Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
1.2.2 Radioactivity
1.2.3 The Nuclear Atom
|
Particle |
Charge |
Mass (amu) |
|
Proton |
Positive |
1.0073 |
|
Neutron |
None |
1.0087 |
|
Electron |
Negative |
5.486*10-4 |


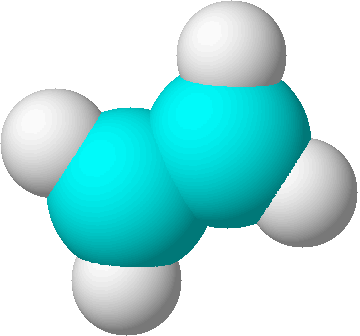
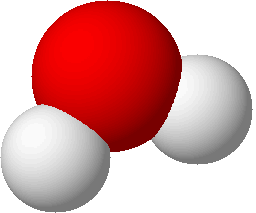
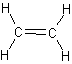 structural formulas
structural formulas perspective drawing
perspective drawing
 ball-and-stick models
ball-and-stick models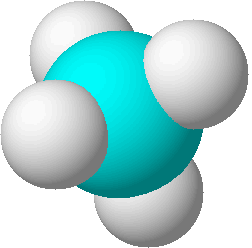
|
Anion |
Acid |
|
____ide |
Hydro____ic acid |
|
____ate |
_____ic acid |
|
____ite |
_____ous acid |
|
Prefix |
Meaning |
|
Mono- |
1 |
|
Di- |
2 |
|
Tri- |
3 |
|
Tetra- |
4 |
|
Penta- |
5 |
|
Hexa- |
6 |
|
Hepta- |
7 |
|
Octa- |
8 |
|
Nona- |
9 |
|
Deca- |
10 |