Trigonometry deals with the relations between angles and sides of triangles.
The 180 degree rule: The three angles of any triangle add up to 180 degrees. Therefore of 2 angles of a triangle or known the other can be calculated by simply subtracting the sum of the two given angles from 180.
A right triangle is one which contains a 90 degree angle.
- We know that the other 2 angles add up to 90 degrees.
- The side opposite of the right angle is termed the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse will always be the longest side of a right triangle.
- The angles are labeled A, B, C with the hypotenuse being C
- The side opposite angle A is labeled a.
- The side opposite angle B is labeled b.
- The side opposite angle C is labeled c.
c2 = a2 + b2
Three common functions of an angle are called
sine (sin)
cosine (cos)
tangent (tan)
For any angle q, (A,B, or C) these functions are expressed as:
a) sin q = opposite side / hypotenuse
b) cos q = adjacent side / hypotenuse
c) tan q = opposite side / adjacent side
Angle A in a right triangle is 30O, the hypotenuse is 8.0 cm, what is the length of side b?
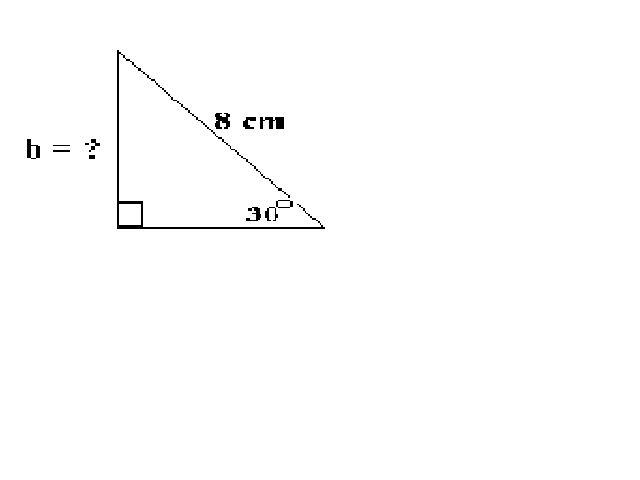
q = A = 30O Cos q = adjacent (b) / hypotenuse (c)
C = 90O b = Cos q * c
c = 8.0 cm b = Cos 30O * 8.0 cm
b = ? b = 6.9 cm