Chemistry Principles
Whether it be organic or inorganic chemistry, the basic principles of chemistry apply to molecules universally. The chemical principles that most influence the chemistry of viruses and medication are same things that effect protein and DNA conformation.
Understanding how proteins work in general would help create proteins that would interact and interfere with HIV. Proteins, like any other macro molecules, obey the same rules of chemistry.
Understanding proteins:
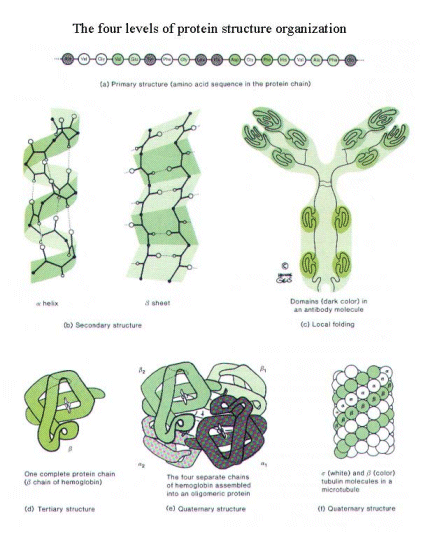
Proteins are polymers of amino acids, they consist of a chain of amino acids covalently bonded. The covalent bonding between amino acids can be predicted by the VESPER theory. Proteins differ from each other by the arrangement of the amino acids as well as the conformation of the protein. There are four levels to describe the structure of a protein but three are important for our purpose.
-
Primary structure of a protein is the order of the amino acids. The bonds in-between are covalent bonds and are determined by VESPER theory. Those covalent bonds are called peptide bonds.
-
The secondary structure of a protein is its three-dimensional shape that results from hydrogen bonding between the amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids. Electro negativity and other weak forces play a major role in the 2nd degree structural conformation.
-
The 3rd structure is caused by stronger forces than in secondary structure and also help determine the protein's 3d conformation. Hydrogen bonding and Ionic bonding plays a major role in formation of the tertiary structure. Hydrophobic effect is also present in formation of tertiary structure. It is determined by the polar nature of water molecules which often surround the protein.
There are outside
factors that effect the structure of the protein. One key thing that we have
studied recently in class is the acidity. Acidity of the solution that a
protein in often changes the conformation of the protein and can be used to
make protein less or more effective.
Another factor that effects the structure of a protein is temperature. A
large degree of change in temperature is known to alter the structure of
protein so much that it makes it no longer work properly. This is called
"denaturing".