 |

Index |
Civil Aviation |
Military Aviation |
Equipment |
Articles |
People |
Tanks |
Military Forum |
Military Encyclopedia

|
|
The MiG-21 Fishbed
in Cuba
By Rubén
|
 |
  The
best second generation soviet fighter, and one of the main fighters in
the world in the 60-80’s. Begin to be created in 1954, its prototyp
performs the first flight May 28, 1958 by the pilot V.A. Nefedov.
25 main modifications were built in series and 30 experimental versions.
In the USSR in 1960-1983 were built 10,158 fighters. They were produced
too by licence in Czechozlovakia (194 aircrafts Aero MiG-21F-13), India
(600 HAL MiG-21FL, M and bis) and China (1,000 Jian J-7/F-7), with a total
of MiG-21 built of over 12,000, that was the more numerous second
generation fighter in the world. It has 17 World records registered by
the FAI. Fought in almost all the important conflicts of the 60-90’s.
Numerically the MiG-21 has been the most important warplane in the Cuban
Air Force for most of its existence. The
best second generation soviet fighter, and one of the main fighters in
the world in the 60-80’s. Begin to be created in 1954, its prototyp
performs the first flight May 28, 1958 by the pilot V.A. Nefedov.
25 main modifications were built in series and 30 experimental versions.
In the USSR in 1960-1983 were built 10,158 fighters. They were produced
too by licence in Czechozlovakia (194 aircrafts Aero MiG-21F-13), India
(600 HAL MiG-21FL, M and bis) and China (1,000 Jian J-7/F-7), with a total
of MiG-21 built of over 12,000, that was the more numerous second
generation fighter in the world. It has 17 World records registered by
the FAI. Fought in almost all the important conflicts of the 60-90’s.
Numerically the MiG-21 has been the most important warplane in the Cuban
Air Force for most of its existence.
 Cuban Missiles Crisis
Cuban Missiles Crisis
The first unit of the USSR in receiving the MiG-21 and
to be list was the 32° Fighter Regiment of the Guard (32° Gv.IAP),
of the Colonel N.V. Shibanov, based in Kubinka (near Moscow), that begins
to receive the MiG-21F-13 in 1961. The Regiment already was ready in the
first half of 1962, when in June of 1962 receives the secret order of disarming
again the MiG-21F-13 and to be prepared to be transferred in train to the
port Baltiisk and then to Cuba. The Regiment has of 40 MiG-F-13,
6 trainers MiG-15UTI and a liason airplane Yak-12. For the secret operation,
it was renamed then as 213° IAP. They leave at the beginning of September
to Cuba and arrive two weeks later. The 213° regiment formed part of
the 12° Anti-Aircraft Defense Division of the soviets troops in Cuba.
The MiG-21F-13 are frantically assembled in Santa Clara and the September
18, 1962 the first MiG-21F-13 does its first flight in Cuba. To end of
September already all the regiment was ready. On October 22 begins the
Missile Crisis, and that was the first combat alarm. By the danger to be
attacked in ground, the regiment is dispersed on October 24 between San
Antonio, Santa Clara and Camaguey.
American airplanes performed daily recon flights over them, and November
4 by San Antonio two F-104C Starfighter of the 479° Tactical Wing are
intercepted by a MiG-21F-13, that imitates to open fire, and the F-104C
retire in full speed. The Americans do not appear more over the MiG-21
bases. These MIG-21F-13 don´t carried any national insignia.
This encounter has its consequences. The Cubans and Russian monitoring
the US radio notice, that the F-104C pilot reported being intercepted by
“Pirats planes without insignia”. Immediately all the MiG-21 were painted
with the Cuban insignia.
The supposed western reports that the MiG-21 in Cuba during that Crisis
fought in any form against the American airplanes, have noy base. Neither
the VVS neither the FAR claim any shoot down or fights, neither shot its
arm never.
During the Missile Crisis the USAF discovered that the radars APS-95
(a modernized APS-20) of his EC-121 of the airborne early warning and Control
(AEW & C, precursor of the AWACS) cannot detect low-flying MiG-21 because
the ground clutter. As a measurement of emergency was developed the system
QRC-248 to interrogate the IFF systems of the MiG-21. With this solution
they can detect the low-level Cuban MiG-21, and that system was later employed
in Vietnam.

|

|

|

|

|
|
Photo taked by an U-2 spy plane during the Crisis.
The MiG-21 of the VVS beside the FAR´s MiG-15 in the Santa Clara
AB
|
Fidel Castro beside an MiG-21F-13 the DAAFAR Day
in San Antonio, April 17 of 1963. Photo Mijail Isaev
|
The Cuban pilots beside theirs MiG-21F-13 during
the official delivery to the FAR. San Antonio, August 10 of 1963 (Enrique
Carreras, Por el dominio del aire)
|
Some MiG-21F-13 passing in low level over the
public during an exibition at the Havana coast, 1966
|
Technicians beside the MiG-21F-13 N°25 with
IR missiles R-3S, of an Fighter Squadron Holguin (Photo Henry Pérez,
Piloto Maestro)
|
 The First Mach 2 fighter in Latin America
The First Mach 2 fighter in Latin America
After the Crisis, at the beginning
of 1963 the Soviet Government decide to transfer their equipment to Cuba,
and to trained the Cubans pilots and technicians in the MiG-21. In April
of 1963 Cuban pilot first soloed. In summer already was ready the first
FAR MiG-21F-13 Regiment, his Leader are Alvaro
Prendes. On August 10 the soviets finally deliver all the MiG-21F-13
and go home. Entering the MiG-21 in service in Cuba officially on
August 10, 1963, the FAR becomes one of its first users, at the same time
that important allies of the USSR as East Germany, Czechoslovakia, China,
Poland and the India, what shows the level of priority of the Cuban FAR
in the USSR. In the same summer of 1963 the MiG-21 piloted by Cubans
do their first combat exercises over the Havans’s coast, sinking a ship
in company with the MiG-15bis.

|

|

|

|

|
|
MiG-21F-13 in low flight over an ZU-23-4 in the
Havana coast, 1966
|
MiG-21F-13 in the same exercises over Habana in
1966
|
MiG-21F-13 Squadron in San Antonio, on the 60´s
|
A MiG-21UM Mongol B in 1985, the maining trainning
plane
|
The MiG-21MF arrives in 1974 and some are in service
today
|
 Cuban MiG-21 in combat
Cuban MiG-21 in combat
The participation of the Cuban MiG-21
in others conflicts are described in the articles about the Angolan
War, the Ethiopian War (Ogaden), the"Operation
Pico" against the Dominican Republic, and actions against Bahamas.
 The MiG-21 today in Cuba
The MiG-21 today in Cuba
 Little
time after the arrival of the MiG-21F-13 in 1962, the park of the FAR is
reinforced with new versions of this fighter, as the PF. In 1966 arrives
an MiG-21PFM Squadron, another Squadron with MiG-21PFMA, and the first
two seats training versions MiG-21U. All are based in San Antonio.
In 1967 arrives a second Squadron of MiG-21PFMA to San Antonio, and is
transferred to Holguin an MiG-21F-13 Squadron. In 1968 arrive the MiG-21MF
and two seats trainers UM for San Antonio, then passes to Holguin the second
MiG-21F-13 Squadron. Arrive the Recon Fighter MiG-21R, that helps in the
exploration and maneuvers. In 1975 arrives two MF Squadrons, one is sent
to Angola in January of 1976. In October of 1976 in San Antonio are assembled
the better version of this fighter, the MiG-12bis, of the third generation.
Other Squadrons of MiG-21bis follow being received in the 80’s, and in
1989-1990 various fighters return from Angola, being the more numerous
equipment of the FAR. Little
time after the arrival of the MiG-21F-13 in 1962, the park of the FAR is
reinforced with new versions of this fighter, as the PF. In 1966 arrives
an MiG-21PFM Squadron, another Squadron with MiG-21PFMA, and the first
two seats training versions MiG-21U. All are based in San Antonio.
In 1967 arrives a second Squadron of MiG-21PFMA to San Antonio, and is
transferred to Holguin an MiG-21F-13 Squadron. In 1968 arrive the MiG-21MF
and two seats trainers UM for San Antonio, then passes to Holguin the second
MiG-21F-13 Squadron. Arrive the Recon Fighter MiG-21R, that helps in the
exploration and maneuvers. In 1975 arrives two MF Squadrons, one is sent
to Angola in January of 1976. In October of 1976 in San Antonio are assembled
the better version of this fighter, the MiG-12bis, of the third generation.
Other Squadrons of MiG-21bis follow being received in the 80’s, and in
1989-1990 various fighters return from Angola, being the more numerous
equipment of the FAR.
In total from 1962 to 1989 to Cuba arrives some 270 MiG-21 fighters
in 9 versions
-
MiG-21F-13 Fishbed C -1962 (built in 1958-1965)
-
MiG-21PF Fishbed D -1964 (1962-1964)
-
MiG-21PFM Fishbed F -1966 (1964-1968)
-
MiG-21PFMA Fishbed J -1966 (1968-1971)
-
MiG-21U Mongol A -1966 (1962-1968)
-
MiG-21MF Fishbed J -1974 (1970-1974)
-
MiG-21R Fishbed H -1968 (1965-1971)
-
MiG-21UM Mongol B -1968 (1971-1974)
-
MiG-21bis Fishbed N -1976 (1972-1983)
Today are in service some 150 MiG-21 in service in 10 Squadron of 5 Regiments
(30 MiG-21 in each): They are 90 MiG-21bis, 60 MiG-21MF and 10 two seats
MiG-21UM Mongol B. Their mission are air defense, and attack. Almost all
these equipment are in good state, in part are in conservation to save
the parts stocks and the motor resource, that are received in very limited
quantities since 1990.
| Zona Aérea Occidental. 2°
Brigada de la Guardia "Playa Girón" |
21° Regimiento de Caza, San Antonio (211° y 212° Escuadrones,
30 MiG-21bis/UM)
22° Regimiento de Caza, Baracoa (221° y 222° Escuadrones,
30 MiG-21bis/UM) |
| Zona Aérea Central. 1°
Brigada de la Guardia "Batalla de Santa Clara" |
11° Regimiento de Caza, Santa Clara (111° y 112° Escuadrones,
30 MiG-21bis/UM)
12° Regimiento de Caza, Sancti Spiritus (121° y 122° Escuadrones,
30 MiG-21MF/UM) |
| Zona Aérea Oriental. 3°
Brigada de la Guardia "Cuartel Moncada" |
| 31° Regimiento de Caza, Camagüey (311° y 312° Escuadrones,
30 MiG-21MF/UM) |
 Characteristics of the Cubans MiG-21 Fishbed
Characteristics of the Cubans MiG-21 Fishbed
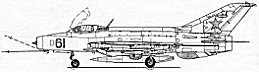
 MiG-21F-13 Fishbed
C (type 74). Diurnal fighter without radar, with radiometr SRD-5M Kvant. MiG-21F-13 Fishbed
C (type 74). Diurnal fighter without radar, with radiometr SRD-5M Kvant.
Built in 1958-1965 in three factories of the USSR. Canopy of
one piece, open toward to protect pilot.
Two missiles under wings. |
|
 MiG-21PF Fishbed D
(type
76). Radar Sapfir RP-21. Built in 1962-1964. Better engine. Without internal
gun, alone suspended, two missiles under wings. Canopy of two pieces,
additional fuel. MiG-21PF Fishbed D
(type
76). Radar Sapfir RP-21. Built in 1962-1964. Better engine. Without internal
gun, alone suspended, two missiles under wings. Canopy of two pieces,
additional fuel. |

|
 MiG-21PFM Fishbed
F (type 77). Built in 1964- 1968. Radar Sapfir RP-21M. Four point
under wings for missiles, internal gun. New engine with the system SPS
for the blown of the flaps. Parachute in the tail base. MiG-21PFM Fishbed
F (type 77). Built in 1964- 1968. Radar Sapfir RP-21M. Four point
under wings for missiles, internal gun. New engine with the system SPS
for the blown of the flaps. Parachute in the tail base. |

|
 MiG-21PFMA Fishbed
J (type 96). Export version of the PFM. Built in 1968-1971. Radar RP-22S.
System SPS, more combat load. MiG-21PFMA Fishbed
J (type 96). Export version of the PFM. Built in 1968-1971. Radar RP-22S.
System SPS, more combat load. |

|
 MiG-21R Fishbed H
(type 94R). Version based on the recon PFM version, with pod under fuselage
that load photo and TV cameras, IR sensors and laser or SLAR, equipment
of electronic countermeasures under wings. MiG-21R Fishbed H
(type 94R). Version based on the recon PFM version, with pod under fuselage
that load photo and TV cameras, IR sensors and laser or SLAR, equipment
of electronic countermeasures under wings. |

|
 MiG-21MF Fishbed J
(type 96F). Built in 1970-1974. More powerful engine, new radar RP-22,
mirror, additional tank of fuel of greater volume. Close combat missiles
R-60 MiG-21MF Fishbed J
(type 96F). Built in 1970-1974. More powerful engine, new radar RP-22,
mirror, additional tank of fuel of greater volume. Close combat missiles
R-60 |

|
 MiG-21bis Fishbed
N (type 75B). Third generation fighter, the best version, optimized
for agile combats at low level, combat load expanded. Radar Sapfir-21.
Additional fuel and new engine. MiG-21bis Fishbed
N (type 75B). Third generation fighter, the best version, optimized
for agile combats at low level, combat load expanded. Radar Sapfir-21.
Additional fuel and new engine. |

|
 MiG-21U Mongol A.(Type
66). Two seat training version of the F-13. First flight October 17, 1960.
Built in Moscow in 1964-1968. Fuel reduced to 2350 liters, two point under
wings, without radar. MiG-21U Mongol A.(Type
66). Two seat training version of the F-13. First flight October 17, 1960.
Built in Moscow in 1964-1968. Fuel reduced to 2350 liters, two point under
wings, without radar. |

|
 MiG-21UM Mongol B.
(Type 69). Two seat training version of the PFM. Built in Tbilisi
since 1971. Four point under wings, parachute, vertical tail of greater
surface, more fuel and modernized engine MiG-21UM Mongol B.
(Type 69). Two seat training version of the PFM. Built in Tbilisi
since 1971. Four point under wings, parachute, vertical tail of greater
surface, more fuel and modernized engine |

|
| Nombre |
MiG-21
F-13
Fishbed
C
|
MiG-21
PF
Fishbed
D
|
MiG-21
PFM
Fishbed
F
|
MiG-21
PFMA
Fishbed
J
|
MiG-21
MF
Fishbed
J
|
MiG-21
bis
Fishbed
N
|
MiG-21
R
Fishbed
H
|
MiG-21
U
Mongol
A
|
MiG-21
UM
Mongol
B
|
Year
Dimensions
Lenght, m
Wingspan,m
Height, m
Wing area, m2
Weights
Empty weight, kg
Normal weight, kg
Max weight, kg
Internal fuel, kg
Adicional fuel, kg
Engine
Type Tumansky, version
Dry thrust, kg
After/b thrust, kg
Performances
Max speed at 0,kmh
Max speed, km/h
Ceiling, m
Climb, m/s
Range, km
Range with load,km
G |
1958
-
15,76
7,15
4,10
22,95
-
4980
7370
8625
2115
665
-
R-11F-300 3900
5740
-
1150
2175
19000
130
1300
1670
7
|
1962
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
-
7750
8770
2280
665
-
R-11F2-300 3950
6120
-
1300
2175
19000
160
1400
1770
8
|
1964
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
5350
7820
9080
2200
665
-
R-11F2S-300 3900
6175
-
1300
2230
19000
160
1300
1670
8,5
|
1968
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
5950
8200
-
2200
665
-
R-11F2S-300 3900
6175
-
1300
2230
17300
204
1050
1420
8,5
|
1970
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
5350
8200
9400
2200
810
-
R-13-300 4070
6490
-
1300
2230
18200
204
1050
1420
8,5
|
1972
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
5450
8725
10420
2390
810
-
R-25-300
4100*
7100-9900 -
1300
2175
17500
225
1120
1470
8,5
|
1965
-
14,50
7,15
4,71
22,95
-
-
8100
-
2330
810
-
R-11F2S-300 3900
6175
-
1150
2230
15100
-
1130
1600
8,5
|
1960
-
15,76
7,15
4,80
22,95
-
-
7800
-
1950
665
-
R-11F-300 3900
5740
-
1150
2175
18300
-
1210
1460
7,0
|
1971
-
14,41
7,15
4,80
22,95
-
-
8000
-
2030
665
-
R-11F2S-300 3900
6175
-
1150
2175
17300
-
1210
1460
7,0
|
* The MiG-21bis engine have an adicional afterburning regime with 9,900kg
thrust during 3 minuts.
 Armament
Armament
| MiG-21F-13 |
One Gun NR-30 x 30mm with 30 rounds, 2 blocs UB-16-57U
or UB-32-57U with 16-32 rockets S-5 x 57mm, or 2 rockets S-24, or 2 bombs
of 50-500kg, 2 air- air missiles R-3S. Combat load 1,000 kg |
| MiG-21PF |
Withouth gun. Two K-13 or R-3S missiles. Rockets and bombs like the
F-13 |
| MiG-21PFM |
One GSh-23 gun x 23mm. Four missiles K-13, R-3S, RS-2US (K-5) or air-surface
rockets X-66, pod GP-9 under fuselage with GSh-23 Gun x 23mm |
| MiG-21PFMA |
One GSh-23 gun x 23mm with 200 rounds. Four missiles K-13M, RS-2UM,
R-55, R-3S/R, rockets x 57 and 240mm, bombs until 500kg. Combat load 1,300
kg |
| MiG-21MF |
One GSh-23 gun x 23mm with 200 rounds. Four misiles K-13M, RS-2UM,R-3S/R,
R-55, R-60, R-60M, rockets x 57 and 240mm, bombs until 500kg. Combat load
1,300kg |
| MiG-21bis |
One GSh-23 gun x 23mm with 200 rounds. Four missiles K-13M, RS-2UM,R-3S/R,
R-60, R-60M, four rockets blocs UV-16-57 x 57mm, four rockets x 240mm,
bombs until 500kg. Combat load 2,000kg |
| MiG-21R |
GP-9 with GSh-23 gun x 23mm with 200 rounds in the place of the recon
pod. Two air -air missiles K-13 or R-3S. |
| MiG-21U, UM |
Machine gun A-12,7 x 12,7mm, 2 missiles K-13. Combat load 1,000 kg |
 Photos
Photos

|

|

|

|
 |
|
MiG-21R in the DAAFAR Museum (Photo Rubén)
|
A MiG-21R landing with this D pod of 285kg with
recon equipment
|
MiG-21bis and MiG-21UM in the San Antonio AB (Courtesy
of Air & Space Power Journal)
|
Official delivery of some MiG-21bis and MiG-21UM
to the FAR. San Antonio, 1981
|
The candidat to cosmonaut Captain Jose López
Falcon in a MiG-21bis
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
MiG-21bis exhited to the public in Havana
(Courtesy Tulio Soto)
|
Pair of MiG-21bis with different camouflage
|
Photo of SR-71 with MiG-21 in the San Julian AB,
80´s
|
MiG-21R with R pod (Courtesy of Air & Space
Power Journal)
|
Rafael del Pino and his son Ramsés in a
MiG-21UB
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
MiG-21bis (Courtesy of Luis P.)
|
MiG-21 Profiles
|
|
|
|
|

 Little
time after the arrival of the MiG-21F-13 in 1962, the park of the FAR is
reinforced with new versions of this fighter, as the PF. In 1966 arrives
an MiG-21PFM Squadron, another Squadron with MiG-21PFMA, and the first
two seats training versions MiG-21U. All are based in San Antonio.
In 1967 arrives a second Squadron of MiG-21PFMA to San Antonio, and is
transferred to Holguin an MiG-21F-13 Squadron. In 1968 arrive the MiG-21MF
and two seats trainers UM for San Antonio, then passes to Holguin the second
MiG-21F-13 Squadron. Arrive the Recon Fighter MiG-21R, that helps in the
exploration and maneuvers. In 1975 arrives two MF Squadrons, one is sent
to Angola in January of 1976. In October of 1976 in San Antonio are assembled
the better version of this fighter, the MiG-12bis, of the third generation.
Other Squadrons of MiG-21bis follow being received in the 80’s, and in
1989-1990 various fighters return from Angola, being the more numerous
equipment of the FAR.
Little
time after the arrival of the MiG-21F-13 in 1962, the park of the FAR is
reinforced with new versions of this fighter, as the PF. In 1966 arrives
an MiG-21PFM Squadron, another Squadron with MiG-21PFMA, and the first
two seats training versions MiG-21U. All are based in San Antonio.
In 1967 arrives a second Squadron of MiG-21PFMA to San Antonio, and is
transferred to Holguin an MiG-21F-13 Squadron. In 1968 arrive the MiG-21MF
and two seats trainers UM for San Antonio, then passes to Holguin the second
MiG-21F-13 Squadron. Arrive the Recon Fighter MiG-21R, that helps in the
exploration and maneuvers. In 1975 arrives two MF Squadrons, one is sent
to Angola in January of 1976. In October of 1976 in San Antonio are assembled
the better version of this fighter, the MiG-12bis, of the third generation.
Other Squadrons of MiG-21bis follow being received in the 80’s, and in
1989-1990 various fighters return from Angola, being the more numerous
equipment of the FAR.


 The
best second generation soviet fighter, and one of the main fighters in
the world in the 60-80’s. Begin to be created in 1954, its prototyp
performs the first flight May 28, 1958 by the pilot V.A. Nefedov.
25 main modifications were built in series and 30 experimental versions.
In the USSR in 1960-1983 were built 10,158 fighters. They were produced
too by licence in Czechozlovakia (194 aircrafts Aero MiG-21F-13), India
(600 HAL MiG-21FL, M and bis) and China (1,000 Jian J-7/F-7), with a total
of MiG-21 built of over 12,000, that was the more numerous second
generation fighter in the world. It has 17 World records registered by
the FAI. Fought in almost all the important conflicts of the 60-90’s.
Numerically the MiG-21 has been the most important warplane in the Cuban
Air Force for most of its existence.
The
best second generation soviet fighter, and one of the main fighters in
the world in the 60-80’s. Begin to be created in 1954, its prototyp
performs the first flight May 28, 1958 by the pilot V.A. Nefedov.
25 main modifications were built in series and 30 experimental versions.
In the USSR in 1960-1983 were built 10,158 fighters. They were produced
too by licence in Czechozlovakia (194 aircrafts Aero MiG-21F-13), India
(600 HAL MiG-21FL, M and bis) and China (1,000 Jian J-7/F-7), with a total
of MiG-21 built of over 12,000, that was the more numerous second
generation fighter in the world. It has 17 World records registered by
the FAI. Fought in almost all the important conflicts of the 60-90’s.
Numerically the MiG-21 has been the most important warplane in the Cuban
Air Force for most of its existence.







































