5.2.3 Endothermic and Exothermic Processes
- endothermic absorption of heat by system
- exothermic evolution of heat
5.2.4 State Functions
- state function property of system determined by specifying its conditions
- value of state function does not depend on particular history of sample only its present conditions
- E is a state function - D
E depends only on initial and final states
5.3 Enthalpy
- enthalpy heat absorbed or released under constant pressure
- change in enthalpy equals heat gained or lost by system when process occurs under constant pressure
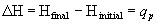
- +D
H system gains heat, endothermic
- -D
H system releases heat, exothermic
5.4 Enthalpies of Reaction
- D
H = H(products) H(reactants)
- enthalpy of reaction energy change in a reaction
- thermochemical equations balanced equations that show enthalpy change
- guidelines for using thermochemical equations and enthalpy diagrams
- 1) enthalpy is an extensive property
- magnitude of D
H directly proportional to amount of reactant consumed in process
- 2) enthalpy change for reaction equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to D
H for reverse reaction
- 3) enthalpy change for a reaction depends on state of reactants and products
5.5 Calorimetry
- calorimetry measurement of heat flow
- calorimeter measures heat flow
5.5.1 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat
- heat capacity amount of heat required to raise temperature by 1K or 1°
C
- molar heat capacity heat capacity of 1mol of substance
- specific heat heat capacity of 1g of substance
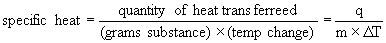
5.5.2 Constant Pressure Calorimetry

- dilute aqueous solutions have specific heats that are the same as water
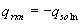
- temperature increase (+D
T) reaction is exothermic (-qrxn)
5.5.3 Bomb Calorimeter (constant volume calorimeter)
- bomb calorimeter used to study combustion in reactions
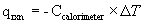
- Ccalorimeter heat capacity of calorimeter
- Because constant volume heat transferred corresponds to energy change rather than enthalpy change
5.6 Hesss Law
- Hesss Law if a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, D
H for the reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps
- Always get same value of D
H for overall reaction, regardless of steps
5.7 Enthalpies of Formation
- enthalpy of formation enthalpy change from formation of a compound (D
Hf)
- standard state 1atm and 298K (25°
C)
- standard enthalpy enthalpy change when reactants and products in standard states (D
H°
)
- standard enthalpy of formation change in enthalpy for reaction that forms 1mol of compound from elements, with all substances in standard states (D
Hf°
)
- standard enthalpy of formation of most stable form of any element is zero
5.7.1 Using Enthalpies of Formation to Calculate Enthalpies of Reaction

- n, m stoichiometric coefficients of reaction
- first term formation of reaction of products
- second term reverse formation reactions of reactants
5.8 Foods and Fuels
- fuel value energy releases when 1g of material is combusted
5.8.1 Foods
- body uses chemical energy from foods for:
- maintaining body temperature, drive muscles, construct and repair tissues
- fats serve as bodys energy reserve
- 1) insoluble in water
- 2) produce more energy per gram
- average fuel value for fat 38kJ/g (9 kcal/g)
- average fuel value of proteins and carbohydrates 17kJ/g (4 kcal/g)
5.8.2 Fuels
- the greater then percentage of carbon and hydrogen in a fuel, the higher the fuel value
- fossil fuels coal, petroleum, natural gas
- natural gas gaseous hydrocarbons, mostly methane, small amounts of ethane, propane, and butane
- petroleum mostly hydrocarbons; rest composed of compounds containing sulfur, nitrogen, or oxygen
- coal hydrocarbons of high molecular weight, and compounds of sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen
- coal gasification
- coal + steam ®
complex mixture ®
mixture if CH4, H2, and CO (syngas)
- syngas easier to transport, less air pollution
5.8.3 Other Energy Sources