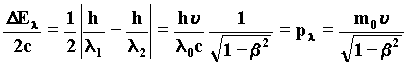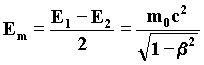Energy and its variations The waves of every particle-source of waves that is in motion compared with an ideal observer, are seen by him as endowed with wavelenghts having values that are analogous to the relativistic Doppler effect formula.
Fig. 5
We mark with E1the energy of the waves in front of the particle in motion, and with E2 the energy of the waves behind the particle, (that are different because of the Doppler effect). Firstly, the real observer sees the particle getting closer to him, after, passing in front of him and finally, going away. This experimented variation is DE.
18)
DE = E1 - E2 He verifies an energy variation deriving from the particle and describes the observable energy variation starting from the energy of the rest particle that cannot be observed:
The theory could be originally falsified with the verification of an experiment aiming at showing the possible perception of a photon composed by decreasing frequencies, and coming from a particle in an
uniform motion, (for example, setting a detector on a rotating drum, and reflecting this photon in a "mirror at optic coniugio of phase", that is a mirror endowed with a device that inverts the sequence of wavefronts, compared with the normal reflection ).
This would be an original, experimental, Popperian attempt to falsify the new wave model.Actually, if we consider the energy of the particle:
Fig. 6
we see that the values of a perceivable energy oscillate around E = mc2.
It follows that the average of the variation of the really observed wave energy is equivalent to the relativistic momentum of the particle:
19)
pl is the same momentum described by De Broglie for the wave that is associated with the particle in motion having a wavelenght:
20)
In this way the energy variation is identified with the energy of the photon that can be perceived by the real observer:
21)
while the medium energy of the particle is its relativistic energy:
22)
So we have connected the wave dynamics, of the new wave model, with the DeBroglie wave and with the relativistic dynamics.