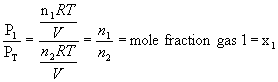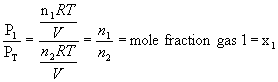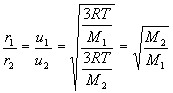Chapter 10: Gases
10.1 Characteristics of Gases
nonmetallic, low molar mass, simple molecular formula
vapors – liquid in gaseous state
volume gas = volume container
increase pressure, decrease volume
gases for homogeneous mixtures
10.2 Pressure
10.2.1 Atmosphere Pressure and the Barometer
- F = ma
- 1 pa = 1 N/M2
- standard atmospheric pressure
- 760mm Hg = 1.01325 x 105 pa
- 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = 1.01325 x 105 pa
10.2.2 Pressures of Enclosed Gases and Manometers
- Pgas = Ph1 closed end manometer
- Pgas + Ph2 = Patm open end (less than atmospheric pressure)
- Pgas = Patm + Ph3 gas pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure
10.3 The Gas Laws
- four variable to define physical condition (state) of gas
- T, P, V, and amount (moles, n)
10.3.1 The Pressure – Volume Relationship; Boyle’s law
- Boyle’s Law – the volume of a fixed quantity of gas maintained at constant temp is inversely proportional to pressure
- V = constant x 1/P or PV = constant
10.3.2 The Temperature – Volume relationship: Charles’s law
- Charles’s law = volume is directly proportional to absolute temperature at constant pressure
- V = constant x T or V/T = constant
10.3.3 The Quantity – Volume Relationship: Avogadro’s Law
- Avogadro’s hypothesis – equal volumes of gases at same temperature and pressure have equal number of molecules
- Avogadro’s law = volume of gas is directly proportional to number of moles of gas at constant temperature and pressure
- V = constant x n
10.4 The Ideal – Gas Equation
- ideal gas equation = PV = nRT
- R = gas constant
- STP = 0 degrees Celsius and 1 atm
10.4.1 Relationship Between the Ideal – Gas Equation and the Gas Laws
- PV = nRT = constant or PV = constant
- P1V1 = P2V2
- PV/T = nR = constant so P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
10.5 Further Applications of the Ideal – Gas Equation
10.5.1 Gas Densities and Molar Mass
10.5.2 Volume of Gases in Chemical Reactions
- calculate volume of gases consumed or produced
10.6 Gas Mixtures and Partial Pressures
- Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure – total pressure of mixture of gases = sum of pressure that each would exist if alone
- PT = P1 + P2 + P3 + …
- PT = nT x RT/V
10.6.1 Partial Pressures and Mole Fractions
- 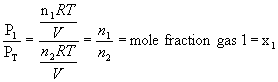
10.6.2 Collecting Gases Over Water
10.7 Kinetic – Molecular Theory
- kinetic molecular theory
- 1) gases of large # molecules are in continuous random motion
- 2) volume of Molecules negligible compared to total volume of container
- 3) attractive and repulsive forces negligible
- 4) energy can be transferred in collisions but average kinetic energy stays same if constant temperature
- 5) average kinetic energy of molecules proportional to absolute temperature
- individual molecules in gases have varying speeds
- root – mean square (rms) speed, u, varies in proportion to square root of absolute temperature and inversely with square root of molar mass
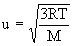
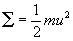
(average kinetic energy of gas molecules)
10.7.1 Application to the Gas Laws
- 1)effect of volume increases at constant temperature
- pressure decreases, fewer collisions with container wall
- 2) effect of temperature increase at constant volume
- change in momentum of collisions increase, pressure increases
10.8 Molecular Effusion and Diffusion
- effusion – escape of gas molecule through tiny hole into evacuated space
- diffusion – speed of one substance throughout space
10.8.1 Graham’s law of Effusion
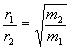 rate of effusion directly proportional to rms
rate of effusion directly proportional to rms
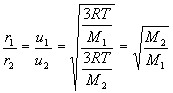 10.8.2 Diffusion and Mean free path
diffusion faster for light molecules
diffusion slower than molecular speeds because of collisions
mean free path – average distance traveled by a molecule between collisions
10.8.2 Diffusion and Mean free path
diffusion faster for light molecules
diffusion slower than molecular speeds because of collisions
mean free path – average distance traveled by a molecule between collisions
10.9 Real Gases: Deviation from Ideal Behavior
- gases deviate from ideal behavior at higher pressure
- gases deviate from ideal behavior with decrease in temperature
- molecules in ideal gas assumed to occupy no space and have no attractions for one another
- real molecules have finite volumes and attract one another
- at high pressures impact on container wall from molecules lessened
- temperature determines how effective attractive forces are; decrease in temp = more effective
10.9.1 The van der Waals equation
- van der Waals equation:
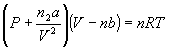
- a, b different for each gas
- a, b increase with increase in mass and complexity of structure
- larger, massive molecule have larger volumes, greater intermolecular attractive forces