector")
{dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1; A=pi*dh*dh/4.0; }
else if(shape=="right_triangle")
{
dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
A=d1*d2/2.0;
}
}
void change_d2(double dim2)
{
d2=dim2;
double pi=4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
if(shape=="circular")
{ d2=0;A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
{
A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
{dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
{dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
{dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1; A=pi*dh*dh/4.0; }
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
{
dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
A=d1*d2/2.0;
}
}
pipe(String pn,
String sh,
String gn,
double dim1,
double dim2,
double m,double e,
double pp,
double k,
double length)
{
// direct assignment constructor
// this constructor can assign all
// the required values directly without
// going to the data file
pipeName=pn;
l=length;
shape=sh;
try{
g=new Gmix(gn);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
double pi= 4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
d1=dim1;
d2=dim2;
if(shape.equals("circular"))
//d1 is diameter of the pipe
{ A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;d2=0;}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
// d1 and d2 are two sides of the rectangle
{ A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
// d1 and d2 are inrernal and external diameters
//of the concentric annulus
{ dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
// d1 is diameter and d2 is the angle of the circular segment
{ dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
//d1 is the diameter, d2 is the height of the circular section
{ dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1; A=pi*dh*dh/4.0; }
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
// d1 and d2 two sides of right triangle
{
dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
A=d1*d2/2.0;
}
eps=e;
mass_flow_rate=m;
P=pp;
KL=k;
}
pipe(String pn,
String sh,
Gmix gmix1,
double dim1,
double dim2,
double m,
double e,
double pp,
double k,
double length)
{
// direct assignment constructor
// this constructor can assign all
// the required valued directly without
// going to the data file
pipeName=pn;
shape=sh;
//setup gas name
try{
g=new Gmix(gmix1);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
double pi= 4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
d1=dim1;
d2=dim2;
l=length;
if(shape.equals("circular"))
//d1 is diameter of the pipe
{ A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;d2=0;}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
// d1 and d2 are two sides of the rectangle
{ A=d1*d2;dh=4.0*d1*d2/(2.0*d1+2.0*d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
// d1 and d2 are inrernal and external diameters
//of the concentric annulus
{ dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
// d1 is diameter and d2 is the angle of the circular segment
{ dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
//d1 is the diameter, d2 is the height of the circular section
{ dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1; A=pi*dh*dh/4.0; }
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
// d1 and d2 two sides of right triangle
{ dh=2.0*d1*Math.sin(d2)/(1.0+Math.sin(d2)+Math.cos(d2)); A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
eps=e;
mass_flow_rate=m;
P=pp;
KL=k;
}
void change_gas(String str1)
{
try{
g=new Gmix(str1);
}
catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
}
void change_pipe(
String pn,
String sh,
String gn,
double dim1,
double dim2,
double e,
double m,
double pp,
double k)
{
// change assignment
// this constructor can assign all
// the required valued directly without
// going to the data file
pipeName=pn;
shape=sh;
try{
g=new Gmix(gn);
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
double pi= 4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
d1=dim1;
d2=dim2;
if(shape.equals("circular"))
//d1 is diameter of the pipe
{ A=pi*d1*d1/4;dh=d1;}
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
// d1 and d2 are two sides of the rectangle
{ A=d1*d2;dh=2.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2);
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
// d1 and d2 are inrernal and external diameters
//of the concentric annulus
{ dh=Math.abs(d2-d1);A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
// d1 is diameter and d2 is the angle of the circular segment
{ dh=d1*(1+Math.sin(2.0*d2)/2.0/(pi-d2));A=pi*dh*dh/4.0;}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
//d1 is the diameter, d2 is the height of the circular section
{ dh=d2/(1+d2)*d1; A=pi*dh*dh/4.0; }
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
// d1 and d2 two sides of right triangle
{ dh=4.0*d1*d2/(d1+d2+ Math.pow((d1*d1+d2*d2),0.5));
A=d1*d2/2.0;
}
eps=e;
mass_flow_rate=m;
P=pp;
KL=k;
}
public double get_d1()
//getting the first dimension
{
return d1;
}
public double get_d2()
//getting the first dimension
{
return d2;
}
public double velocity(double t)
{
// velocity of the pipe m/x
double d =g.M/g.v(t,P);
return (double)(mass_flow_rate/d/A);
}
public double Re(double t)
{
// reynold's number
double d=g.M/g.v(t,1.0);
double vis=g.vis(t);
double vv=velocity(t);
double res=(dh*vv*d/vis);
return res;
}
public double f(double t)
{
// this function calculated friction coefficient
// for both laminar and turnulent flow for various
// cross sections
double Rey=Re(t); //Reynold's number
double C=64;
if(Rey<2000)
{
String c = "circular";
String r = "rectangular";
String co_an = "concentric_annulus";
String cir_seg = "circular_segment";
String cir_sec = "circular_sector";
String rig_tri;
rig_tri=new String("right_triangle");
if(shape.equals(c))
//circular cross section, laminar flow
{ C=64.0; }
else if(shape.equals(r))
{
// Laminar rectangular channel friction factor
double x=d1/d2;
if(x>1) x=1/x;
double a1[];
a1=new double[6];
a1[0]= .959923253176985E+02;
a1[1]= -.130364643234979E+03;
a1[2]= .188053177394400E+03;
a1[3]= -.166159826967448E+03 ;
a1[4]= .952739160606451E+02;
a1[5]= -.258949934514987E+02 ;
C=a1[5];
for(int i=4;i>=0;i--) { C=C*x+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals(co_an))
{
//concentric annulus laminar friction factor
double x=d2/d2;
if(x>1) x=1/x;
double a1[];
a1=new double[5];
a1[0]= .717068909524062E+02;
a1[1]= .932037998655195E+03;
a1[2]= -.947586946520906E+04;
a1[3]= .204346570871727E+05;
a1[4]= -.118665325115712E+05;
C=a1[4];
for(int i=4;i>=0;i--) {C=C*x+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals(cir_seg))
{
//circular segment laminar friction factor
double a1[];
a1=new double[5];
a1[0]= .639999999999997E+02;
a1[1]= -.162338014624008E+01;
a1[2]= .162620455430327E+01;
a1[3]= -.827251633703104E+00 ;
a1[4]= .138590724447624E+00;
C=a1[4];
for(int i=3;i>=0;i--) {C=C*d2+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals(cir_sec))
{
//circular section laminar friction factor
double a1[];
a1=new double[4];
a1[0]= .480000000000000E+02;
a1[1]= .227909935649730E+02;
a1[2]= -.134959915493607E+02;
a1[3]= .325095868081599E+01;
C=a1[3];
for(int i=2;i>=0;i--) {C=C*d2+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals(rig_tri))
{
//right triangle laminar friction factor
double a1[];
a1=new double[5];
a1[0]= .480001792918036E+02;
a1[1]= .127207559700323E+02;
a1[2]= -.108590518340935E+02;
a1[4]= .158423382029386E+01;
a1[5]= .115425033696128E+01;
C=a1[5];
for(int i=4;i>=0;i--) {C=C*d2+a1[i];}
}
return C/Rey;
}
else
{
double eod=eps/dh;
double fc=fcol(Rey,eod);
return fc;
}
}
public double lentry(double t)
{
//hydraulic entry length
double Rey=Re(t);
double le;
if(Rey<2000) le=0.06*dh*Rey;
else le=4.4*dh* Math.pow(Rey,(1.0/6.0));
return le;
}
public double dP(double t,double P)
{
// pipe pressure drop for the given length plus
// local KL factors
double V=velocity(t);
return (KL+f(t)*l/dh)*(g.M/g.v(t,P))*V*V/2.0*1e-5;
}
public double dP(double t)
{
double P=1;
// pipe pressure drop for the given length plus
// local KL factors
double V=velocity(t);
return (KL+f(t)*l/dh)*(g.M/g.v(t,P))*V*V/2.0*1e-5;
}
public double dPl_e(double t,double P)
{
double Q=mass_flow_rate*g.v(t,P)/g.M;
double a=d1/2.0;
double b=d2/2.0;
double x=0;
double pi=4.0*Math.atan(1.0);
for(int i=1;i<8000;i+=2)
{
x+=tanh(pi*b*i/d1)/(double)(i*i*i*i*i);
}
x=1.0-192.0*a/(pi*pi*pi*pi*pi*b)*x;
double xx=b*a*a*a/(6.0*g.vis(t))*x;
xx=Q/xx*l*1e-5;
return xx;
}
void change_length(double l1)
{ l=l1; }
void change_mass_flow_rate(double mfr)
{ mass_flow_rate=mfr; }
void change_P(double Pin)
//change inlet pressure
{ P=Pin; }
void change_KL(double klin)
//change local pressure drop coefficient
{KL=klin; }
void change_e(double e)
{ eps=e; }
public double hc(double t)
{
//convective heat transfer coefficient
double Rey=Re(t);
double Nu=0;
if(Rey<2000)
{
if(shape.equals("circular"))
{ Nu=3.66; }
else if(shape.equals("rectangular"))
{
// Laminar rectangular channel friction factor
double x=d1/d2;
if(x>1) x=1/x;
double a1[];
a1=new double[7];
a1[0]= .754000000000580E+01;
a1[1]= -.193789080028494E+02;
a1[2]= .333861212302836E+02;
a1[3]= -.170496495070800E+02 ;
a1[4]= -.304226226912837E+02;
a1[5]= .495297442580787E+02;
a1[6]= -.206246852871550E+02;
Nu=a1[6];
for(int i=5;i>=0;i--) {Nu=Nu*x+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals("concentric_annulus"))
{
double x=d2/d2;
if(x>1) x=1/x;
double a1[];
a1=new double[4];
a1[0]= .401698044199492E+01;
a1[1]= .921803331830132E+00;
a1[2]= -.307845192109755E+00;
a1[3]= .229092480046921E+00;
Nu=a1[3];
for(int i=2;i>=0;i--) {Nu=Nu*x+a1[i];}
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_segment"))
{
Nu=3.66;
}
else if(shape.equals("circular_sector"))
{
Nu=3.66;
}
else if(shape.equals("right_triangle"))
{
Nu=2.47;
}
}
else
{
double fr = f(t);
Rey = Re(t);
double Prt = g.Pr(t);
// Gnielinski equation
// Gnielinski, V, Int. Chem Eng., 16, 359,1976
// Valid for 2000 < Re <5e5, 0.5 < Pr < 2000
Nu=fr/8.0*(Rey-1000.0)*Prt/
(1+12.7* Math.sqrt(fr/8.0)*( Math.pow(Prt,(2.0/3.0))-1.0));
}
double kt = g.k(t);
// double Prt = g.Pr(t);
double result;
result=Nu*kt/dh;
return result;
}
public double Nu(double t)
//Nusselt's Number
{
return hc(t)*dh/g.k(t);
}
} //end of class pipe
Program veri dosyası Pipe.txt (sadece birkaç örnek durum listelenmiştir.)
example
circular
air
0.1
0.11
p18_natural
circular
natural
18e-3
1.0589996e-4
p18_air
circular
air
18e-3
4.244105e-3
pipe_6
rectangular
prereformer_output
30e-3 1.6e-3
8.727136e-4
veri dosyası boru ismi, boru şekli(circular, rectangular..), gazkarışımının
adı(Gmix.txt dosyasında tanımlanmış olmalıdır), boru çapı veya boru en ve
boyu ve akış debisi(kg/s) bilgilerini içerir. Bu programın kullanıldığı
çıktı veren bir insan arayüzü programına göz atalım :
Program 10.23 pipeProperty.java
//======================================================
// Thermodynamics package in java
// pipeProperty class to calculate pipe
// user interface (applet)
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// =====================================================
import pipe;
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.util.*;
public class pipeProperty extends Applet implements ActionListener,ItemListener
{
protected Panel inputPanel;
protected Label promptGmixName; // Label prompt GmixName
protected Label promptTemperature; // Label prompt Temperature
protected Label promptPressure; // Label prompt Pressure
protected Label promptPipeLength; // Label prompt Pipe Length
protected Label promptShape; // Label prompt cross-section
shape
protected Label promptD1; // Label prompt first dimension
protected Label promptD2; // Label prompt second dimension
protected Label promptKL; // LP local PD coefficient
protected Label promptMass; // LP mass flow rate
protected Label prompte; // LP pipe equivalent roughness
protected Choice inputGmixName; // input GmixName
protected TextField inputTemperature; // input Temperature
protected TextField inputPressure; // input Pressure
protected TextField inputPipeLength; // input pipe length
protected Choice inputShape;
protected String pipeShapeArray[]={"circular","rectangular",
"concentric_annulus","circular_segment","circular_sector","right_triangle"};
protected TextField inputD1;
protected TextField inputD2;
protected TextField inputKL;
protected TextField inputMass;
protected TextField inpute;
double T;
double P;
double TK;
double pipeLength;
String pipeShape;
double D1,D2;
String GmixName;
String pipeName;
double mass_flow_rate;
Gmix g1;
pipe p1;
double KL;
double e;
StringTokenizer token;
public void init()
{
//adding max-min prompts and input fields
inputPanel=new Panel();
inputPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(10,2));
GmixName=new String("natural");
try{
g1=new Gmix(GmixName);
token=new StringTokenizer(g1.readGmixNames());
} catch(IOException ioe) {System.out.println("IOException");}
pipeName=new String("P18_natural");
T=27.0;
TK=T+273;
P=1.0;
pipeLength=1.0;
KL=0.0;
D1=0.005;
D2=0.005;
e=0.00001;
mass_flow_rate=0.01;
pipeShape =new String("circular");
promptGmixName= new Label(" Gas mixture Name : ");
inputGmixName=new Choice();
while(token.hasMoreTokens())
{
inputGmixName.add(token.nextToken());
}
//inputGmixName=new TextField(15);
promptTemperature= new Label(" Temperature (øC) : ");
inputTemperature=new TextField(15);
promptPressure= new Label(" Pressure (Bars) : ");
inputPressure=new TextField(15);
promptPipeLength= new Label(" Pipe Length, m : ");
inputPipeLength=new TextField(15);
promptShape= new Label(" Pipe Shape : ");
inputShape=new Choice();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
inputShape.add(pipeShapeArray[i]);
}
promptD1= new Label(" Pipe Dimension D1, m : ");
inputD1= new TextField(15);
promptD2= new Label(" Pipe Dimension D2, m : ");
inputD2= new TextField(15);
promptKL= new Label(" Pipe Local PD coefficient, : ");
inputKL= new TextField(15);
promptMass= new Label(" mass flow rate , kg/s : ");
inputMass= new TextField(15);
prompte= new Label(" Pipe equivalent roughness, m: ");
inpute= new TextField(15);
//********
inputGmixName.addItemListener(this);
inputTemperature.addActionListener(this);
inputPressure.addActionListener(this);
inputPipeLength.addActionListener(this);
inputShape.addItemListener(this);
inputD1.addActionListener(this);
inputD2.addActionListener(this);
inputKL.addActionListener(this);
inputMass.addActionListener(this);
inpute.addActionListener(this);
//********
inputPanel.add(promptGmixName);
inputPanel.add(inputGmixName);
inputPanel.add(promptTemperature);
inputPanel.add(inputTemperature);
inputPanel.add(promptPressure);
inputPanel.add(inputPressure);
inputPanel.add(promptPipeLength);
inputPanel.add(inputPipeLength);
inputPanel.add(promptShape);
inputPanel.add(inputShape);
inputPanel.add(promptD1);
inputPanel.add(inputD1);
inputPanel.add(promptD2);
inputPanel.add(inputD2);
inputPanel.add(promptKL);
inputPanel.add(inputKL);
inputPanel.add(promptMass);
inputPanel.add(inputMass);
inputPanel.add(prompte);
inputPanel.add(inpute);
inputTemperature.setText(Double.toString(T));
inputPressure.setText(Double.toString(P));
inputPipeLength.setText(Double.toString(pipeLength));
inputD1.setText(Double.toString(D1));
inputD2.setText(Double.toString(D2));
inputKL.setText(Double.toString(KL));
inputMass.setText(Double.toString(mass_flow_rate));
inpute.setText(Double.toString(e));
//inputGmixName.setText(GmixName);
inputD1.setText(Double.toString(D1));
inputD2.setText(Double.toString(D2));
inputD2.setEditable(false);
inputKL.setText(Double.toString(KL));
inputMass.setText(Double.toString(mass_flow_rate));
inpute.setText(Double.toString(e));
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add( inputPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH);
p1= new pipe(pipeName,
pipeShape,
GmixName,
D1,
D2,
mass_flow_rate,
e,
P,
KL,
pipeLength);
}
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent ev)
{
//pipeShape=pipeShapeArray[inputShape.getSelectedIndex()];
pipeShape=inputShape.getSelectedItem();
if(pipeShape.equals("circular"))
{
inputD2.setEditable(false);
}
else
{
inputD2.setEditable(true);
}
GmixName=inputGmixName.getSelectedItem();
p1= new pipe(pipeName,
pipeShape,
GmixName,
D1,
D2,
mass_flow_rate,
e,
P,
KL,
pipeLength);
repaint();
showStatus(pipeShape);
}//end of itemStateChange
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
TK=T+273;
g.drawString("Pressure Drop , bars : ",20,250);
g.drawString(""+p1.dP(TK,P),250,250);
g.drawString("f friction : ",20,265);
g.drawString(""+p1.f(TK),250,265);
g.drawString("Velocity , m/s : ",20,280);
g.drawString(""+p1.velocity(T),250,280);
g.drawString("Reynold's number Re : ",20,295);
g.drawString(""+p1.Re(TK),250,295);
g.drawString("Prandl's number Pr : ",20,310);
g.drawString(""+p1.g.Pr(TK),250,2310);
g.drawString("Nusselt's number Nu : ",20,325);
g.drawString(""+p1.Nu(TK),250,325);
g.drawString("Hydraulic entry length, m : ",20,340);
g.drawString(""+p1.lentry(TK),250,340);
g.drawString("Viscosity , N s/m^2 : ",20,355);
g.drawString(""+p1.g.vis(TK),250,355);
g.drawString(p1.g.toString("formula"),20,370);
g.drawString(p1.g.toString("composition"),20,385);
g.drawString("shape : "+pipeShape,20,400);
}//end of method
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent ee)
{
GmixName=inputGmixName.getSelectedItem();
Double valTemp=new Double(inputTemperature.getText());
T=valTemp.doubleValue();
Double valPressure=new Double(inputPressure.getText());
P=valPressure.doubleValue();
Double valpipeLength=new Double(inputPipeLength.getText());
pipeLength=valpipeLength.doubleValue();
Double valD1=new Double(inputD1.getText());
D1=valD1.doubleValue();
Double valD2=new Double(inputD2.getText());
D2=valD2.doubleValue();
Double valKL=new Double(inputKL.getText());
KL=valKL.doubleValue();
Double valMass=new Double(inputMass.getText());
mass_flow_rate=valMass.doubleValue();
Double valuee=new Double(inpute.getText());
e=valuee.doubleValue();
p1= new pipe(pipeName,
pipeShape,
GmixName,
D1,
D2,
mass_flow_rate,
e,
P,
KL,
pipeLength);
repaint();
}
}
Appletviewer olarak program çıktısı:
7. Thermodinamik
özellikler serisinden bir adım daha ileri gidip gazları kimyasal reaksiyonlara
sokabiliriz. Bu sınıfımız Reaction.java ismini taşıyor. Gazların termodinamik
reaksiyona girdiklerinde enerji dengelerini,adyabatik alev sıcaklıklarını
ve reaksiyon sabitlerini (k) hesaplama kapasitesinde bir program. Program
veridosyası Reaction.txt adında. Bu dosyada reaksiyonun ismi, toplam gaz
sayısı, bu gazın reaksiyona giren ve reaksiyondan çıkan moleküllerinin sayısı
liste olarak veriliyor. Reaksiyon kütle denklik hesabı program tarafından
yapılmamaktadır. Doğru molekül sayılarının verilmesi kullanıcıya bırakılmıştır.
Bu dosyadan birkaç örnek veri setine göz atalım:
hidrojen
3
h2o 1 0
h2 0 1
o2 0 0.5
c2h4comb
5
c2h4 1 0
o2 3 0
n2 11.28 11.28
co2 0 2
h2o 0 2
LPG
6
c3h8 0.3 0
c4h10 0.7 0
o2 6.05 0
n2 22.7595 22.7595
co2 0 3.7
h2o 0 4.7
dogal_1.05
8
ch4 0.906 0
c2h6 0.056 0
c3h8 8e-4 0
c4h10 2e-4 0
co2 0.018 0
n2 8.116375 8.116375
o2 2.155125 0.102625
h2o 0 2.017
dogal_1.1
8
ch4 0.906 0
c2h6 0.056 0
c3h8 8e-4 0
c4h10 2e-4 0
co2 0.018 0
n2 8.5024405 8.5024405
o2 2.27575 0.20525
h2o 0 2.017
Programımızın listesi:
Program 10.24 Reaction.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import Text;
class Reaction
{
//======================================================//
// Dr. Turhan Coban //
// TUBITAK Marmara Research Center //
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute //
// Phone : 90 (262) 641 2300-3917 //
// email : turhan@mam.gov.tr //
//======================================================//
// Class Description :
//------------------------------------------------------
// This program calculates energy, adiabatic flame temperature
// entropy and gibbs free energy for a given reaction
// Basic reaction data is given in the file called Reaction.dat
// Format of the data :
// reactionname
// number_of_the_chemicals
// gas_name reactant_mole prodoct_mole
// .......
// gas_name reactant_mole prodoct_mole
//-----------------
// sample data :
//-----------------
// c2h6combustion
// 5
// c2h6 1 0
// o2 3 0
// n2 11.28 11.28
// co2 0 2
// h2o 0 2
//------------------
// the available gas_name's can be checked from data file
// Gas.dat
// Variable Identification
//-----------------------------------------------------
// ngas : number of gases in reaction (integer variable)
// reacname : reaction name (String variable)
// gasR,gasP: gas objects for reactants and products
// (array objects of class Gas)
// see Gas.java for details
// natom : number of atoms in the reaction
// nr,np : number of Moles of reactants and products
// (double vector array)
// nrt,npt : total number of moles for reactants and products
// reacFile : reaction file channel variable (Class File)
// atomList : list of the atoms in the reaction
public int ngas;
String reacName;
Gas gasR[],gasP[];
public int natom;
Atom atomList[];
File reacFile;
double nr[],np[];
double nrt,npt;
public Reaction(String name) throws IOException
{
reacFile=new File("Reaction.txt");
reacFile=new File(reacFile.getAbsolutePath());
try
{
DataInputStream cfin=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(reacFile));
int ierror=1;
natom=0;
try
{
while(cfin!=null)
{
reacName=Text.readString(cfin);
if(reacName.equals(name)) {ierror=0;break;}
}
}
catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required gas mixture "+name+" is not
found");
cfin.close();return;
}
ngas=Text.readInt(cfin);
gasR=new Gas[ngas];
gasP=new Gas[ngas];
nr=new double[ngas];
np=new double[ngas];
nrt=0;
npt=0;
String tempGasName;
Double n1,n2;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
tempGasName=Text.readString(cfin);
nr[i]=Text.readDouble(cfin);
np[i]=Text.readDouble(cfin);
nrt+=nr[i];
npt+=np[i];
gasR[i]=new Gas(tempGasName,nr[i]);
gasP[i]=new Gas(tempGasName,np[i]);
}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fnfe) {System.out.println("File Not
Found");}
arrange_atoms();
} //end of constructor
public void arrange_atoms() throws IOException
{
// atomic structure of the reactants
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<gasR[i].natom;j++)
{
add_atom(i,j);
}
}
}
public int add_atom(int i,int j) throws IOException
{
//determine and order the atomic structure
int k;
for(k=0;k<natom;k++)
{
if(gasR[i].atomList[j].symbol.equals(atomList[k].symbol))
{
atomList[k]=new Atom(atomList[k].symbol,atomList[k].N+gasR[i].atomList[j].N*gasR[i].N);
return 1;
}
}
Atom atomL[];
atomL=new Atom[natom+1];
for(k=0;k<natom;k++)
atomL[k]=new Atom(atomList[k]);
atomL[natom]=new Atom(gasR[i].atomList[j].symbol,gasR[i].atomList[j].N*gasR[i].N);
atomList=atomL;
natom+=1;
return 2;
}
public String toString()
{
// writes chemical reaction in chemistry norm
String s="";
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(nr[i]==1)
{ s+=gasR[i].toString(); }
else if(nr[i]!=0)
{ s+=nr[i]+" "+gasR[i].toString(); }
if(i!=(ngas-1) && nr[i]!=0 ) s+=" + ";
}
if(s.endsWith(" + "))
s=s.substring(0,s.length()-3);
s+=" --> ";
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]==1)
{ s+=gasP[i].toString(); }
else if(np[i]!=0)
{ s+=np[i]+" "+gasP[i].toString(); }
if(i!=(ngas-1) && np[i]!=0 ) s+=" + ";
}
if(s.endsWith(" + "))
s=s.substring(0,s.length()-3);
return s;
}
public String toString(String ch)
{
//return the c
String s="";
int i,j;
if(ch.equals("name"))
s=s+reacName+"\n";
else if(ch.equals("formula"))
{
s=toString();
}
else if(ch.equals("composition"))
{
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
s=s+atomList[i].toString()+" ";
}
return s;
}
public double H(double TR,double TP)
{
//reaction enthalpy
double HH=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
HH+=gasP[i].HT(TP);
HH-=gasR[i].HT(TR);
}
return HH;
}
public double S(double TR,double TP,double pt)
{
//reaction entropy
double SS=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]!=0)
SS+=gasP[i].S(TP,np[i]/npt*pt);
if(nr[i]!=0)
SS-=gasR[i].S(TR,nr[i]/nrt*pt);
}
return SS;
}
public double S(double TR,double TP)
{
//reaction entropy
double SS=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]!=0)
SS+=gasP[i].S(TP,np[i]/npt);
if(nr[i]!=0)
SS-=gasR[i].S(TR,nr[i]/nrt);
}
return SS;
}
public double G(double TR,double TP,double pt)
{
// reaction gibbs energy
double GG=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]!=0)
GG+=gasP[i].GT(TP,np[i]/npt*pt);
if(nr[i]!=0)
GG-=gasR[i].GT(TR,nr[i]/nrt*pt);
}
return GG;
}
public double G(double TR,double TP)
{
// reaction gibbs energy
double GG=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]!=0)
GG+=gasP[i].GT(TP,np[i]/npt);
if(nr[i]!=0)
GG-=gasR[i].GT(TR,nr[i]/nrt);
}
return GG;
}
public double G0(double TR,double TP)
{
// reaction gibbs free energy
double GG=0;
for(int i=0;i<ngas;i++)
{
if(np[i]!=0)
GG+=gasP[i].GT(TP);
if(nr[i]!=0)
GG-=gasR[i].GT(TR);
}
return GG;
}
public double K(double TR,double TP)
{
//Equilibrium costant. Usually TR and Tp will be in
// thesame temperature
return Math.exp(G0(TR,TP)/(-8.3145*TP));
}
public double Taf(double TR,double xl,double xu)
{
// Adyabatic flame temperature using Bisection method
// bisection method to find roots of zero energy change
// Q=0
// defination of variables :
// xl : lower guess
// xu : upper guess
// xr : root estimate
// es : stopping criterion
// ea :approximate error
// maxit : maximum iterations
// iter : number of iteration
double test;
double xr=0;
double es,ea;
double fxl,fxr;
int maxit=500,iter=0;
es=0.000001;
ea=1.1*es;
while((ea>es)&&(iter<maxit))
{
xr=(xl+xu)/2.0;
iter++;
if((xl+xu)!=0)
{ ea=Math.abs((xu-xl)/(xl+xu))*100;}
fxl= H(TR,xl);
fxr= H(TR,xr);
test= fxl*fxr;
if(test==0.0) ea=0;
else if(test<0.0) xu=xr;
else
{
xl=xr;
}
} //end of while
return xr;
}
}
programımızı bir örnekte test edelim.
Program 10.25 ReactionTest.java
import java.io.*;
import Reaction;
class ReactionTest
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
Reaction R2;
R2=new Reaction("hid");
System.out.println(R2.toString("name"));
System.out.println(R2.toString("formula"));
System.out.println(R2.toString("composition"));
double Tadyabatikalev= R2.Taf(299,299, 3000)-273;
System.out.println("T adyabatik alev = "+Tadyabatikalev+" derece
C");
}
}
program çıktısı :
hid
0.17 H2 + 1.72 O2 + 6.47 N2 --> 1.635 O2 + 6.47 N2 + 0.17 H2O
H0.34 O3.44 N12.94
T adyabatik alev = 194.51268483046442 derece C
8. Termodinamik
serisinden bir diğer program. Bu program gerçek gazların termodinamik
özelliklerini hesaplıyor. Programın ismi LeeKesler.java, veri dosyası RealGas.txt
Program Listesi :
//======================================================
// Thermodynamic Package in java
// Class Lee Kesler Properties of real gases
// Dr. Turhan Coban
// TUBİTAK Marmara Research Center
// Energy Systems and Environmental Research Institute
// email : turhan@mam.gov.tr
// File Name : LeeKesler.java
// This file contains the LeeKesler class
// this class sets basic properties of real gases
// required data is read from LeeKesler.txt
// =====================================================
// Description : This file contains the LeeKesler class
// class LeeKesler calculates thermophysical properties
of
// perfect gasses
// DATA FILE DEFINATION
// datas are written in the data file "RealGas.txt"
//============================================================
// VARIABLE IDENTIFICATION
//============================================================
// GasEquation : String type variable
// values : "LeeKesler"
//
//
// Formula : Fluid chemical formula
// Name : Fluid name
// atomList : Array of atom class, structral information
// natom : number of atoms
// M : Molecular weight as calculated from atomic structure
// through class atom and atomList
// MolWt : Molecular Weigth from data file RealGas
// Tfp : Normal freezing point (1 atm), K
// Tb : Normal Boiling point (1 atm), K
// Tc : Critical temperature, K
// Pc : Critical pressure, bar
// Vc : Critical volume, cm^3/mole
// Zc : Critical compresibility factor PcVc/RTc
// Omega : Pitzer's accentric factor
// Dipm : Dipole moment, debyes
// CPVAPA,CPVAPB,CPVAPC,CPVAPD : constants to calculate the
// isobaric heat capacity of the ideal gas Cp kJ/(kmolK)
// DELHF : formation enthalpy, 298.2 K, 1.01325 bar, KJ/kmol
// DELGF : formation gibbs free energy, 298.2 K, 1.01325 bar,KJ/kmol
// Vpeq : vapor pressure equation number
// VPA,VPB,VPC,VPD : vapor pressure equation coefficients
// Tmin : minimum twmp. K
// Tmax : maximum temp. K
// LDEN : liquid density, g/cm^3
// TDEN : temperature that liquid density is given, K
//============================================================
// Reference : The Properties of Gases & Liquids,
// Robert C. Reid, John M. Prausnitz, Bruce E. Pouling
// McGraw-Hill Book Company, ISBN 0-07-051799-1
//==============================================
import java.io.*;
import Text;
import Atom;
import complex;
//==============================================
// implementation of constructors functions
// for class cubicEquationofState
public class LeeKesler
{
String GasEquation;
int natom;
Atom atomList[];
int No;
String Formula,Name;
double M,MolWt,Tfp,Tb,Tc,Pc,Vc,Zc,Omega,Dipm;
double CPVAPA,CPVAPB,CPVAPC,CPVAPD,DELHF,DELGF;
int VPEq;
double VPA,VPB,VPC,VPD,Tmin,Tmax,LDEN,TDEN;
int ierror;
BufferedReader fin;
double R=8314.5; //(J/kmolK)
double a,b,u,w;
//000000
//================================//
// Equation of State coefficients //
//================================//
//Simple Fluid (omega=0) :
//------------------------
double b0[]=new double[4];
double c0[]=new double[4];
double d0[]=new double[2];
double beta0;
double gama0;
double omega0;
//Reference Fluid (n-octane) :
//------------------------
double bR[]=new double[5];
double cR[]=new double[5];
double dR[]=new double[3];
double betaR;
double gamaR;
public LeeKesler(String s1,double le) throws IOException
{
GasEquation="Peng Robinson";
//setting the simple fluid coefficients :
b0[0]=0.1181193;
b0[1]=0.265728;
b0[2]=0.15479;
b0[3]=0.030323;
c0[0]=0.0236744;
c0[1]=0.0186984;
c0[2]=0.0;
c0[3]=0.042724;
d0[0]=0.155488e-4;
d0[1]=0.623689e-4;
beta0=0.65392;
gama0=0.060167;
omega0=0.3978;
//setting the reference fluid coefficients :
bR[0]=0.2026579;
bR[1]=0.331511;
bR[2]=0.027655;
bR[3]=0.203488;
cR[0]=0.0313385;
cR[1]=0.0503618;
cR[2]=0.016901;
cR[3]=0.041577;
dR[0]=0.48736e-4;
dR[1]=0.0740336e-4;
betaR=1.226;
gamaR=0.03754;
int i;
String atomName[];
double atomN[];
int anatom;
ierror=1;
String tempName="";
String tempFormula="";
String aFormula,aName;
double aMolWt,aTfp,aTb,aTc,aPc,aVc,aZc,aOmega,aDipm ;
double aCPVAPA,aCPVAPB,aCPVAPC,aCPVAPD,aDELHF,aDELGF;
int aVPEq;
double aVPA,aVPB,aVPC,aVPD,aTmin,aTmax,aLDEN,aTDEN ;
try{
fin=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("RealGas.txt"));
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.err.println("Error Opening File RealGas.dat\n"+e.toString());
System.exit(1);
}
try{
while(fin!=null)
{
aFormula=Text.readString(fin);
aName=Text.readString(fin);
anatom=Text.readInt(fin);
atomName=new String[anatom];
atomN=new double[anatom];
for(i=0;i<anatom;i++)
{
atomName[i]=Text.readString(fin);
atomN[i]=Text.readDouble(fin);
}
aMolWt=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTfp=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTb=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTc=Text.readDouble(fin);
aPc=Text.readDouble(fin);
aVc=Text.readDouble(fin);
aZc=Text.readDouble(fin);
aOmega=Text.readDouble(fin);
aDipm=Text.readDouble(fin);
aCPVAPA=Text.readDouble(fin);
aCPVAPB=Text.readDouble(fin);
aCPVAPC=Text.readDouble(fin);
aCPVAPD=Text.readDouble(fin);
aDELHF=Text.readDouble(fin);
aDELGF=Text.readDouble(fin);
aVPEq=Text.readInt(fin);
aVPA=Text.readDouble(fin);
aVPB=Text.readDouble(fin);
aVPC=Text.readDouble(fin);
aVPD=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTmin=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTmax=Text.readDouble(fin);
aLDEN=Text.readDouble(fin);
aTDEN=Text.readDouble(fin);
if (aName.equals(s1) || aFormula.equals(s1) )
{
Name=aName;
Formula=aFormula;
MolWt=aMolWt;
Tfp=aTfp;
Tb=aTb;
Tc=aTc;
Pc=aPc;
Vc=aVc;
Zc=aZc;
Omega=aOmega;
Dipm=aDipm;
CPVAPA=aCPVAPA;
CPVAPB=aCPVAPB;
CPVAPC=aCPVAPC;
CPVAPD=aCPVAPD;
DELHF=aDELHF;
DELGF=aDELGF;
VPEq=aVPEq;
VPA=aVPA;
VPB=aVPB;
VPC=aVPC;
VPD=aVPD;
Tmin=aTmin;
Tmax=aTmax;
LDEN=aLDEN;
TDEN=aTDEN;
natom=anatom;
atomList=new Atom[natom];
M=0;
for(i=0;i<natom;i++)
{
atomList[i]=new Atom(atomName[i],atomN[i]);
M+=atomList[i].mass;
}
ierror=0;
break;
}
}
} catch(EOFException e_eof)
{
System.out.println("error required gas "+s1+" is not found");
fin.close();return;
}
fin.close();
}
public String toString()
{
//return the chemical symbol of the gas
String s="";
for(int i=0;i<natom;i++)
s=s+atomList[i].toString();
return s;
}
public double Z(double T, double V)
{
double Tr=T/Tc;
double Vr=V/Vc;
double B0,C0,D0;
double BR,CR,DR;
double Z0,ZR,ZX;
B0=b0[0]-b0[1]/Tr-b0[2]/(Tr*Tr)-b0[3]/(Tr*Tr*Tr);
C0=c0[0]-c0[1]/Tr+c0[2]/(Tr*Tr*Tr);
D0=d0[0]+d0[1]/Tr;
Z0=1+B0/Vr+C0/(Vr*Vr)+D0/(Vr*Vr*Vr*Vr*Vr)
+ c0[3]/(Tr*Tr*Tr*Vr*Vr)*(beta0+gama0/(Vr*Vr))*Math.exp(-gama0/(Vr*Vr));
BR=bR[0]-bR[1]/Tr-bR[2]/(Tr*Tr)-bR[3]/(Tr*Tr*Tr);
CR=cR[0]-cR[1]/Tr+cR[2]/(Tr*Tr*Tr);
DR=dR[0]+dR[1]/Tr;
ZR=1+BR/Vr+CR/(Vr*Vr)+DR/(Vr*Vr*Vr*Vr*Vr)
+ cR[3]/(Tr*Tr*Tr*Vr*Vr)*(betaR+gamaR/(Vr*Vr))*Math.exp(-gamaR/(Vr*Vr));
ZX=Z0+Omega/0.3978*(ZR-Z0);
return ZX;
}
double P(double T, double V)
{
double Tr=T/Tc;
double Vr=V/Vc;
return Z(T,V)*Tr/Vr;
}
/*
public double V(double T, double P)
{
return Z(T,P)*R*T/(P*1e5);
}
public double Pvp(double T)
{
switch ( VPEq)
double cPvp;
case 1:
{
cPvp=Pc*Math.exp((VPA*x+VPB*Math.pow(x,1.5)+VPC*x*x*x+VPD*x*x*x*x*x*x)/(1-x));
break;
}
case 2:
{
cPvp=VPA-VPB/T+VPC*Math.log(T)+VPD
break;
}
case 3:
{
break;
}
return cPvp;
}
*/
}
Programın veri dosyasından bazı gazların özelliklerini örnek olarak verirsek:
H2 Hydrogen
1
H 2
2.016 14 20.3 33 12.9 64.3 0.303 -0.216 0
27.14 9.274e-3 -1.381e-5 7.645e-9 0 0
1 -5.57929 2.60012 -0.85506 1.70503 14 33 0.071 20
H2O Water
2
H 2
O 1
18.015 273.2 373.2 647.3 221.2 57.1 0.235 0.334 1.8
3.224 1.924e-3 1.055e-5 -3.596e-9 -2.42e5 -2.288e5
1 -7.76451 1.45838 -2.7758 -1.23303 275 647.3 0.998 293
CH4 Methane
2
C 1
H 4
16.043 90.7 111.6 190.4 46 99.2 0.288 0.011 0
19.25 5.213e-2 1.197e-5 -1.132e-8 -7.49e4 -5.087e4
1 -6.00435 1.1885 -0.83408 -1.22833 91 190.4 0.425 112
Sanırım son birkaç örnek gerçek programlama ortamında veri dosyalarının
kullanılması hakkında daha iyi bir fikir vermiştir. Buradaki tüm örnekler
sıralı (sequential) tip veri dosyası işlemektedir. Aynı işlemler veri tabanı
kullanılarak da yapılabilirdi.
<< index
< bölüm 9
> bölüm 11
bölüm başı










